4. Masquerading IP Address
Masquerade also known as Network Address Translation (NAT), which is basically a simple method for allowing a computer to connect with internet with the help of base machine just a intermediary work.
Here, we will see how to forward a port to outside network. For example, if I want to do a ssh into my home virtual machine from anywhere, I need to forward my ssh port 22 to different port (i.e. 2222).
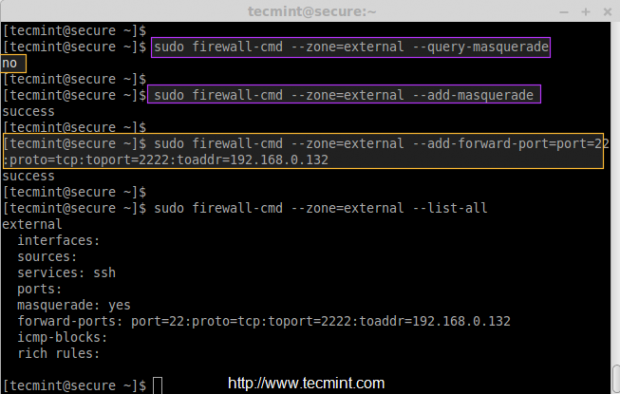
Before doing a port forwarding, first make sure check whether Masquerade enabled for external zone, because we are going to access the machine from outside network.
# firewall-cmd --zone=external --query-masquerade
If it’s not enabled, you can enable it by following command.
# firewall-cmd --zone=external --add-masquerade
Now let’s forward all ssh port 22 connections to port 2222 for IP address 192.168.0.132.
# firewall-cmd --zone=external --add-forward-port=port=22:proto=tcp:toport=2222:toaddr=192.168.0.132 # firewall-cmd --zone=external --list-all
5. How to Block and Enable ICMP
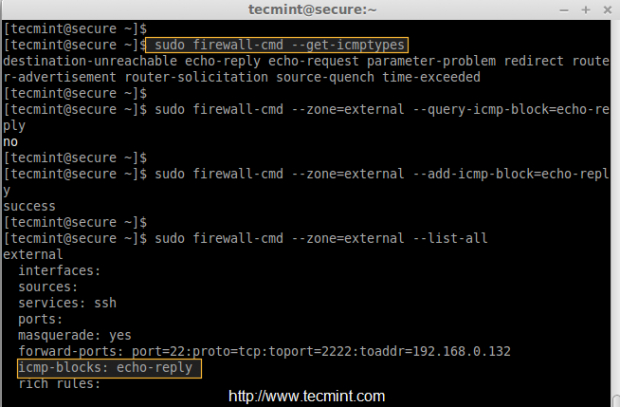
First, check the type of icmp we are using with below command.
# firewall-cmd --get-icmptypes
To add icmp block on any zone, you can use the following command. For example, here I am going to add icmp block on external zone, before blocking, just do a icmp ping to confirm the status of icmp block.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-icmp-block=echo-reply
If you get ‘no‘, that means there isn’t any icmp block applied, let’s enable (block) icmp.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-icmp-block=echo-reply
6. Adding and Removing Chain using Direct Interface
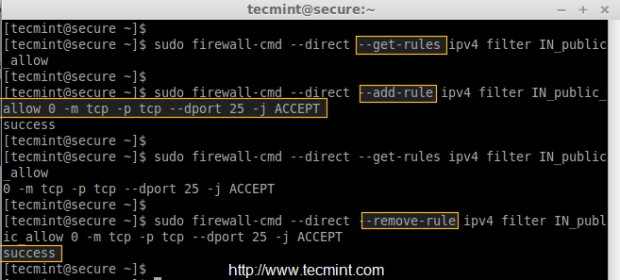
To add a Custom direct interface rule, we can use ‘–direct‘ option in any chain (Public, Work, Internal, External). For example, here we’re going to add a rule in Public Zone.
Before adding any rule, first make sure to list all the current rules in public zone using ‘–get-rules‘.
# irewall-cmd --direct --get-rules ipv4 filter IN_public_allow
To add the rules use ‘–add-rules‘ as show below.
# firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter IN_public_allow 0 -m tcp -p tcp --dport 25 -j ACCEPT
To remove the rules just replace ‘–add-rule‘ with ‘–remove-rule‘.
# firewall-cmd --direct --remove-rule ipv4 filter IN_public_allow 0 -m tcp -p tcp --dport 25 -j ACCEPT
7 Firewalld Lockdown Rules
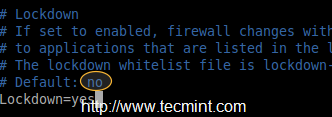
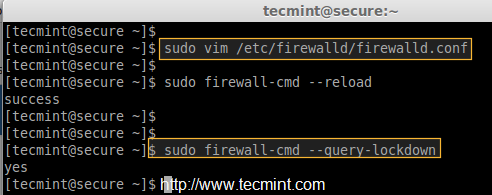
It’s possible to change the firewalld rules by any local applications, which have the root privileges. To avoid making changes to firewalld rules, we have to put a lock-down in ‘firewalld.conf‘ file. This mostly used to protect the firewalld from any unwanted rules changes by any applications.
# vim /etc/firewalld/firewalld.conf
Change no to yes
Lockdown=yes
To make it permanent reload the changes using ‘–reload‘.
# firewall-cmd --reload
After making above changes, make sure to verify whether firewalld was lockdown using query.
# firewall-cmd --query-lockdown
To On/Off lockdown mode, use the following combination.
# firewall-cmd --lockdown-on # firewall-cmd --lockdown-off
8: Enabling Fail2ban-firewalld Support
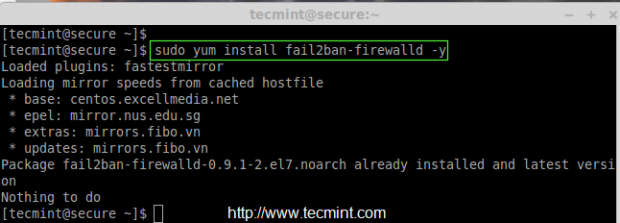
To enable support of fail2ban in firewalld, we need to install the package called ‘fail2ban-firewalld‘ by enabling epel repository under RHEL/CentOS systems. The fail2ban support provides some additional secure rules for SSH, SSH-DDOS, MariaDB, Apache etc..
After enabling epel, let’s install the ‘fail2ban-firewalld‘ package using the following command.
# yum install fail2ban-firewalld -y
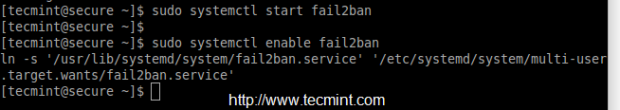
After installing the package, start the ‘fail2ban‘ service and enable to make it persistent.
# systemctl start fail2ban # systemctl enable fail2ban
9. Adding & Blocking IP Addresses
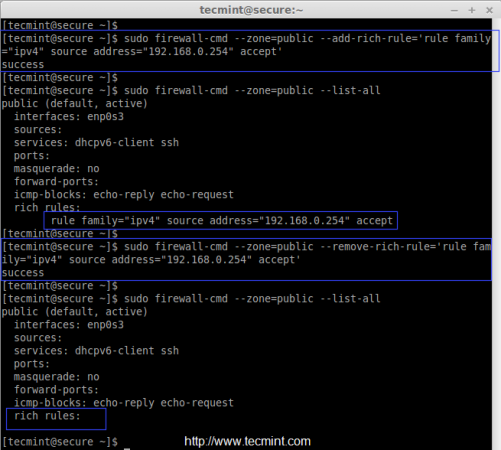
To add specific IP address (192.168.0.254) to trusted public zone, use the following command.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-rich-rule='rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.0.254" accept'
After adding above rule, don’t forget to list all the trusted public zone rules.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
To remove any added rule, just replace the ‘–add-rich-rule‘ with remove ‘–remove-rich-rule‘ as show in below command.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-rich-rule='rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.0.254" accept'
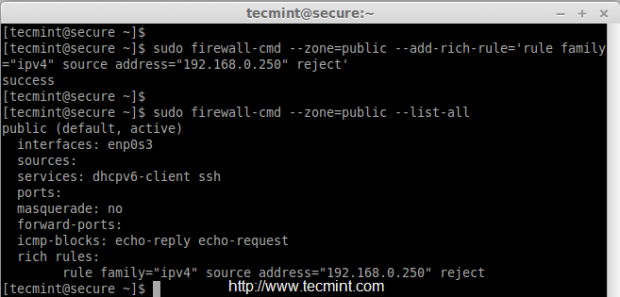
To reject or drop a IP address from the trusted zones, just replace ‘accept‘ with ‘reject‘ as shown in the below command.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-rich-rule='rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.0.250" reject' # firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
Conclusion
Here we have seen how to configure some of the rules and default services in firewalld. If there any query regarding above firewalld rules, feel free to leave your valuable comments below.






Hi, I want to know if I could add certain I.P.s (approx 5 I.P.s) to access my Linux Server using SSH so that no one except those I.P.s would be able to access the server. I don’t want to use rich-rule. How can I do that?
My server is RHEL 7.4.
Hi Naushad,
Yes, you can add alias IP for a single NIC, or you can add those individual IP for separate NIC’s to access the server. Kindly follow below article for the same requirement.
https://www.tecmint.com/create-multiple-ip-addresses-to-one-single-network-interface/
Thanks & Regards,
Babin Lonston
Thanks Babin ..
Babin,
I followed the url you have provided in your above comment. Looking at that I think I was not able to brief my problem.
Actually I have a Linux server on a network. I have 100s of other computers (running windows) on the same network. All of them can access my server but I want to allow only 5 I.P.s (i.e. 5 other computers) which are on the same network to access my Linux server using ssh. So I want to set up a firewall-cmd rule so that apart from those 5 I.P.s no one on the network would be able to access my Linux server. How can I do that?
Once again thanks for your earlier response.
@Naushad,
We assume your 5 IP’s are in 192.168.1.x range.
Thanks & Regards,
Babin Lonston
Thanks Babin for your kind response. Now I have got it. Doing this will automatically block all the other users except those which are added by add- source option, right?
But I didn’t get why I need to remove my interface.
Sure, I understand your requirement now.
To achieve this, you can use the firewall-cmd command to configure the firewall rules on your Linux server.
Here’s how you can set it up to allow only specific IP addresses to access your server via SSH:
Replace ‘IP_ADDRESS_1’, ‘IP_ADDRESS_2’, etc., with the actual IP addresses you want to allow SSH access from. Also, replace ‘NOT_IP_ADDRESS_1’, ‘NOT_IP_ADDRESS_2’, etc., with the IP addresses you want to block.
After executing these commands, only the specified IP addresses will be able to access your Linux server via SSH, while all other connections will be rejected by the firewall. Make sure to adjust the rules according to your specific requirements.
Is it possible to add networks like 172.5.0.0/24?
@Oppa,
yes you can add for network range. 172.5.0.x is a network.
Yes, you can certainly add networks in CIDR notation like ‘172.5.0.0/24’ to the firewall rules.
Here’s how you would modify the commands to allow SSH access from a specific network range:
Just replace ‘IP_ADDRESS_1’, ‘IP_ADDRESS_2’, etc., with the specific IP addresses you want to allow SSH access from, or replace ‘172.5.0.0/24’ with the desired network range.
All other connections will be rejected by the firewall.
Note that fail2ban does not monitor any services by default, so simply installing it will achieve nothing without configuring it.
Observo que se hace referencia al bloqueo de un IP pero lo único que se bloquea es el acceso a servidor sin embargo pueden navegar al internet usando como puerta de enlace el servidor.
¿ Cuál sería la forma de bloquear un IP para que no navegue a través del servidor?.
============
I note that referred to the blockade of IP, but the only thing that is blocking access to server but can browse the internet using Gateway as the server.
What would be the way to block an IP to not navigate through the server ?.
@Christian
I don’t understand what your requirement can you please make it little more clear.
Thanks a million for your really great tutorials.
Although I am having a problem blocking ICMP . I get ‘yes’‘, that means there is a icmp block applied, and it’s enabled. However, when I –zone e=external –list-all there are no entries for icmp-blocks: (empty).
Using Fedora 21 Workstation. Thanks again for your invaluable articles.