On 16th August 2016, the Debian project has celebrated its 23rd anniversary, making it one of the oldest popular distribution in open source world. Debian project was conceived and founded in the year 1993 by late Ian Murdock. By that time Slackware had already made a remarkable presence as one of the earliest Linux Distribution.

Ian Ashley Murdock, an American Software Engineer by profession, conceived the idea of Debian project, when he was a student of Purdue University. He named the project Debian after the name of his then-girlfriend Debra Lynn (Deb) and his name. He later married her and then got divorced in January 2008.
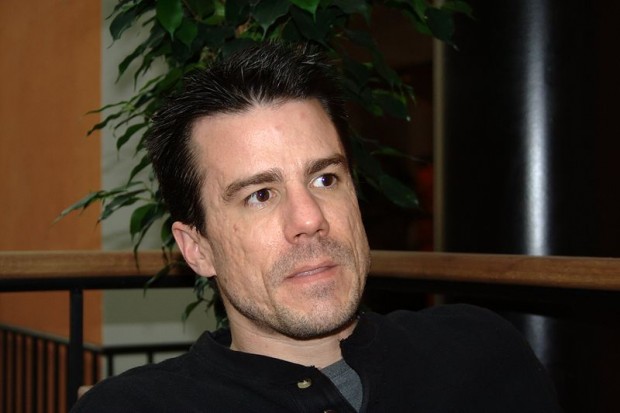

Debian (as Slackware) was the result of unavailability of up-to mark Linux Distribution, that time. Ian in an interview said – “Providing the first class Product without profit would be the sole aim of Debian Project. Even Linux was not reliable and up-to mark that time. I Remember…. Moving files between file-system and dealing with voluminous file would often result in Kernel Panic. However the project Linux was promising. The availability of Source Code freely and the potential it seemed was qualitative.”
I remember … like everyone else I wanted to solve problem, run something like UNIX at home, but it was not possible…neither financially nor legally, in the other sense . Then I come to know about GNU kernel Development and its non-association with any kind of legal issues, he added.
He was sponsored by Free Software Foundation (FSF) in the early days when he was working on Debian, it also helped Debian to take a giant step though Ian needed to finish his degree and hence quited FSF roughly after one year of sponsorship.
Debian Development History
- Debian 0.01 – 0.09 : Released between August 1993 – December 1993.
- Debian 0.91 – Released in January 1994 with primitive package system, No dependencies.
- Debian 0.93 rc5 : March 1995. It is the first modern release of Debian, dpkg was used to install and maintain packages after base system installation.
- Debian 0.93 rc6: Released in November 1995. It was last a.out release, deselect made an appearance for the first time – 60 developers were maintaining packages, then at that time.
- Debian 1.1: Released in June 1996. Code name – Buzz, Packages count – 474, Package Manager dpkg, Kernel 2.0, ELF.
- Debian 1.2: Released in December 1996. Code name – Rex, Packages count – 848, Developers Count – 120.
- Debian 1.3: Released in July 1997. Code name – Bo, package count 974, Developers count – 200.
- Debian 2.0: Released in July 1998. Code name: Hamm, Support for architecture – Intel i386 and Motorola 68000 series, Number of Packages: 1500+, Number of Developers: 400+, glibc included.
- Debian 2.1: Released on March 09, 1999. Code name – slink, support architecture Alpha and Sparc, apt came in picture, Number of package – 2250.
- Debian 2.2: Released on August 15, 2000. Code name – Potato, Supported architecture – Intel i386, Motorola 68000 series, Alpha, SUN Sparc, PowerPC and ARM architecture. Number of packages: 3900+ (binary) and 2600+ (Source), Number of Developers – 450. There were a group of people studied and came with an article called Counting potatoes, which shows – How a free software effort could lead to a modern operating system despite all the issues around it.
- Debian 3.0 : Released on July 19th, 2002. Code name – woody, Architecture supported increased– HP, PA_RISC, IA-64, MIPS and IBM, First release in DVD, Package Count – 8500+, Developers Count – 900+, Cryptography.
- Debian 3.1: Release on June 6th, 2005. Code name – sarge, Architecture support – same as woody + AMD64 – Unofficial Port released, Kernel – 2.4 qnd 2.6 series, Number of Packages: 15000+, Number of Developers : 1500+, packages like – OpenOffice Suite, Firefox Browser, Thunderbird, Gnome 2.8, kernel 3.3 Advanced Installation Support: RAID, XFS, LVM, Modular Installer.
- Debian 4.0: Released on April 8th, 2007. Code name – etch, architecture support – same as sarge, included AMD64. Number of packages: 18,200+ Developers count : 1030+, Graphical Installer.
- Debian 5.0: Released on February 14th, 2009. Code name – lenny, Architecture Support – Same as before + ARM. Number of packages: 23000+, Developers Count: 1010+.
- Debian 6.0 : Released on July 29th, 2009. Code name – squeeze, Package included : kernel 2.6.32, Gnome 2.3. Xorg 7.5, DKMS included, Dependency-based. Architecture : Same as previous + kfreebsd-i386 and kfreebsd-amd64, Dependency based booting.
- Debian 7.0: Released on may 4, 2013. Code name: wheezy, Support for Multiarch, Tools for private cloud, Improved Installer, Third party repo need removed, full featured multimedia-codec, Kernel 3.2, Xen Hypervisor 4.1.4 Package Count: 37400+.
- Debian 8.0: Released on May 25, 2015 and Code name: Jessie, Systemd as the default init system, powered by Kernel 3.16, fast booting, cgroups for services, possibility of isolating part of the services, 43000+ packages. Sysvinit init system available in Jessie.
- Debian 8.5: Released on June 4, 2016
Note: Linux Kernel initial release was on October 05, 1991 and Debian initial release was on September 15, 1993. So, Debian is there for 23 Years running Linux Kernel which is there for 25 years.
Debian Facts
Year 1994 was spent on organizing and managing Debian project so that it would be easy for others to contribute. Hence no release for users were made this year however there were certain internal release.
Debian 1.0 was never released. A CDROM manufacturer company by mistakenly labelled an unreleased version as Debian 1.0. Hence to avoid confusion Debian 1.0 was released as Debian 1.1 and since then only the concept of official CDROM images came into existence.
Each release of Debian is a character of Toy Story.
Debian remains available in old stable, stable, testing and experimental, all the time.
The Debian Project continues to work on the unstable distribution (codenamed sid, after the evil kid from the Toy Story). Sid is the permanent name for the unstable distribution and is remains ‘Still In Development‘. The testing release is intended to become the next stable release and is currently codenamed jessie.
Debian official distribution includes only Free and OpenSource Software and nothing else. However the availability of contrib and Non-free Packages makes it possible to install those packages which are free but their dependencies are not licensed free (contrib) and Packages licensed under non-free softwares.
Debian is the mother of a lot of Linux distribution. Some of these Includes:
- Damn Small Linux
- KNOPPIX
- Linux Advanced
- MEPIS
- Ubuntu
- 64studio (No more active)
- LMDE
Debian is the world’s largest non commercial Linux Distribution. It is written in C (32.1%) programming language and rest in 70 other languages.

Image Source: Xmodulo
Debian project contains 68.5 million actual loc (lines of code) + 4.5 million lines of comments and white spaces.
International Space station dropped Windows & Red Hat for adopting Debian – These astronauts are using one release back – now “squeeze” for stability and strength from community.
Thank God! Who would have heard the scream from space on Windows Metro Screen :P
The Black Wednesday
On November 20th, 2002 the University of Twente Network Operation Center (NOC) caught fire. The fire department gave up protecting the server area. NOC hosted satie.debian.org which included Security, non-US archive, New Maintainer, quality assurance, databases – Everything was turned to ashes. Later these services were re-built by debian.
The Future Distro
Next in the list is Debian 9, code name – Stretch, what it will have is yet to be revealed. The best is yet to come, Just Wait for it!
A lot of distribution made an appearance in Linux Distro genre and then disappeared. In most cases managing as it gets bigger was a concern. But certainly this is not the case with Debian. It has hundreds of thousands of developer and maintainer all across the globe. It is a one Distro which was there from the initial days of Linux.
The contribution of Debian in Linux ecosystem can’t be measured in words. If there had been no Debian, Linux would not have been so rich and user-friendly. Debian is among one of the disto which is considered highly reliable, secure and stable and a perfect choice for Web Servers.
That’s the beginning of Debian. It came a long way and still going. The Future is Here! The world is here! If you have not used Debian till now, What are you Waiting for. Just Download Your Image and get started, we will be here if you get into trouble.