This tutorial will guide you on how you can install Debian 7 (Wheezy) directly from a network location using DNSMASQ as a PXE Server (Preboot eXecution Environment), in case your server doesn’t provide any method to boot from a CD/DVD/USB media drive or it just can operate with an attached monitor, keyboard and mouse.

DNSMASQ is a lightweight network infrastructure server which can provide crucial network services such as DNS, DHCP and Network Boot, using a build-in DNS, DHCP and TFTP server.
Once the PXE server is up and running you can instruct all your clients machines to directly boot from network, with the specifications that your clients must own a network card that supports network booting, which can be enabled from BIOS under Network Boot or Boot Services option.
Requirements
Step 1: Install and Configure DNSMASQ Server
1. On first hand, after you install Debian Server assure that your system uses a Static IP Address, because, besides network booting, will also provide DHCP service for your entire network segment. Once the Static IP Address has been configured run the following command from root account or using a user with root powers to install DNSMASQ server.
# apt-get install dnsmasq
2. Once DNSMASQ package installed, you can start editing its configuration file. First create a backup of the main configuration and then start editing dnsmasq.conf file by issuing the following commands.
# mv /etc/dnsmasq.conf /etc/dnsmasq.conf.backup # nano /etc/dnsmasq.conf

3. The above backup process consisted on renaming the main configuration file, so the new file should be an empty one. Use the following excerpt for DNSMASQ configuration file as described below.
interface=eth0 domain=debian.lan dhcp-range=192.168.1.3,192.168.1.253,255.255.255.0,1h dhcp-boot=pxelinux.0,pxeserver,192.168.1.100 pxe-prompt="Press F8 for menu.", 60 #pxe-service types: x86PC, PC98, IA64_EFI, Alpha, Arc_x86, Intel_Lean_Client, IA32_EFI, BC_EFI, Xscale_EFI and X86-64_EFI pxe-service=x86PC, "Install Debian 7 Linux from network server 192.168.1.100", pxelinux enable-tftp tftp-root=/srv/tftp
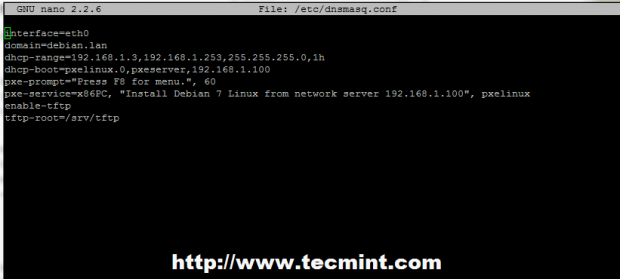
- interface – The network interface that the server should listen.
- domain – Replace it with your domain name.
- dhcp-range – Replace it with your network IP range defined by your network mask.
- dhcp-boot – Leave it as default but replace the IP statement with your server IP Address.
- pxe-prompt – Leave it as default – requires F8 key strike to enter menu 60 with seconds wait time.
- pxe=service – Use x86PC for 32-bit/64-bit architectures and enter a menu description prompt under string quotes. Other values types can be: PC98, IA64_EFI, Alpha, Arc_x86, Intel_Lean_Client, IA32_EFI, BC_EFI, Xscale_EFI and X86-64_EFI.
- enable-tftp – Enables the build-in TFTP server.
- tftp-root – Use /srv/tftp is the location for Debian netboot files.
Step 2: Download Debian Netboot Files and Open Firewall Connection
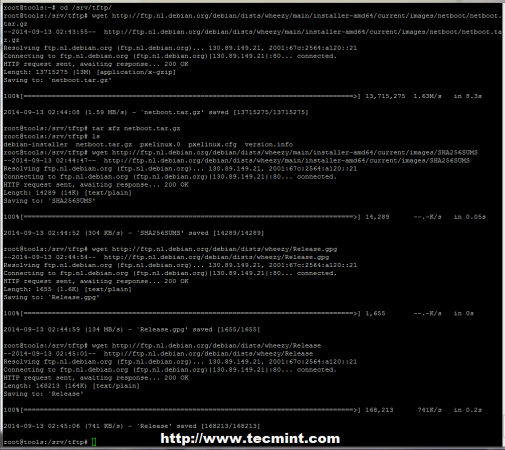
4. Now it’s time to download Debian Network Boot files. First, change your current working directory path to TFTP Root location defined by the last configuration statement (/srv/tftp system path ).
Go to a offical page mirror of Debian Netinstall – Network boot section and grab the following files depending on your system architecture that you want to install it on your clients.
Once, you download netboot.tar.gz file, extract archive at the same time (this procedure describes only for 64-bit but the same procedure applies for other system architectures).
# cd /srv/tftp/ # wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz # tar xfz netboot.tar.gz # wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/SHA256SUMS # wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/Release # wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/Release.gpg
Also it may be necessary to make all files in TFTP directory readable for TFTP server.
# chmod -R 755 /srv/tftp/
Use the following variables for Debian Netinstall mirrors and architectures.
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-"$ARCH"/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz # wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-"$ARCH"/current/images/SHA256SUMS # wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/Release # wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/Release.gpg
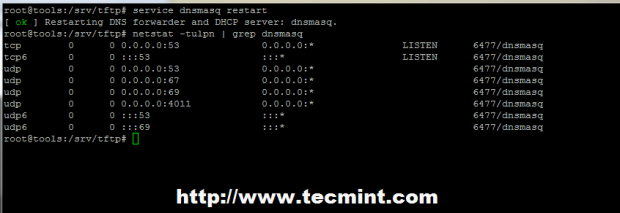
5. On the next step start or restart DNSMASQ daemon and run netstat command to get a list of ports that the server is listening.
# service dnsmasq restart # netstat -tulpn | grep dnsmasq
6. Debian based distribution usually ships with UFW Firewall package. Use the following commands to open the required DNSMASQ port numbers: 67 (Bootps), 69 (TFTP) 53 (DNS), 4011 (proxyDHCP) udp and 53 tcp (DNS).
# ufw allow 69/udp # ufw allow 4011/udp ## Only if you have a ProxyDHCP on the network # ufw allow 67/udp # ufw allow 53/tcp # ufw allow 53/udp

Now, the PXE loader located on your client network interface will load pxelinux configuration files from /srv/tftp/pxelinux.cfg directory using this order.
- GUID files
- MAC files
- Default file
Step 3: Configure Clients to Boot from Network
7. To enable network boot for a client computer enter your system BIOS configuration (please consult the hardware motherboard vendor documentation for entering BIOS settings).
Go to Boot menu and select Network boot as the primary boot device (on some systems you can select the boot device without entering BIOS configuration just by pressing a key during BIOS POST).
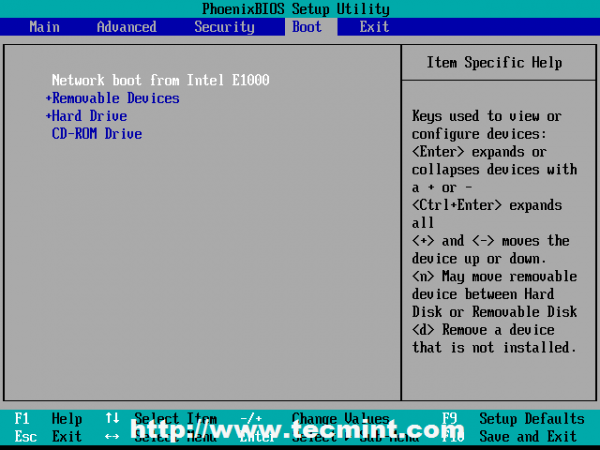
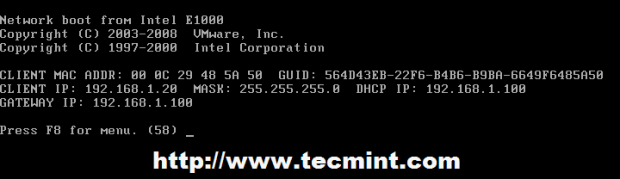
8. After editing the boot order sequence, usually, press F10 to save BIOS settings. After reboot, your client computer should boot directly from network and the first PXE prompt should appear demanding you to press F8 key to enter menu.
Next, hit F8 key to move forward and a new prompt should appear. Hit Enter key again and the main Debian Installer prompt should appear on your screen as in the screenshots below.
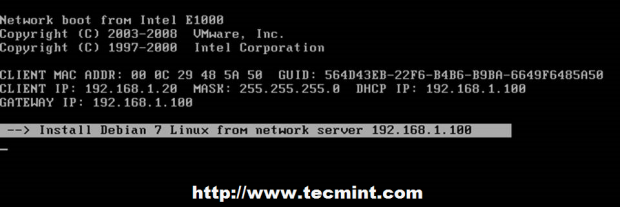

From here on you can start install Debian on your machine using the Debian 7 Wheezy procedure (installation link given above), but you can also need to make sure that your machine has an active Internet connection in order to be able to finish installation process.
Step 4: Debug DNSMASQ Server and Enable it System-Wide
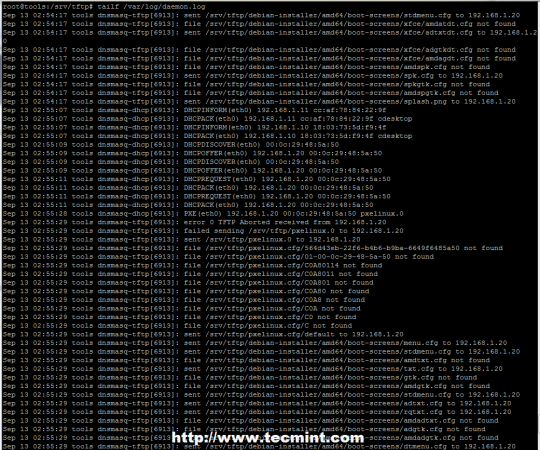
9. To diagnosticate the server for eventual occurred problems or other information offered to clients run the following command to open log file.
# tailf /var/log/daemon.log
10. If everything is in place during server tests you can now enable DNSMASQ daemon to automatically start after system reboot with the help of sysv-rc-conf package.
# apt-get install sysv-rc-conf # sysv-rc-conf dnsmaq on

That’s all! Now your PXE server is ready to allocate IP addresses (DHCP) and to offer the required boot information for all your network segment clients which will be configured to boot and install Debian Wheezy from network.
Using PXE network boot installation has some advantages on networks with an increased number of server hosts because you can set up the entire network infrastructure in a short period of time or the same time, facilitates the distribution upgrading process, and, can also automate the entire installation process using kickstart files.






Hi, now what I do in my lab is preseeding. Yes have to boot each system by installer cd and provide the preseed file path which is my system. why I am doing in this method is to install certain applications and users to be created automatically when the installation is done…is it possible to have the same preseed file and dhcp fixed ip settings according to mac address with pxe booting..? Or is it just fresh installation… ?