It’s no brainier that PHP is one of the most used server scripting programming languages. It makes sense for an attacker to find various ways by which he can manipulate PHP as it is often paired with MySQL and enable access to the private data of your users.
By any means, we are not claiming PHP is vulnerable or has some serious issues by default but we have to make sure that we tweak PHP in such a way that it can be more robust than ever before.
1. Remove Unnecessary PHP Modules
By default, you get a set of PHP modules that can be helpful in various tasks but some unnecessary modules might not be useful for each project. To list available PHP modules, utilize the given command:
$ php -m

The modules are located at /etc/php.d/ directory and can easily change our current directory to /etc/php.d/ by using the following cd command.
cd /etc/php.d/
The reason why we are changing the directory to remove modules is modules are named quite differently in the original directory. Now, list available modules by the given command:
$ ls
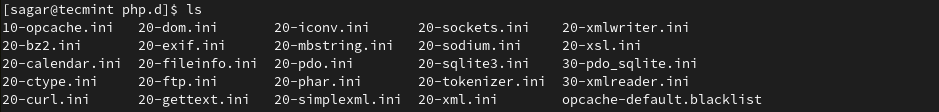
For example, let’s remove the curl module by utilizing the given command:
$ sudo rm -r 20-curl.ini
2. Disable Remote PHP Code Execution
In most cases, remote connections can not be trusted. By disabling access to fopen wrappers, they can only access local files. To disable fopen, we need to open the PHP configuration file by utilizing the given command:
$ sudo nano /etc/php.ini
Now, use CRTL + w and type allow_url_fopen which will land us on specific lines from where we will disable those options.
allow_url_fopen=Off allow_url_include=Off
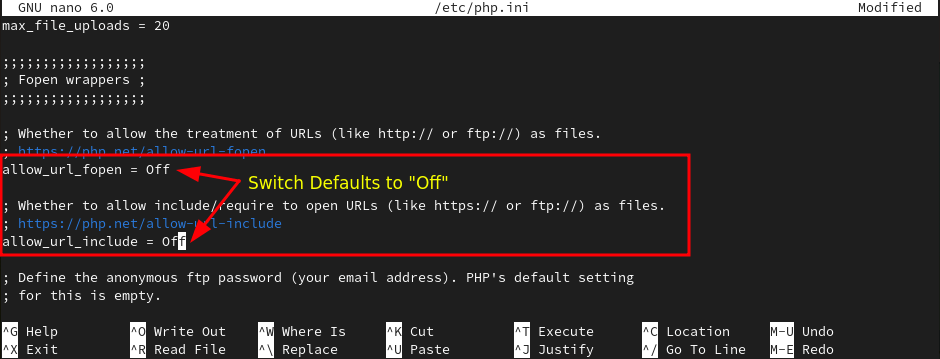
Once you are done with changes, save the config file by CTRL + O and hit Enter.
3. Disable PHP Information Leakage
When not disabled, the world can easily identify which version of PHP is currently used by our web server. This may not sound like a big deal but letting the attacker know the exact version can be dangerous.
$ sudo nano /etc/php.ini
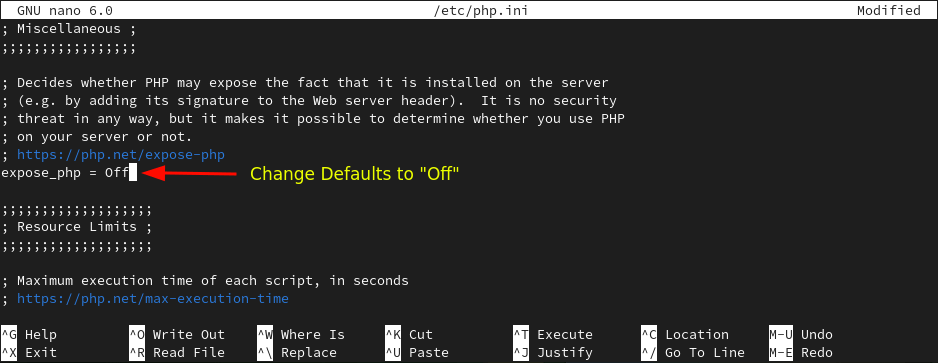
Now, change the defaults to “Off”.
expose_php=Off
4. Disable PHP Error Logs
By default, each error of our web server is visible to our visitors, including attackers. To ensure that none of the errors are visible to anyone, we have to make changes in our PHP config file.
$ sudo nano /etc/php.ini
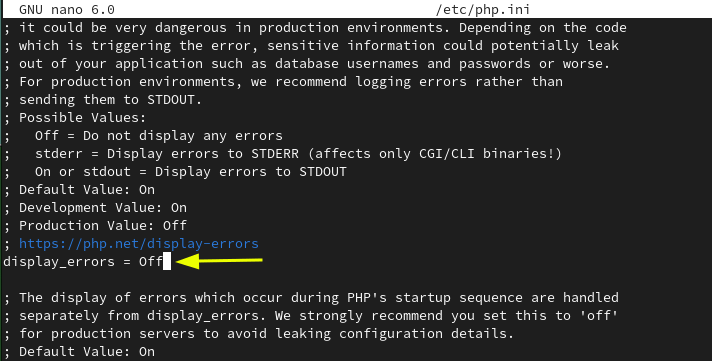
And change the default setting of displaying error logs to “Off”.
display_errors = Of
But what if you’re a developer and need to have error logs to overcome development issues? Don’t worry, there is a way to get your log files by just making a slight change in the same config file.
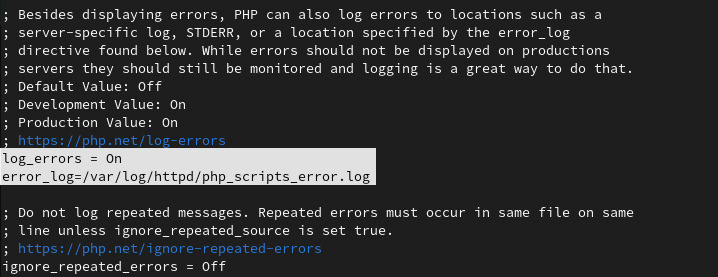
We just have to enable log_errors and give a path to error_log where our log files will be stored.
log_errors=On error_log=/var/log/httpd/php_scripts_error.log
5. PHP Resource Control
According to us, managing resources is the most crucial part when securing PHP. Here, we are going to allocate a fixed amount of execution time, input time, and memory limit so if somehow our script gets compromised, the execution will be stopped after a certain time.
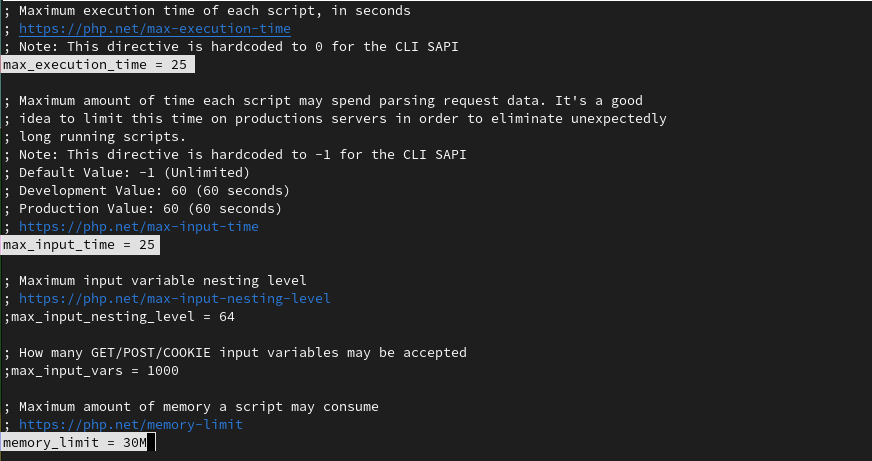
We have chosen 25 seconds for execution and input time and 30MB of memory limit. Sure you can customize it as per your needs.
max_execution_time = 25 max_input_time = 25 memory_limit = 30M
6. Restrict PHP File Access
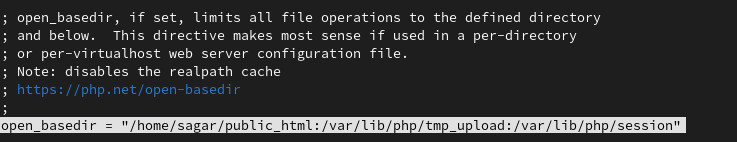
To restrict file access, we are going to enable open_basedir which will ensure that PHP can only include files from our listed directories.
Important: This will blocklist all the other directories and requires us to add important directories manually which also includes adding temporary files and session directories.
open_basedir = "/home/sagar/public_html:/var/lib/php/tmp_upload:/var/lib/php/session"
7. Configure PHP File Uploads
If your application does not require uploading files from the user’s end, it is always advised to disable file uploads. This prevents attackers to upload dangerous scripts which might end up damaging the whole application in the end.
file_uploads = Off
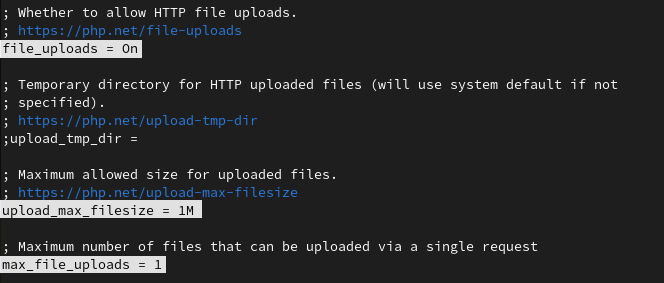
But what if your application is designed to get files from the user’s end? In that case, you have to enable file uploads but try to reduce maximum space and reduce the number of maximum files that can be uploaded from a single request.
file_uploads = On upload_max_filesize = 1M max_file_uploads = 1
In PHP, by default, the temporary files are placed in a directory that all the system users can write. The default location must be switched to a more secure place and make sure it is not located within the web root.
As we have utilized open_basedir, we will be using the same location as we have already whitelisted it.
upload_tmp_dir = /var/lib/php/tmp_upload
8. Disable Dangerous PHP Functions
PHP has various functions enabled by default and can be helpful for development purposes. But many functions can be used by hackers to exploit our webs server and disabling them will add a layer of security.
We have a disabled set of functions and make sure to cross-check them before making changes to the configuration file.
disable_functions = exec,passthru,shell_exec,system,proc_open,popen,curl_exec,curl_multi_exec,parse_ini_file,show_source

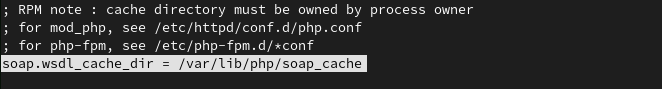
9. Change SOAP Cache Directory
As we changed the default temp directory and session, the same applies to the SOAP cache as it should not be saved to the default directory. Make sure it is saved to a safe place.
soap.wsdl_cache_dir = /var/lib/php/soap_cache
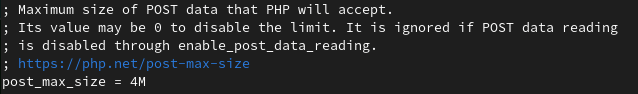
10. Control PHP POST Size
By controlling POST size, we can secure our server from a hacker attempting to clot server resources by sending huge files. This saves us from unwanted server crashes and slow response time.
post_max_size=4M
11. Protect PHP Configurations
While removing unnecessary files, we often remove some crucial files or even directories. So we must tweak settings in such a way that even root users can’t delete them. To make files and directories, we will be utilizing chattr with different flags.
Once you use the given command, you can no longer modify a specific file or remove it.
$ sudo chattr +i /etc/php.ini
While trying to remove an immutable file, it will show an error saying “Operation not permitted”.
$ sudo rm -r /etc/php.ini

But what if you want to keep writing those files while making them immutable? You can easily achieve that by using the +a flag instead of +i.
$ sudo chattr +a /etc/php.ini
There might be some cases where you no longer need the old config file and in that case, we have to unset attributes.
$ sudo chattr -i /etc/php.ini
Similarly, if you went with +a attributes in process of making files immutable, you can reverse it by utilizing the given command:
$ sudo chattr -a /etc/php.ini
12. Use SSL Certificates for HTTPS
Nowadays, each modern browser such as Google Chrome, Firefox, Opera, and others recommends using HTTPS for web servers. As HTTPS provides a secured and encrypted accessing channel for untrusted sites, we can provide a reliable experience to our users.
By adding HTTPS, we can get protected against XSS attacks including preventing the hackers to read transported data using codes.
To enable HTTPS, we will install and use the free Let’s Encrypt SSL Certificate on the server.
$ sudo dnf install epel-release $ sudo dnf install certbot python3-certbot-apache mod_ssl $ sudo certbot --apache -d domain.com [For Apache] $ sudo certbot --nginx -d domain.com [For Nginx]
13. Update PHP Regularly
As it is an open-source language, it gets patched on almost day to day basis. It might not seem much of an important step but can save you from major vulnerability. So make sure to keep your PHP packages up to date which will save you from lots of possible vulnerabilities.
# yum update & yum upgrade [On RHEL-based systems] # apt update && apt upgrade [On Debian-based systems]
This was our take on how you can easily enhance the security of PHP in Linux systems. Throughout this tutorial, we have tried to make things simple as we can and if you still have any doubts, please let us know in the comments.



I am getting the error bellow
php -v
PHP Warning: PHP Startup: Unable to load dynamic library ‘suhosin.so’ (tried: /usr/lib64/php/modules/suhosin.so (/usr/lib64/php/modules/suhosin.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory), /usr/lib64/php/modules/suhosin.so.so (/usr/lib64/php/modules/suhosin.so.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory)) in Unknown on line 0
PHP 7.4.24 (cli) (built: Sep 21 2021 11:23:11) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.4.0, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with the ionCube PHP Loader + ionCube24 v10.4.5, Copyright (c) 2002-2020, by ionCube Ltd.
with Zend OPcache v7.4.24, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
Please help me
I am using php 7.4.
What should we do for PHP 5.1?
make install
Installing shared extensions: /usr/lib64/php/modules/?
guys, this is not about a Suhosin *Patch*, it’s just about its extension :)
I got this error. Any thing I missed?
/root/suhosin-0.9.33/suhosin.c: In function âsuhosin_register_cookie_variableâ:
/root/suhosin-0.9.33/suhosin.c:649: error: âstruct _php_core_globalsâ has no member named âmagic_quotes_gpcâ
/root/suhosin-0.9.33/suhosin.c:686: error: âstruct _php_core_globalsâ has no member named âmagic_quotes_gpcâ
/root/suhosin-0.9.33/suhosin.c: In function âsuhosin_register_cookie_variable_safeâ:
/root/suhosin-0.9.33/suhosin.c:717: error: âstruct _php_core_globalsâ has no member named âmagic_quotes_gpcâ
make: *** [suhosin.lo] Error 1
@Ketan,
Can you tell me which PHP version you are running? Suhosin patch is not yet compatible with php 5.4. It will work with upto 5.3 only.
Ah. Thats explain it. I am using 5.4++. Thanks. :)