The Linux command line attracts most Linux enthusiasts. A normal Linux user generally possesses a vocabulary of roughly 50-60 commands to carry out their day-to-day tasks.
Linux commands and their switches remain the most valuable treasure for a Linux user, shell script programmer, and administrator. There are some Linux commands that are lesser-known yet very useful and handy, irrespective of whether you are a novice or an advanced user.
This article aims to shed light on some of the lesser-known Linux commands that will surely help you handle your desktop/server more efficiently.
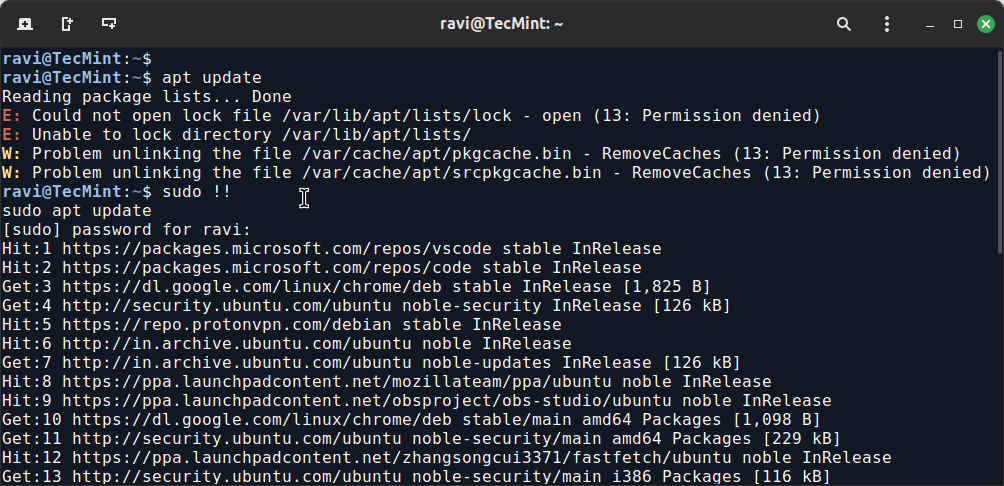
1. sudo !! command
The sudo !! command is a useful shortcut that allows you to repeat the last command with sudo privileges.
For example, running the command without specifying the sudo command will give you a permission denied error. So, you don’t need to rewrite the whole command again just put !! will grab the last command.
apt update sudo !!
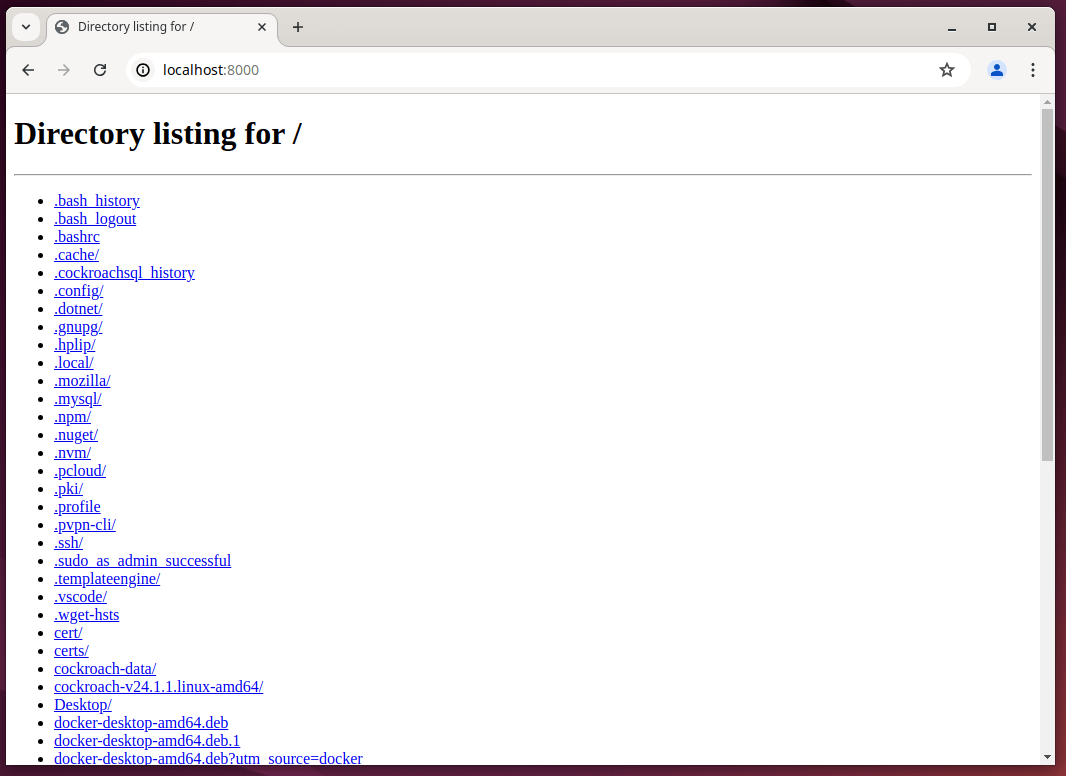
2. Python Command
The command python3 -m http.server 8000 starts a simple HTTP server in Python, which serves files from the current directory over HTTP.
For example, the below command generates a simple web page over HTTP for the directory structure tree and can be accessed at port 8000 in the browser till an interrupt signal is sent.
python3 -m http.server 8000
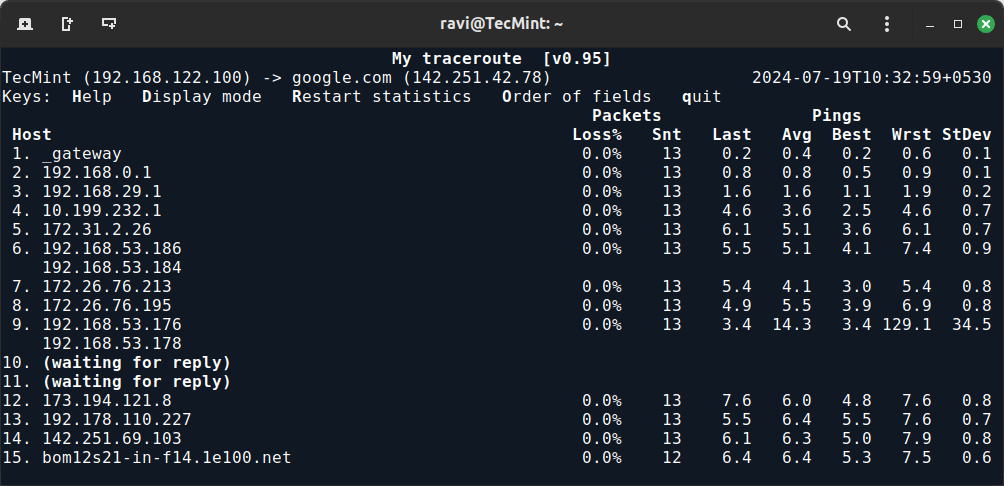
3. mtr Command
Most of us are familiar with ping and traceroute. How about combining the functionality of both commands into one with mtr command.
In case mtr is not installed on your machine, you can install it using your system package manager.
sudo apt install mtr [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install mtr [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/mtr [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add mtr [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S mtr [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install mtr [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install mtr [On FreeBSD]
Now run the mtr command to start investigating the network connection between the host google.com.
mtr google.com
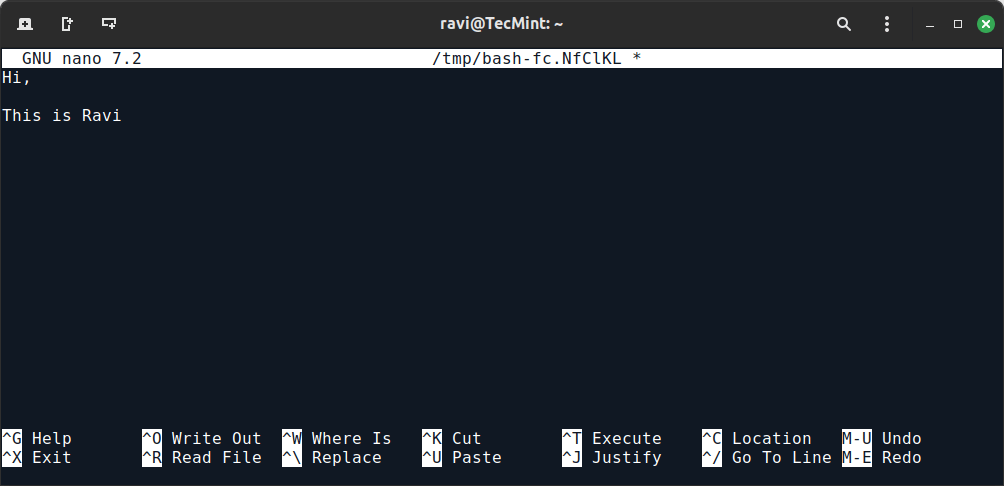
4. Ctrl+x+e Command
The Ctrl+x+e command is very useful for administrators and developers. For day-to-day tasks, administrators often need to open an editor by typing `vi`, `vim`, `nano`, etc.
However, for an instant editor from the terminal, you can use the press Ctrl-x-e from the terminal prompt and start working in the editor.
5. nl Command
The nl command is used to number lines of files or standard input. It’s useful for adding line numbers to the output, which can help in various tasks like reviewing or debugging text files.
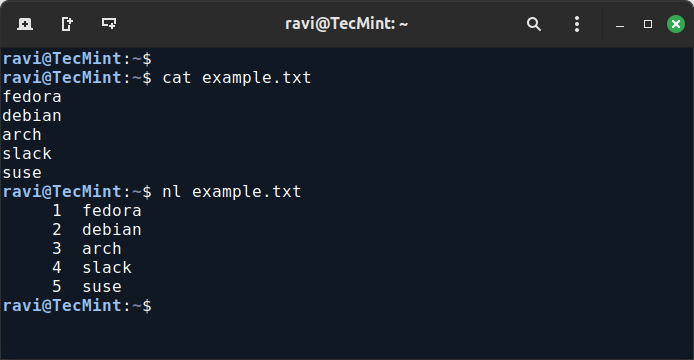
Suppose you have a text file named example.txt with the following content (cat command – list content of a file):
fedora debian arch slack suse
You can use the nl command to number the lines of this file:
nl example.txt
6. shuf Command
The shuf command is used to shuffle lines of text files or input, which is useful for randomizing the order of lines in a file or generating random permutations.
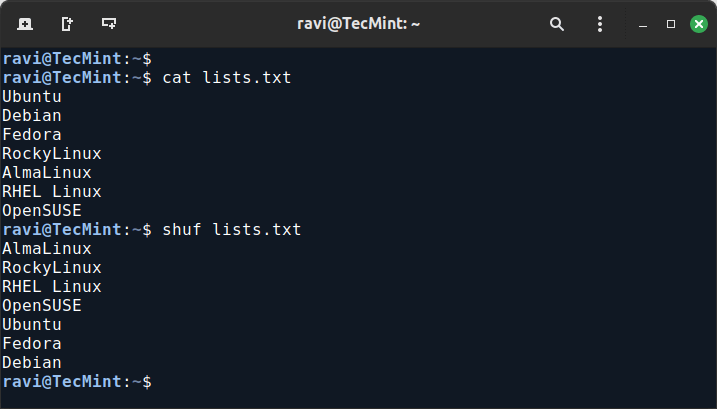
Suppose you have a file named list.txt with the following content:
Ubuntu Debian Fedora RockyLinux AlmaLinux RHEL Linux OpenSUSE
You can use the shuf command to shuffle the lines of this file:
shuf list.txt
7. ss Command
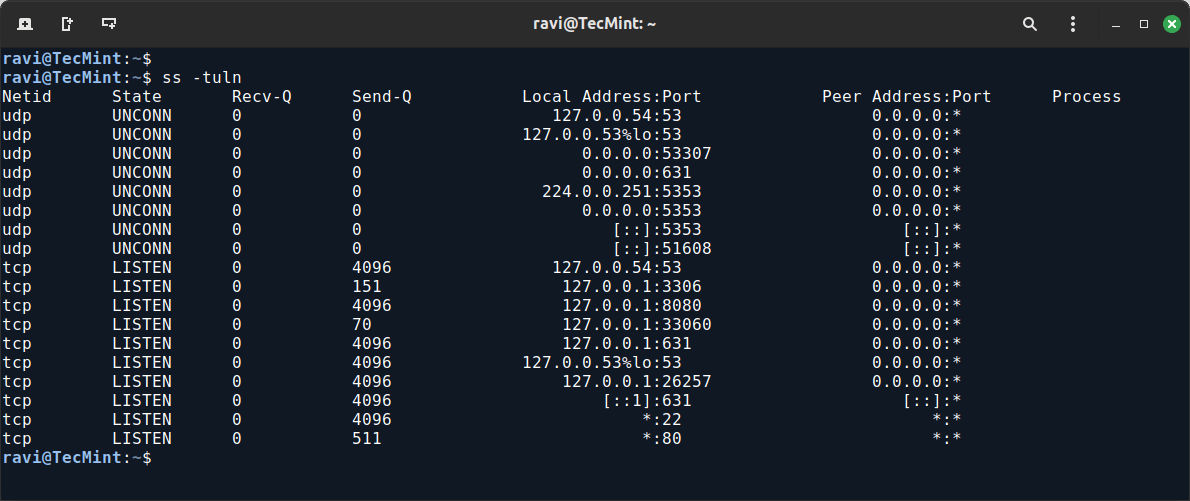
The ss command stands for “socket statistics“, which is used to investigate sockets and displays information similar to the netstat command.
However, ss can show more detailed TCP and state information than other tools.
ss -tuln
8. last Command
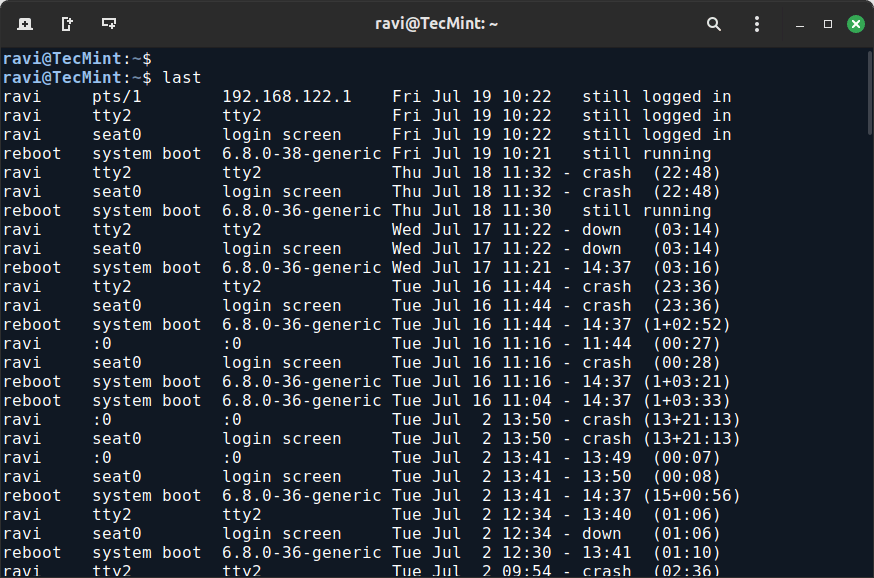
The “last” command shows the history of last logged-in users. This command searches through the file “/var/log/wtmp” and shows a list of logged-in and logged-out users along with tty’s.
last
9. curl ifconfig.me
The curl ifconfig.me command is used to retrieve your public IP address from the ifconfig.me service, which is a quick and convenient way to check your public IP without needing to visit a website.
curl ifconfig.me 49.36.109.114
10. tree Command
The tree command is used to display a hierarchical view of directories and files in a tree-like format, which is useful for visualizing the structure of directories and their contents.
tree
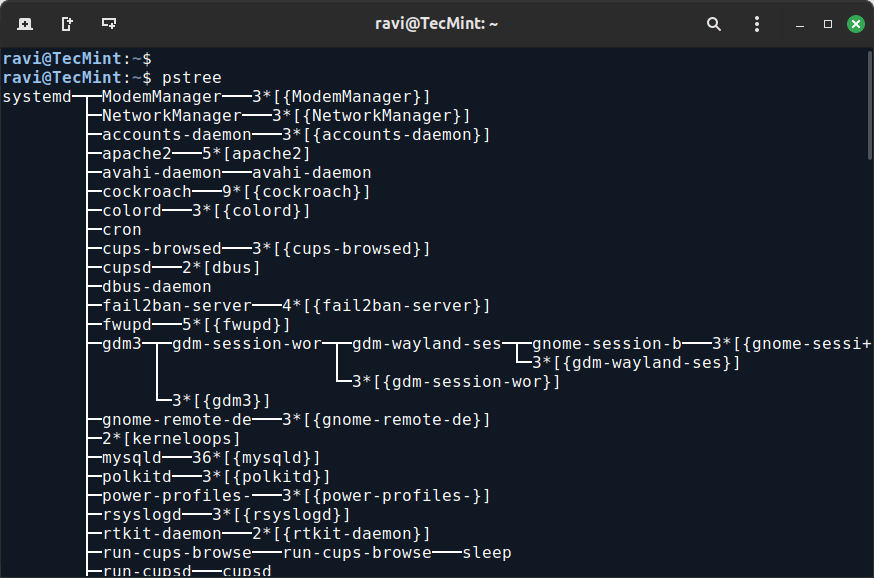
11. pstree Command
The pstree command prints a tree-like diagram of currently running processes, showing how processes are related to each other in a hierarchical manner.
pstree
In this article, we explored some lesser-known yet highly useful Linux commands that can enhance your command-line proficiency and streamline your workflows.
Read Also:





Excellent article. Some commands I had once known and then forgotten and some new ones. Thanks!
Very useful – despite working with Linux for years, there is always new/surpising stuff hidden there.
Tecmint team is happy knowing this and will keep coming with such stuffs in future. Keep connected!
Thank you very much, sir.
Can I point out that #9 is not really a linux command, as such, but is making use of the website called “http://ifconfig.me”. Your readers should be made clearly aware of that. Many newbie linux users will not be aware, and many come to linux for privacy concerns.
As for the rest, nice work…
and ifconfig.me doesn’t answer anymore either :(
Very informative!!! Thanks a lot Avishek.
@ Long Cao, welcome. Comment of This kind Encourages us (as writer).
python -m http.server
? @ ovi did u faced any problem in executing this python script. well the command is python -m SimpleHTTPServer.
Avishek, I think what @ ovi is referring to is that in python 3 SimpleHTTPServer has been merged into the http.server module.
Thus his command is correct in python 3 and yours in python 2.
This is described in detail in the following stackoverflow discussion:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/7943751/what-is-the-python3-equivalent-of-python-m-simplehttpserver
Nice, thanks :)
Actually, `nl ‘ just numbers text lines while `cat -n ‘ numbers all the lines in the file
@ Andrea, Thanks for your concern, we are aware of the fact and will be placing your suggested command in our future post:)
Very gracious sir. It is extremely most pleasant to read such tidbits of knowledge and to savor the taste of victory.
Please provide your private email address so that I can communicate to ask you particular questions of your undoubted authority.
@ Rajiv, Thanks for your feedback. My email is [email protected], as stated above :)
sry sry the reply was not moderated n i thought that my reply was deleted
anyway
i need a help in context of some setting in squid proxy server kindly if u can provide your mail address
1) curl ifconfig.me is nice !!
2) mtr command consumes more cpu usage
@ Rizwan thanks for your feedback.
You stated in your article that Ctrl-x-e would bring up an editor. What it actually does is open the command line editor, which is not the same thing at all.
Also, this behaviour is dependent on several things.
– First, you have to be using bash as your shell.
– Second, you must be in emacs line editing mode.
– Third, the editor that is invoked is determined by the value of the EDITOR environment variable. If that variable isn’t set, then it looks for emacs in your path and tries to invoke it.
If you just want to open a file for editing, then Ctrl-x-e isn’t what you want.
Try this experiment to see why this isn’t a good idea:
Run the following two commands as root at the shell prompt.
# export EDITOR=/usr/bin/vi
# set -o emacs
now, Ctrl-x-e and type the following in the editor session spawned:
cd /
echo rm -rf *
echo “OMG….You just typed rm -rf * in the root filesystem as root”
then exit the editing session with :wq
You will see something like this:
[root@w0140860 ~]# set -o emacs
[root@w0140860 ~]# echo $EDITOR
[root@w0140860 ~]# export EDITOR=/usr/bin/vi
[root@w0140860 ~]#
cd /
echo rm -rf *
rm -rf bin boot dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
echo “OMG….you just ran rm -rf as root in the / directory.”
OMG….you just ran rm -rf as root in the / directory.
Once you are done running this little experiment, be thankful that I put an echo in front of the rm -rf * and you didn’t trash your whole system.
Txtechdog,
Linux user since kernel version 0.12 (that isn’t a typo)
Sr. Linux Administrator / Architect
@ txtechdog,
Your finding is appreciated. we need to verify it on our side, before editing the article. Thanks
Excerpt from section 8.4 of the Bash Reference Manual:
edit-and-execute-command (C-x C-e)
Invoke an editor on the current command line, and execute the result as shell commands. Bash attempts to invoke $VISUAL, $EDITOR, and emacs as the editor, in that order.
Your article is wrong. Please correct it. Tips are great, but incorrect tips are not only not helpful, but can be harmful.
Txtechdog
Excellent write up, the sudo !! is pretty slick!
Thanks @ MAC, for your feedback.
keep visiting tecmint.com
we are coming up with another article of this very series, Yeah! “11 Lesser Known Useful Linux Commands”
Most of these commands will not work unless you install the appropriate software. I wouldn’t call them less known useful linux commands, I would call them “less known useful linux commands that you most likely don’t have installed”
– CTRL+x+e requires emacs to be installed
– Tree must be installed
The rest are good but are not very useful for day to day activities.
You can use a wget on an external website that prints the IP to know what your server’s external IP is. Just one method on top of my head.
“less known useful linux commands that you most likely don’t have installed”
:)
Your feedback is appreciated, @ Fadi.
Very usefull bhai
let us know some more
Thanks @ shaik, for your appreciation.
we are coming up with another article of this section, very soon.
Thanks! These are actually quite useful!
:) welcome @ Stuart Page
Thanks you Avishek Kumar, this article is very very helpful to me. It improves my vision and skill for GNU Linux. Thank you very much
@ Ernst,
Thanks for Your Value-able comment.
Qualitative info
will you provide your mail address so that if i get stuck in around Linux or kind of troubleshooting you could help me out
i am exploring this OS now a days
@ deepanjan
Thanks for your feedback.
Yeah! you can reach me at [email protected] or https://www.facebook.com/Avishek.hacker