Linux is known for its vast set of powerful command-line tools that allow users to interact efficiently with the system. While many Linux users are familiar with popular commands like ls, cd, or grep, there are lesser-known but extremely useful commands and shortcuts that can simplify and improve productivity.
We’re happy to share our last five articles on ‘Lesser Known Linux Commands‘, which include more than 50 commands you may not know.
This article puts all five together in one easy guide, giving a short summary of each command, its function, and an example.
1. sudo !!
If you forgot to run a command with sudo, you don’t need to rewrite the whole command. Just type sudo !! and it will execute the last command with sudo.
apt update Permission denied sudo !! sudo apt update
2. python -m SimpleHTTPServer
Creates a simple web page for the current working directory on port 8000.
python -m SimpleHTTPServer Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 ...
3. mtr Command
Combines ping and traceroute to show the network status in real time.
mtr google.com
4. Ctrl+x+e
Opens the terminal’s default text editor, allowing you to edit the current command before running it.
For example, Press Ctrl+x followed by e in the terminal to open the command in an editor.
5. nl Command
Outputs the content of a text file with line numbers.
nl file.txt 1 This is line 1 2 This is line 2
6. shuf Command
Randomly selects lines from a file or shuffles the content.
shuf -n 3 file.txt
7. ss Command
Displays socket statistics and active connections.
ss -tuln
8. last Command
Displays the history of last logged-in users.
last
9. curl ifconfig.me
Shows the machine’s external IP address.
curl ifconfig.me
10. tree Command
Displays files and directories in a tree-like structure.
tree
11. pstree
Displays a hierarchical view of running processes.
pstree
12. <space> Command
Prevents the command from being saved in the history.
<space> ls
13. stat Command
Displays detailed status information of a file or filesystem.
stat file.txt
14. <alt>. and <esc> .
Reuses the last argument of the previous command.
echo foo <alt>.
15. pv Command
Simulates Hollywood-style text streams.
echo "Loading..." | pv -qL 10
16. mount | column -t
Displays mounted filesystems in a well-formatted manner.
mount | column -t
17. Ctrl + l
Clears the terminal screen instantly by pressing Ctrl + l in the terminal.
18. curl Command
Fetches unread Gmail messages in the terminal.
curl -u username --silent "https://mail.google.com/mail/feed/atom" | perl -ne 'print "$1\n" if /<title>(.*)<\/title>/'
19. screen Command
Detaches and reattaches long-running processes from the terminal.
screen -S session_name
20. file Command
Identifies the type of a file.
file file.txt
21. id Command
Prints user and group ID information.
id
22. ^foo^bar
Replaces foo with bar in the previous command.
echo foo ^foo^bar
23. > file.txt
Flushes the content of a file from the command prompt.
> file.txt
24. at Command
Schedules commands to be run at a later time.
echo "shutdown now" | at 23:00
25. du Command
Shows the size of files and folders within the current directory.
du -h --max-depth=1
26. expr Command
Solves simple mathematical calculations in the terminal.
expr 3 + 5
27. look Command
Checks for a word in the dictionary.
look apple
28. yes Command
Repeatedly outputs a string until interrupted.
yes "I will study Linux!"
29. factor Command
Shows all the factors of a given number.
factor 12
30. ping Command
Pings a host with audible feedback when it comes online.
ping -i 60 -a 8.8.8.8
31. tac Command
Outputs the content of a file in reverse order.
tac file.txt
32. strace Command
Debugging tool to trace system calls.
strace ls
33. disown Command
Runs a command in the background even after the terminal is closed.
sleep 1000 & disown -a && exit
34. getconf Command
Displays the system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
getconf LONG_BIT
35. while Command
Displays the date and time at the top-right corner of the terminal.
while sleep 1; do tput sc; tput cup 0 $(($(tput cols)-29)); date; tput rc; done &
36. convert Command
Converts the output of a command into an image.
convert input.jpg output.png
37. watch Command
Displays an animated digital clock in the terminal.
watch -t -n1 "date +%T|figlet"
38. host and dig Commands
DNS lookup utilities.
host google.com dig google.com
39. dstat Command
Generates real-time system resource statistics.
dstat
40. bind Command
Displays all Bash key bindings.
bind -p
41. touch Command
Forces a file system check on the next reboot.
sudo touch /forcefsck
42. lsb_release Command
Prints Linux distribution information.
lsb_release -a
43. nc Command
Checks if a specific port is open.
nc -zv localhost 22
44. curl ipinfo.io
Outputs geographical information about an IP address.
curl ipinfo.io
45. find Command
Lists all files owned by the user xyz.
find . -user xyz
46. apt Command
Installs all build dependencies for a package.
sudo apt build-dep vim
47. lsof Command
This command lists all services or processes that are currently listening on TCP port 80.
lsof -iTCP:80 -sTCP:LISTEN
48. find -size +100M
This command searches for all files and folders that are larger than 100 megabytes in the current directory and its subdirectories.
find . -size +100M
49. pdftk Command
pdftk is a powerful command-line tool that allows you to manipulate PDF files, including merging multiple PDF files into one.
pdftk file1.pdf file2.pdf cat output combined.pdf
50. ps -LF -u user_name
This command displays all processes and threads for a specified user, including detailed information about each thread’s status.
ps -LF -u john
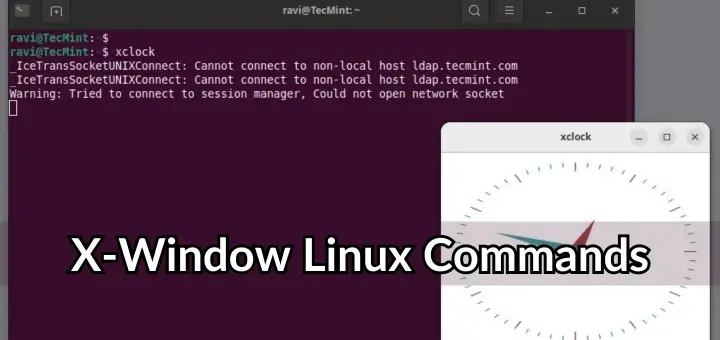
51. startx — :1
This command starts a new X session on display :1, which is useful for running multiple graphical user interfaces simultaneously on different screens.
startx -- :1
That’s all for now! Don’t forget to share your thoughts in the comment section. This isn’t the end of lesser-known Linux commands; we’ll continue bringing more to you in our upcoming articles.
I’ll be back soon with another interesting and useful piece for our readers. Until then, stay tuned and connected to Tecmint.com!