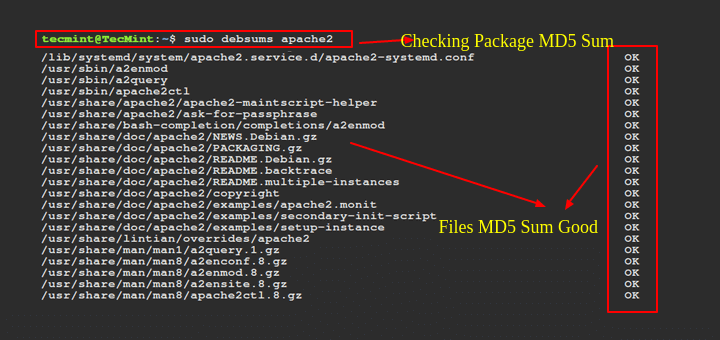
Linux is one of the most popular open source operating system and comes with huge set of commands. The most important and single way of determining the total available space of the physical memory and swap memory is by using “free” command.
The Linux “free” command gives information about total used and available space of physical memory and swap memory with buffers used by kernel in Linux/Unix like operating systems.

This article provides some useful examples of “free” commands with options, that might be useful for you to better utilize memory that you have.
1. Display System Memory
Free command used to check the used and available space of physical memory and swap memory in KB. See the command in action below.
# free
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 1021628 912548 109080 0 120368 655548
-/+ buffers/cache: 136632 884996
Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
2. Display Memory in Bytes
Free command with option -b, display the size of memory in Bytes.
# free -b
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 1046147072 934420480 111726592 0 123256832 671281152
-/+ buffers/cache: 139882496 906264576
Swap: 4294959104 0 4294959104
3. Display Memory in Kilo Bytes
Free command with option -k, display the size of memory in (KB) Kilobytes.
# free -k
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 1021628 912520 109108 0 120368 655548
-/+ buffers/cache: 136604 885024
Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
4. Display Memory in Megabytes
To see the size of the memory in (MB) Megabytes use option as -m.
# free -m
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 997 891 106 0 117 640
-/+ buffers/cache: 133 864
Swap: 4095 0 4095
5. Display Memory in Gigabytes
Using -g option with free command, would display the size of the memory in GB(Gigabytes).
# free -g
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 0 0 0 0 0 0
-/+ buffers/cache: 0 0
Swap: 3 0 3
6. Display Total Line
Free command with -t option, will list the total line at the end.
# free -t
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 1021628 912520 109108 0 120368 655548
-/+ buffers/cache: 136604 885024
Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
Total: 5215924 912520 4303404
7. Disable Display of Buffer Adjusted Line
By default the free command display “buffer adjusted” line, to disable this line use option as -o.
# free -o
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 1021628 912520 109108 0 120368 655548
Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
8. Display Memory Status for Regular Intervals
The -s option with number, used to update free command at regular intervals. For example, the below command will update free command every 5 seconds.
# free -s 5
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 1021628 912368 109260 0 120368 655548
-/+ buffers/cache: 136452 885176
Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
9. Show Low and High Memory Statistics
The -l switch displays detailed high and low memory size statistics.
# free -l
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 1021628 912368 109260 0 120368 655548
Low: 890036 789064 100972
High: 131592 123304 8288
-/+ buffers/cache: 136452 885176
Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
10. Check Free Version
The -V option, display free command version information.
# free -V procps version 3.2.8




How to find out RAM Memory details on an embedded system?
I know from /proc/meminfo vstat, free etc, but none of the commands give you exact RAM i have.
Example, I have checked on a system where i know the RAM size of 256 Mb, but none of the above command displays 256Mb.
is that correct or am i missing something?
Good beginner info on how to read the memory usage in Linux.
#8 says “Dispaly.” It should say “Display.”
Nice and neat info. I believe you meant all the mentioned kb, mb, gb are actually kibi, mebi and gibi rather than kilo, mega and giga.
Hi,
I would request you, please let us know each fields explanation of free -m output. ( Buffer/cache/shared)
Regards,
Sathish
@Sathish,
We already explained each switch used with free command in this article, I hope you gone through it each point, still I will update you that free -m is used to show the amount of memory in megabytes.
Thanks for sharing the commands, your site is good source of information for me…
Hi,
I am newbie to linux. I am practising ubuntu in vmware workstation installed in PC. How do i surf internet using ubuntu while i am in vmware workstation ? Please assist.
@Sam,
Under Vmware there is a Network Settings tab, adjust values there to enable internet in VMware guest OS..
Excellent!
Thank you for the share, great read. How can I reduce the memory consumption used? I am using a virtual box with ubuntu 14.04 LTS. I have only 82M of 500M free memory left?
I might guess it is because the low memory I have assigned to Virtual machine 512M upon initialising it.
@Sinan,
500MB is not enough to run Ubuntu 14.04, you need at least 1G or 2G of ram to run Ubuntu properly..or else you can stop some unwanted applications to reduce memory consumption, you need to use top command to trace the applications which are utilizing high ram usage..
@Sara
That’s not related to memory as df is used to report file system disk space usage, free is the memory (RAM) and swap usage.
I prefer the more tidy look of ‘df -hT’, added plus percentage of the used space. Btw. i enjoy your posts :-)
TQ & 5* i give to you … im newbie in linux … this is my 2nd linux (ubuntu 14.04) 1st i use (fedora19) sory my english .. i read your all your post (tecmint).. & TQ again for good post.. (y)
@Ali,
Thanks for such kind words, we continue to provide such usefull artilces to our newbies like you…:)
Happy New Year Mr.Ravi,
Articles which is published in this website is very useful to beginners like me hats off .God Bless you
@Gautham,
Wishing same to you.. a Very Happy New Year ahead…….and thanks for appreciating our articles..
Thanks for sharing.
Also in Debian, “h” parameter to human readable format (free -h).
@Ramazan,
Thanks for about that ‘-h’ parameter in Debian..