In this article, I will show you how to check the size of MySQL/MariaDB databases and tables via the MySQL shell. You will learn how to determine the real size of a database file on the disk as well as size of data that it present in a database.
Read Also: 20 MySQL (Mysqladmin) Commands for Database Administration in Linux
By default MySQL/MariaDB stores all the data in the file system, and the size of data that exists on the databases may differ from the actual size of Mysql data on the disk that we will see later on.
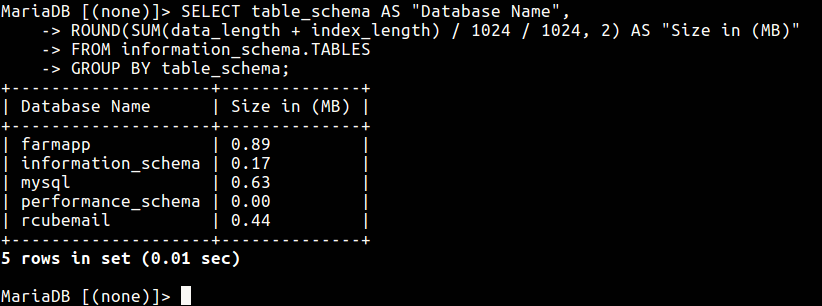
In addition, MySQL uses the information_schema virtual database to store information about your databases and other settings. You can query it to gather information about size of databases and their tables as shown.
# mysql -u root -p MariaDB [(none)]> SELECT table_schema AS "Database Name", ROUND(SUM(data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024, 2) AS "Size in (MB)" FROM information_schema.TABLES GROUP BY table_schema;
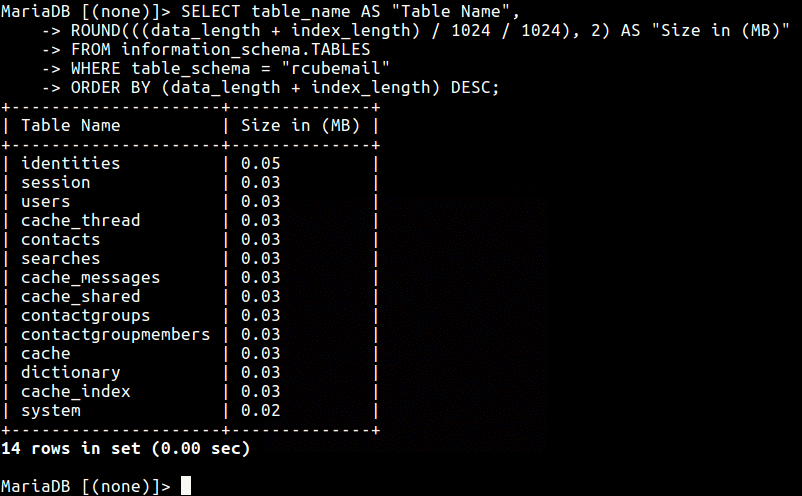
To find out the size of a single MySQL database called rcubemail (which displays the size of all tables in it) use the following mysql query.
MariaDB [(none)]> SELECT table_name AS "Table Name", ROUND(((data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS "Size in (MB)" FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "rcubemail" ORDER BY (data_length + index_length) DESC;
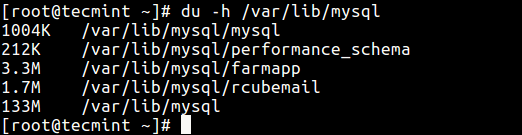
Finally, to find out the actual size of all MySQL database files on the disk (filesystem), run the du command below.
# du -h /var/lib/mysql
You might also like to read these following MySQL related articles.
- 4 Useful Commandline Tools to Monitor MySQL Performance in Linux
- 12 MySQL/MariaDB Security Best Practices for Linux
For any queries or additional ideas you want to share regarding this topic, use the feedback form below.