Systemd (system daemon) is a modern system management daemon for Linux systems. Systemd is a replacement for init system manager; it controls system startup and services, and introduces the idea of units (managed via unit files) to identify different types of system resources such as services, devices, swap, automount, targets, paths, sockets and others.
It ships in with systemctl, a component for controlling systemd’s behavior and units (starting, stopping, restarting, viewing status etc) using the command line. What if you simply want to manage units using keyboard shortcuts, that is where chkservice comes in.
Read Also: How to Manage ‘Systemd’ Services and Units Using ‘Systemctl’ in Linux
Chkservice is an easy-to-use, ncurses-based command line tool for managing systemd units on a terminal. It lists units alphabetically under the categories (services, targets, automounts etc), showing the their status and description, and allows you, with superuser privileges to start, stop, enable and disable units.
Install chkservice in Linux Systems
On Debian and its derivatives, chkservice can be easily installed using its own PPA as shown.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linuxenko/chkservice $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install chkservice
On Fedora Linux distributions.
# dnf copr enable srakitnican/default # dnf install chkservice
On Arch Linux distribution.
# git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/chkservice.git # cd chkservice # makepkg -si
On other Linux distributions, you can build the release version using following commands.
# git clone https://github.com/linuxenko/chkservice.git # mkdir build # cd build # cmake ../ # make
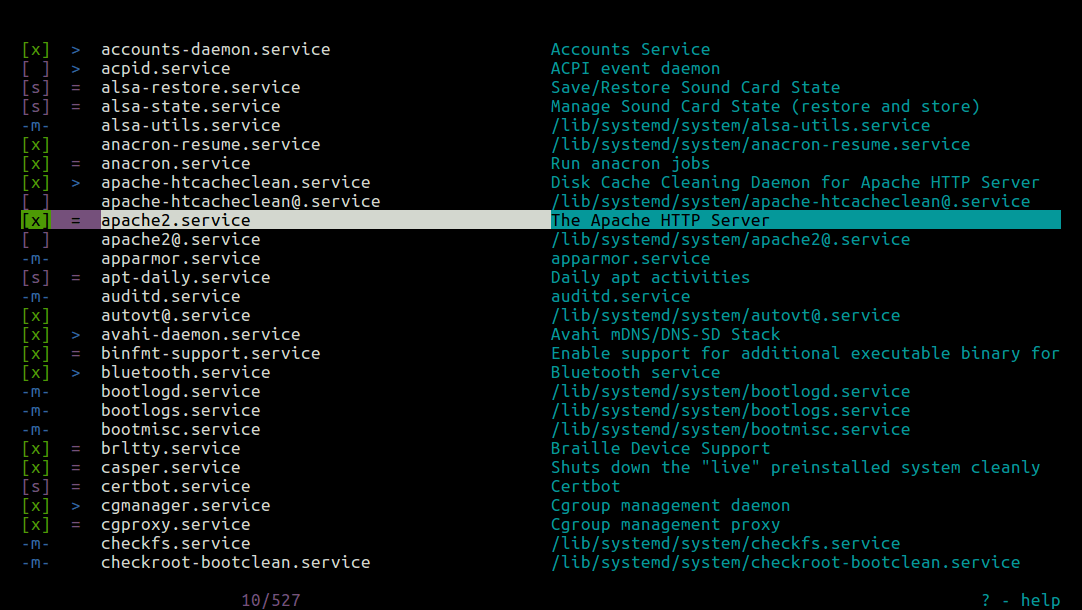
Once you have installed chkservice, launch it with root privileges using the sudo command. It’s output consists of four columns, the first showing enabled/disabled/masked status, the second showing started/stopped status, unit name/type and last column is the unit description.
$ sudo chkservice
Chksericve unit status information:
[x]– shows a unit is enabled.[ ]– shows a unit is disabled.[s]– indicates a static unit.-m-– shows a unit is masked.=– indicates unit has been stopped.>– shows unit is running.
Below are the chkservice navigation keys:
Up/k– move cursor up.Down/j– move cursor down.PgUp/b– move page up.PgDown/f– move page down.
The following are chkservice action keys:
r– updates or reload information.Space bar– used to enable or disable a unit.s– for starting or stopping a unit.q– exit.
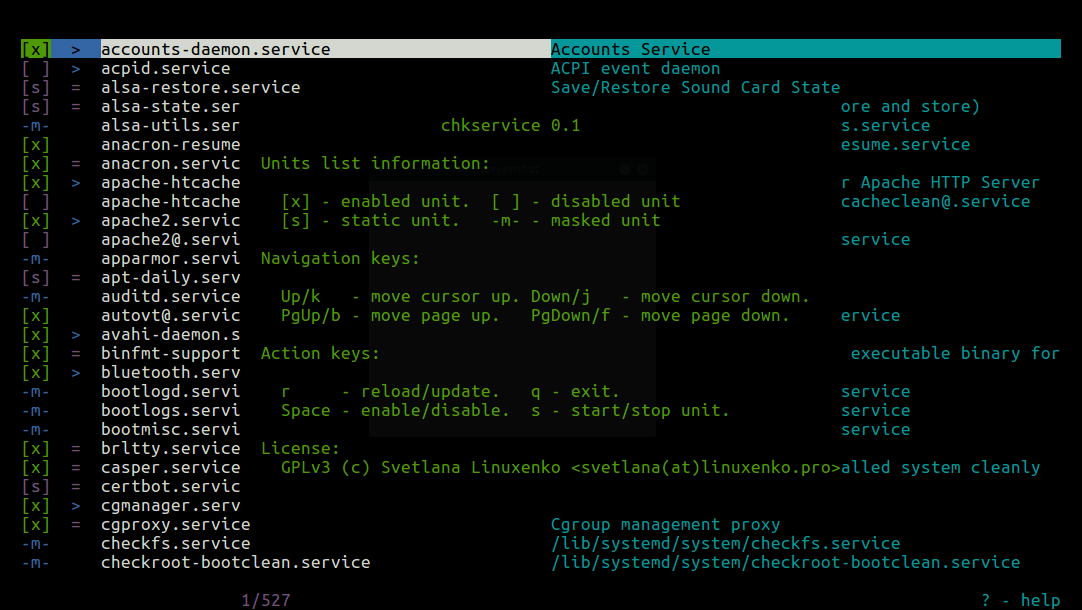
To view the help page as shown in the screenshot below, use ? (press [Shift + /]).
chkservice Github repository: https://github.com/linuxenko/chkservice
You may also like to read these systemd related articles.
- How to Create and Run New Service Units in Systemd Using Shell Script
- Managing System Startup Process and Services (SysVinit, Systemd and Upstart)
- Manage Log Messages Under Systemd Using Journalctl
- How to Change Runlevels (targets) in SystemD
That’s it! If you encountered any errors during installation or want to ask questions, share any thoughts, use the comment form below.