Normally while installing MySQL/MariaDB database server on Linux, it’s recommended to set a MySQL root user password to secure it, and this password is required to access the database server with root user privileges.
Suggested Read: How to Install and Secure MariaDB 10 in CentOS 7
In this guide, we will show you how to connect and run MySQL commands without entering a password (mysql passwordless root login) on the Linux terminal.
How to Set MySQL Root Password
In case you have freshly installed the MySQL/MariaDB server, then it doesn’t require any password to connect to it as root user. To secure it, set the MySQL/MariaDB password for root user with the following command.
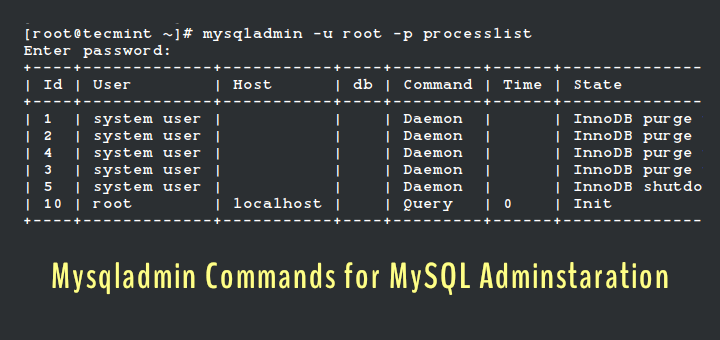
Note that this command is just one of the many MySQL (Mysqladmin) Commands for Database Administration in Linux.
# mysqladmin -u root password YOURNEWPASSWORD
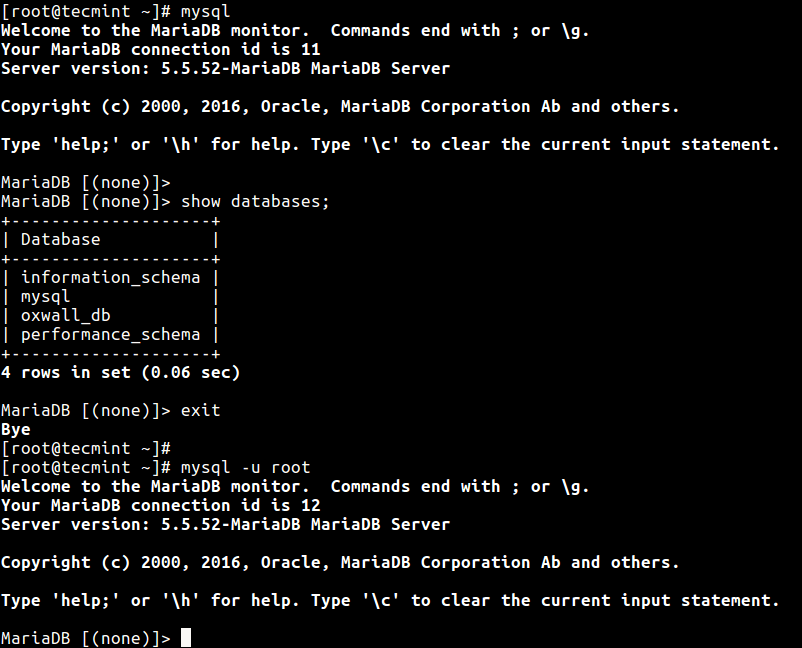
How to Connect or Run MySQL Without Root Password
To run MySQL commands without entering password on the terminal, you can store your user and password in the ~/.my.cnf user specific configuration file in user’s home directory as described below.
Now create the config file ~/.my.cnf and add configurations below in it (remember to replace mysqluser and mysqlpasswd with your own values).
[mysql] user=user password=password
Save and close the file. Then set the suitable permissions on it, to make it only readable and writable by you.
# chmod 0600 .my.cnf
Once you have set user and password in the Mysql configuration file, from now on when you run mysql commands such as mysql, mysqladmin etc, they will read the mysqluser and mysqlpasswd from the above file.
# mysql # mysql -u root
You may also like to read these related articles about MySQL/MariaDB:
-
- 20 MySQL (Mysqladmin) Commands for Database Administration in Linux
- How to Change Root Password of MySQL or MariaDB in Linux
- How to Reset MySQL or MariaDB Root Password in Linux
- 15 Useful MySQL/MariaDB Performance Tuning and Optimization Tips
- 4 Useful Commandline Tools to Monitor MySQL Performance in Linux
In this guide, we showed how to run MySQL commands without entering root password on the terminal. If you have any queries or thoughts to share, do hit us up via the feedback form below.





It didn’t work. I had created the user from cPanel in shared hosting. It did work with:
as my
my.cnffile.@Myname
Thanks for sharing, we will verify this.
Hi
Sorry, I’m here again
I am getting below error when trying to connect to MySQL.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: NO) or … YES)
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tablesdoes it works? the procedure as above was going normally, no remarks!What about the file /etc/mysql/.my.cnf? and the command
chmod 0600 .my.cnf?(Mysql 10.3 / RPI 4 Mod B Buster)
thank you for your help
Max
Thank you, you helped me
“In case you have freshly installed the MySQL/MariaDB server, then it doesn’t require any password to connect to it as root user.”
This is not the case for MySQL 5.7 on CentOS 7.x the MySQL server generate a random password that you need to figure it out with:
@sedlav
Okay, we will cross-check this and perhaps update the article. Many thanks for the feedback.