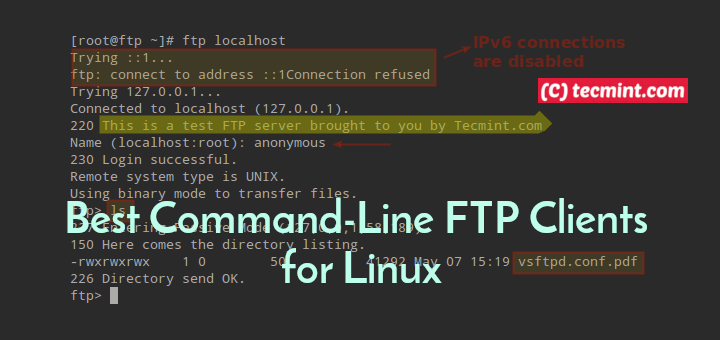
To create an SFTP user in Linux, you can follow a systematic approach that ensures the user has restricted access while being able to transfer files securely.
This guide will provide detailed steps to set up an SFTP-only user on a Linux system, focusing on Ubuntu as a primary example, but the principles apply broadly to other Linux distributions as well.
Overview of SFTP
SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) is a secure version of the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) that uses SSH (Secure Shell) to encrypt the data transferred over the network, which is commonly used for securely transferring files between a client and a server.
Creating a New SFTP User
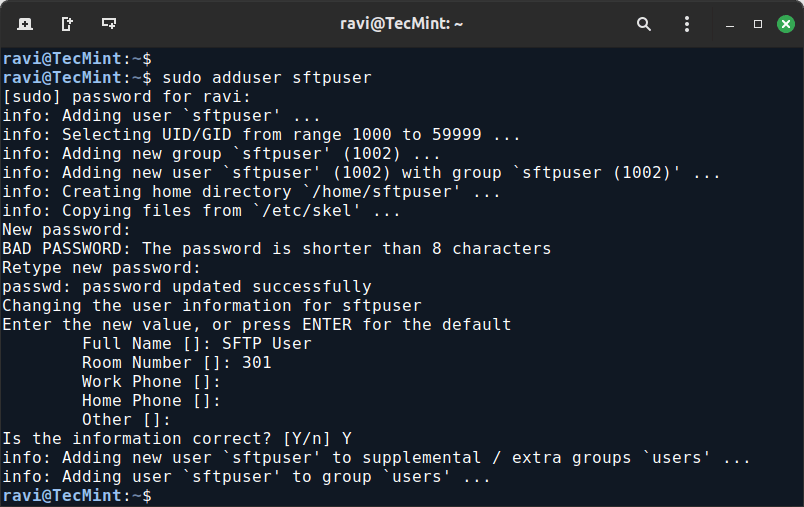
First, you need to create a new sftp user account, which will be used to log in and transfer files using SFTP.
sudo adduser sftpuser
Creating a Directory for SFTP
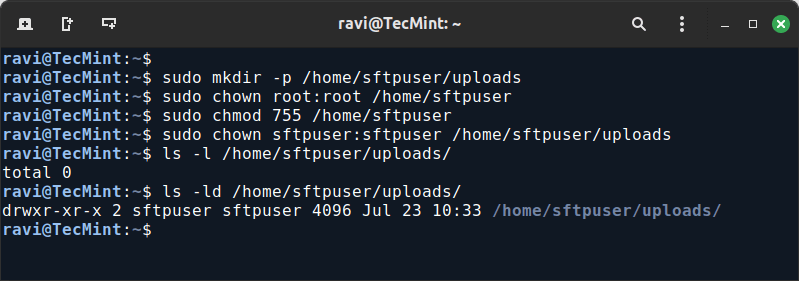
Next, you need to create a directory where the SFTP user can upload and download files, this directory will be their home directory for SFTP purposes.
sudo mkdir -p /home/sftpuser/uploads
To ensure security, set the correct permissions for the directories. The user should only have access to their own directory and not be able to navigate to other parts of the system.
sudo chown root:root /home/sftpuser sudo chmod 755 /home/sftpuser
Then, change the ownership of the uploads directory:
sudo chown sftpuser:sftpuser /home/sftpuser/uploads
Configure SSH for SFTP
You need to edit the SSH server configuration file to configure SSH to allow SFTP for the new user.
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Add the following lines at the end of the file to configure SFTP access:
Match User sftpuser
ChrootDirectory /home/sftpuser
ForceCommand internal-sftp
AllowTcpForwarding no
X11Forwarding no
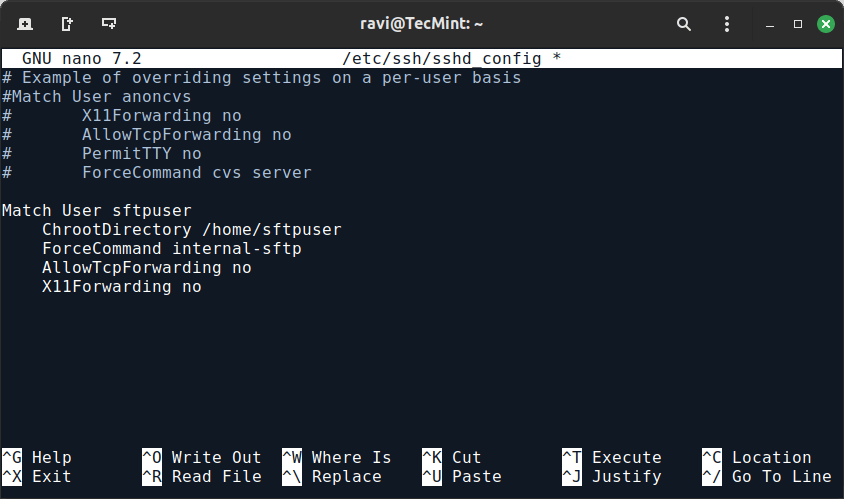
Here’s what each line does:
- Match User sftpuser applies these settings only to the sftpuser.
- ChrootDirectory /home/sftpuser restricts the user’s access to /home/sftpuser.
- ForceCommand internal-sftp forces the user to use SFTP only, disallowing SSH shell access.
- AllowTcpForwarding no and X11Forwarding no are additional security measures to prevent the user from using other SSH features.
After saving your changes, restart the SSH service to apply the changes.
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Testing the SFTP User
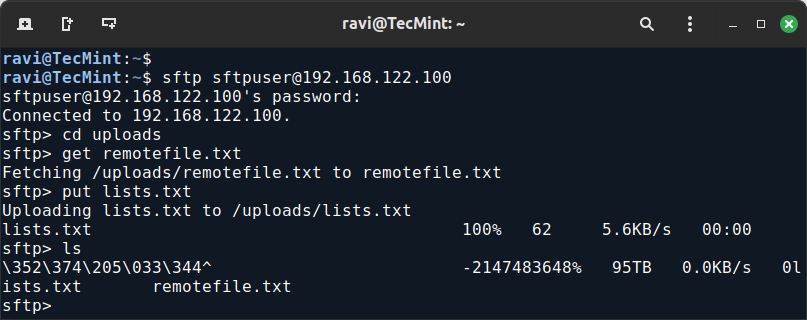
You can now test the connection to the SFTP server using an SFTP client or command line to connect to your server.
sftp sftpuser@your_server_ip
Once connected, you can use SFTP commands to navigate and manage files in the uploads directory.
For example, use the ls command to list files and put to upload files.
sftp> ls sftp> cd uploads sftp> get remotefile.txt sftp> put lists.txt
Conclusion
Creating an SFTP user in Linux is a straightforward process that enhances security and file management capabilities. By following these steps, you can set up a dedicated user for SFTP access, ensuring that your file transfers are secure and restricted to the appropriate directories.