The sudo command allows a user to administer a Linux system with the security privileges of another user, by default, the superuser or root.
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of creating a sudo user in openSUSE i.e create a user and grant them privileges to invoke the sudo command.
For this guide, we will use openSUSE Leap 15.3, the latest release on which the sudo command comes pre-installed. However, if this is not the case for you and the sudo command isn’t installed on your openSUSE operating system, install it as follows.
Install Sudo in openSUSE Linux
First switch to the root account, using the su command, enter the root password when prompted, and then run the zypper command to install sudo as shown:
$ su - # zypper in sudo
This guide also assumes that you have a freshly installed openSUSE operating system on your computer.
Create Sudo User in openSUSE Linux
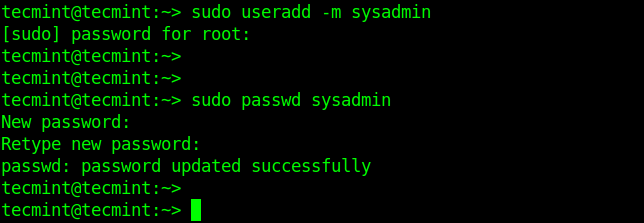
Start by creating a user account (called sysadmin in this example), using the useradd command, and create a secure password for the user as follows. The -m flag instructs to create the user’s home directory.
Note that the user tecmint is the default administrative user that can invoke sudo. Therefore we are using it to create another administrative user that can invoke sudo as well.
$ sudo useradd -m sysadmin $ sudo password sysadmin
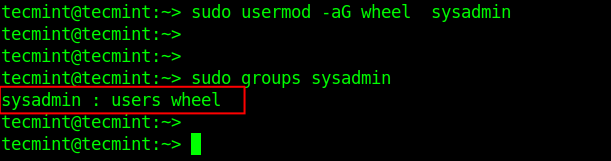
Next, add the user sysadmin to the administrative group called wheel using the usermod command as shown.
In this command, the -a flag means adding the user to the supplementary group specified by the -G flag. Then check the sysadmin’s groups using the groups’ command:
$ sudo usermod -aG wheel sysadmin $ sudo groups sysadmin
Configure Sudo Access and Wheel Group in Sudoers File
Now you need to configure the wheel group to allow users who belong to it to execute any command using sudo. Open the sudoers file for editing by running the following command (by default, visudo uses vim as an editor):
$ sudo visudo
Look for the lines:
Defaults targetpw # ask for the password of the target user i.e. root ALL ALL=(ALL) ALL # WARNING! Only use this together with 'Defaults targetpw'!
and comment them out as shown in the following screenshot.
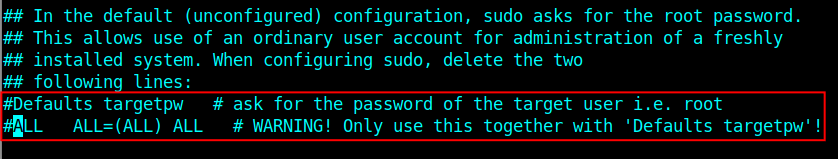
Also, look for the following line.
# %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
and uncomment it to allow members of the group wheel to execute any command by invoking the sudo command:
%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
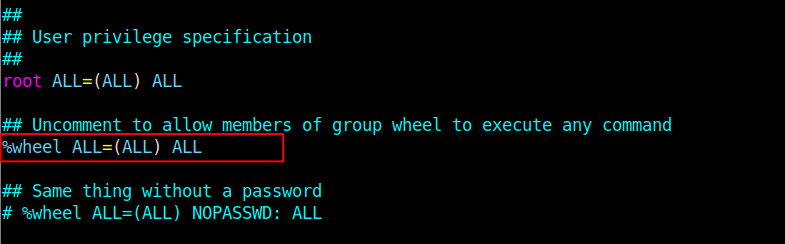
Save the changes in the sudoers’ file and close it.
Note: After the recent changes, the default user account on a freshly installed system is disabled from sudo access. In this case, the user tecmint can no longer invoke the sudo command unless the user is added to the wheel group.
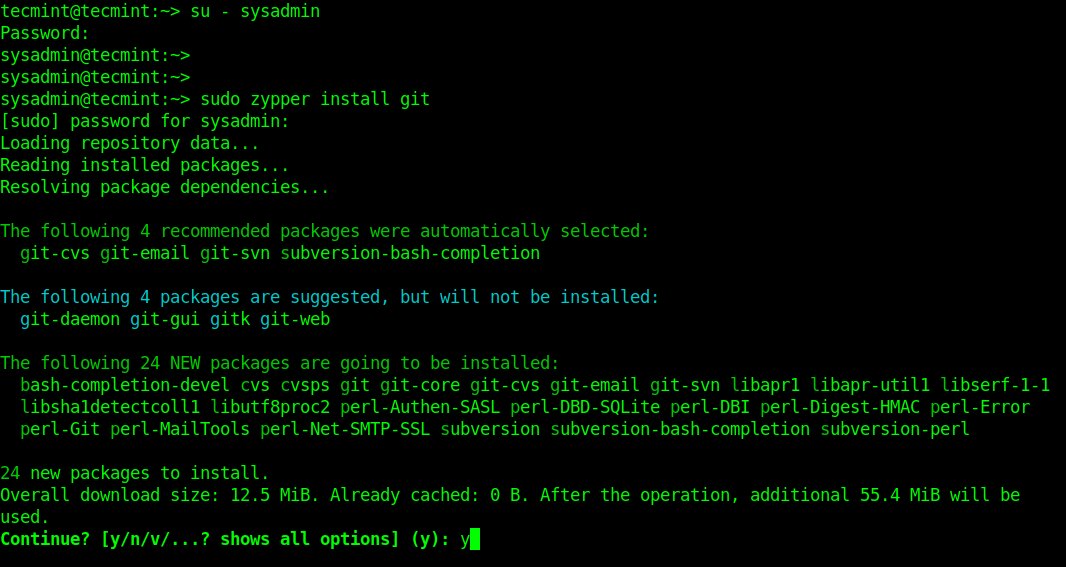
Testing Sudo User in openSUSE Linux
To test if the newly created user account can invoke the sudo command, switch the account using the su command, then run any command using sudo.
$ su - sysadmin $ sudo zypper install git
That’s all! In this guide, we looked at how to create a sudo user in the openSUSE Linux distribution. As usual, reach us via the comment form below for any questions or comments.