If you are a system administrator, a developer, or a DevOps engineer, chances are that at some point you’ve had to set up (or work with) a LAMP (Linux / Apache / MySQL or MariaDB / PHP) stack.
The web and database servers, along with the well-known server-side language, are not available in their latest versions from the major distributions’ official repositories. If you like to play or work with cutting-edge software, you will need to either install them from a source or use a third-party repository.
In this article, we will introduce Remi, a third-party repository that includes up-to-date versions of Apache, MySQL / MariaDB, PHP, and related software, for RHEL-based distributions such as Fedora, CentOS Stream, Rocky Linux, and AlmaLinux.
It is important to note, however, that Remi is currently available (at the time of this writing – August 2022) for the following distributions:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux and CentOS 9/8/7
- Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux 9/8
- Fedora 36/35 and 34
With that in mind, let’s begin.
Installing the Remi Repository in RHEL-based Distributions
Before we can actually install Remi, we need to enable the EPEL repository first. In Fedora, it should be enabled by default, but in RHEL, Rocky Linux, AlmaLinux, and CentOS you will need to do:
Install Epel and Remi Repo in RHEL Systems
--------- On RHEL, CentOS Stream, Rocky & Alma Linux 9 Releases --------- # yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm # yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-9.rpm # yum update --------- On RHEL, CentOS, Rocky & Alma Linux 8 Releases --------- # yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm # yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm # yum update --------- On RHEL/CentOS 7 --------- # yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm # yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm # yum update
Install Remi Repo in Fedora
# dnf install http://rpms.remirepo.net/fedora/remi-release-36.rpm [On Fedora 36] # dnf install http://rpms.remirepo.net/fedora/remi-release-35.rpm [On Fedora 35] # dnf install http://rpms.remirepo.net/fedora/remi-release-34.rpm [On Fedora 34] # dnf install http://rpms.remirepo.net/fedora/remi-release-33.rpm [On Fedora 33]
By default, Remi is not enabled. To enable it temporarily when you need it, you can do:
# yum --enablerepo=remi install package
where package represents the package you want to install.
If you want to enable Remi permanently, edit /etc/yum.repos.d/remi.repo and replace
enabled=0
with
enabled=1
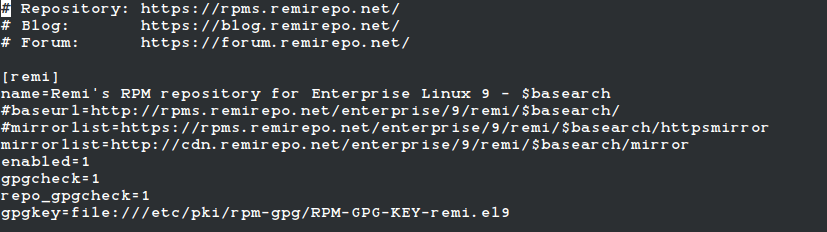
A Closer Look at this Remi Repository
If you decided to enable the repository permanently as suggested earlier, it should be listed when you run:
# yum repolist
As you can see in the following image, another repository named remi-safe is available as well:

This repository provides extensions that are either deprecated (but still used in legacy applications), under work-in-process, or that do not comply with Fedora’s policies.
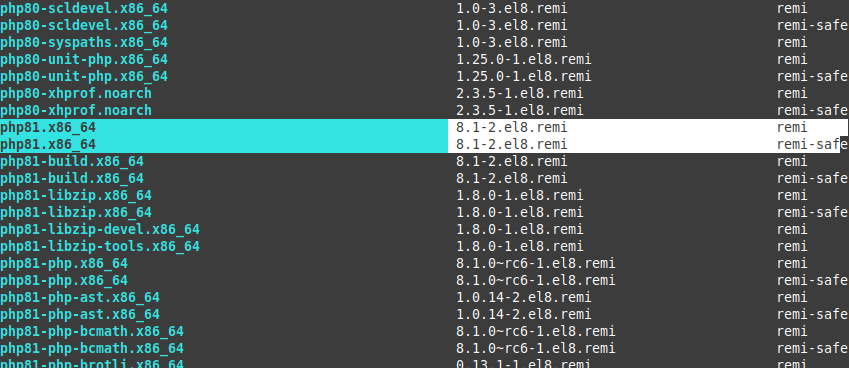
Now let’s search the newly added repositories for PHP-related packages as an example:
# yum list php*
Please note that packages in Remi have the same name as in the official repositories. Consider, for example, php:
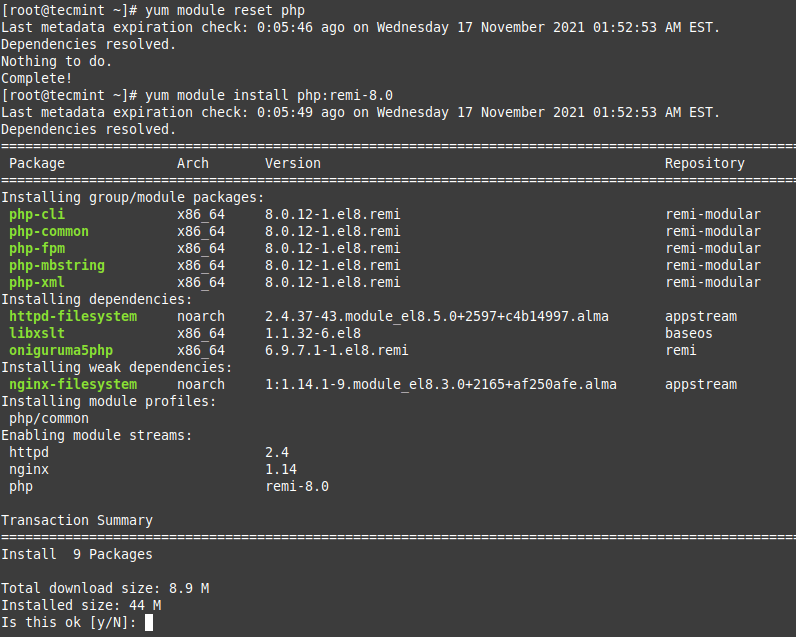
To install the latest stable version of PHP 8.X versions, you can do:
# yum module reset php # yum module install php:remi-8.1 [PHP 8.1 version] # yum module install php:remi-8.0 [PHP 8.0 version] # yum module install php:remi-7.4 [PHP 7.4 version]
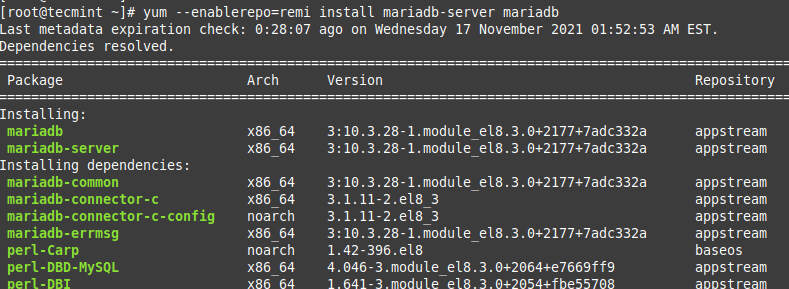
To install the latest stable version of MariaDB, you can do:
# yum --enablerepo=remi install mariadb-server mariadb
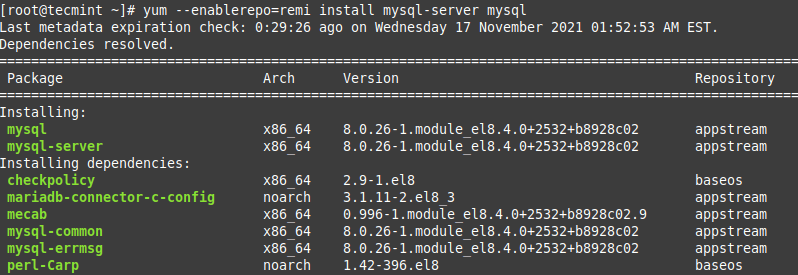
To install the latest stable version of MySQL, you can do:
# yum --enablerepo=remi install mysql-server mysql
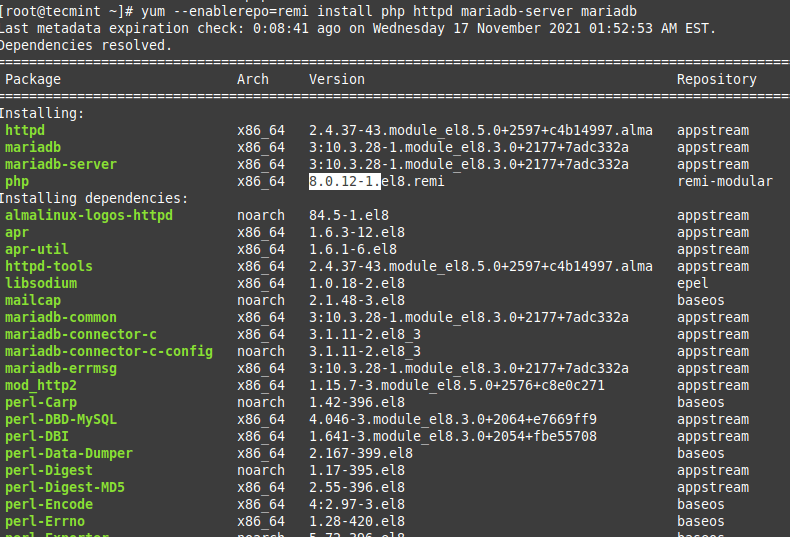
Similarly, to install the latest version of LAMP Stack, do:
# yum --enablerepo=remi install php httpd mariadb-server mariadb OR # yum --enablerepo=remi install php httpd mysql-server mysql
Summary
In this article, we have explained how to enable and use Remi, a third-party repository that provides the latest versions of components of the LAMP stack and related software.
The official website provides a configuration wizard that can be very useful to set it up in other RPM-based distributions.
As always, don’t hesitate to let us know if you have questions or comments about this article. Just drop us a line using the form below and we will respond as soon as possible.