In this editorial, we take a look at a great and powerful utility called apt-fast that you can use to speed up downloading packages by apt, apt-get, or aptitude.
apt-fast is an open-source shell script wrapper for the popular apt, apt-get, and aptitude package managing tools that help to speed the downloading of packages in parallel, with numerous connections per package on Debian-based systems.
Read some of the following articles that discuss apt, apt-get, and aptitude, along with their usage examples:
- APT vs. Aptitude: Understanding Real Difference Between Them
- 16 Useful apt Command Examples for Ubuntu/Debian
- 20 Useful ‘apt-get’ Command Examples for Ubuntu/Debian
- Learn Package Management with Aptitude in Ubuntu/Debian
In this article, we’ll explore how to install and use ‘apt-fast‘ to speed up your package management in Debian-based distributions.
Installing ‘apt-fast’ on Debian Systems
Open a terminal window, add the ‘apt-fast‘ ppa repository, and then update your system package repository.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable sudo apt update
Thereafter, run the command below to install the apt-fast tool.
sudo apt install apt-fast
During the ‘apt-fast’ installation process, you will be prompted to perform some package configuration such as choosing your default package manager used for installation installing, and removing software.
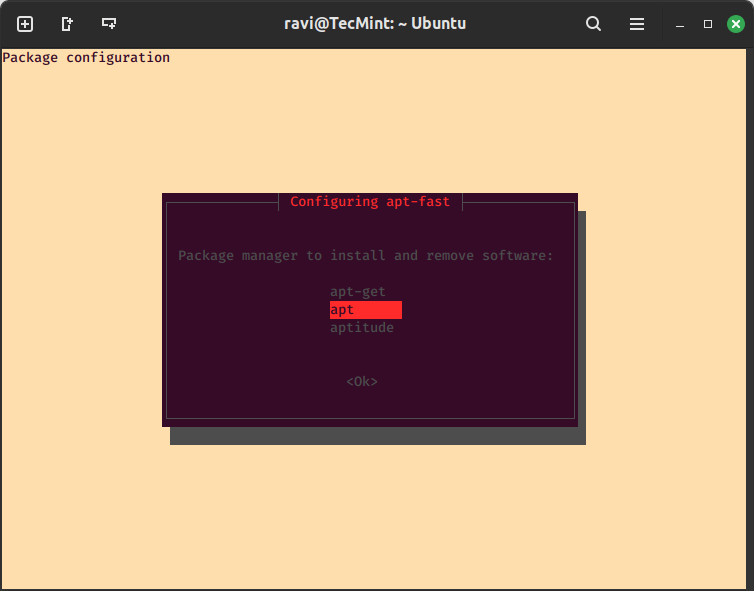
In the screen below, you can set the number of connections allowed, remember, you can also configure it later in the apt-fast configuration file (/etc/apt-fast.conf) using the _MAXNUM directive.
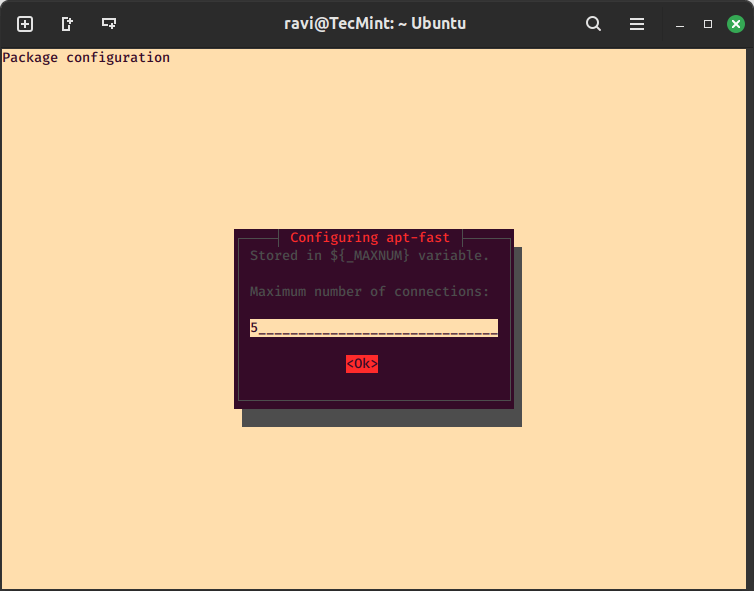
Next, you can also choose to suppress the apt-fast confirmation message every time you want to install a package. But leaving the default value is okay, therefore, choose <No> and hit Enter to advance.
How to Use apt-fast to Speed Up APT Package Downloads
After successfully installing apt-fast, simply use it the same way you run apt or aptitude commands.
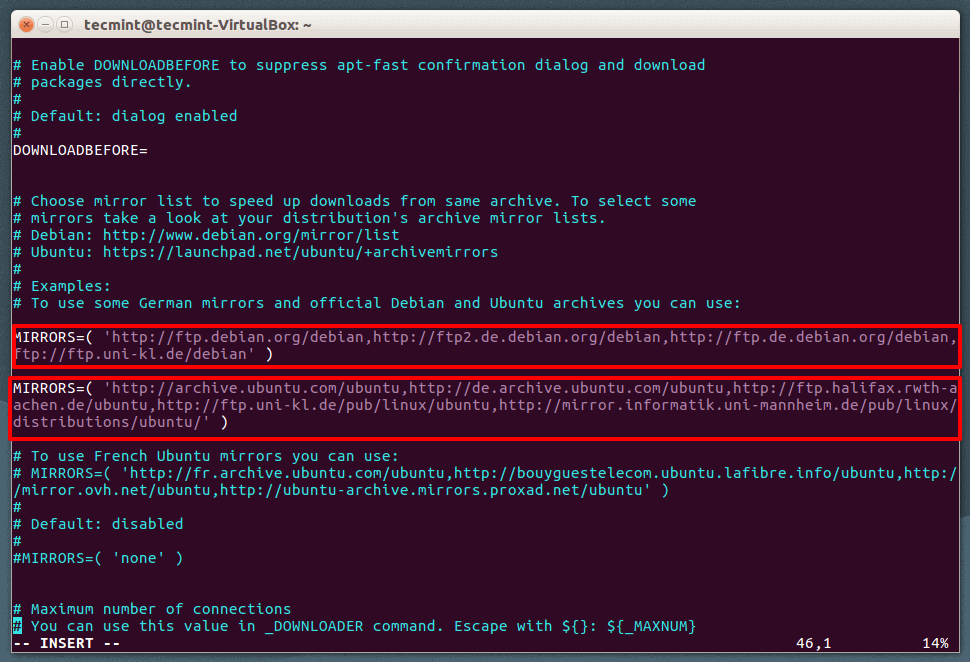
The apt-fast configuration file is: /etc/apt-fast.conf, you can further increase your download speeds by adding multiple mirrors and distributing load, make sure to add the nearest mirrors.
Official mirror lists for Debian and Ubuntu/Linux Mint:
You can add them to whitespace and comma-separated mirrors in the configuration file as follows:
On Debian Systems:
MIRRORS=( 'http://ftp.debian.org/debian, http://ftp2.de.debian.org/debian, http://ftp.de.debian.org/debian, ftp://ftp.uni-kl.de/debian' )
On Ubuntu and Linux Mint:
MIRRORS=( 'http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu, http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu, http://ftp.halifax.rwth-aachen.de/ubuntu, http://ftp.uni-kl.de/pub/linux/ubuntu, http://mirror.informatik.uni-mannheim.de/pub/linux/distributions/ubuntu/' )
Important: To use mirrors in /etc/apt/sources.list or /etc/apt/sources.list.d/, you also need to add them to /etc/apt-fast.conf as well.
$ sudo vi /etc/apt-fast.conf
You also view the man page for apt-fast and apt-fast.conf as follows:
man apt-fast man apt-fast.conf
Now that ‘apt-fast‘ is installed, let’s explore how to use apt-fast to accelerate APT package downloads.
Installing Packages
Instead of using the traditional ‘apt‘ or ‘apt-get‘ commands, simply prepend ‘apt-fast‘ to your installation command.
sudo apt-fast install git
You will be asked to confirm whether to download the package or not, and enter Yes/Y to continue. The image below shows an apt-fast working – downloading git package using several connections.
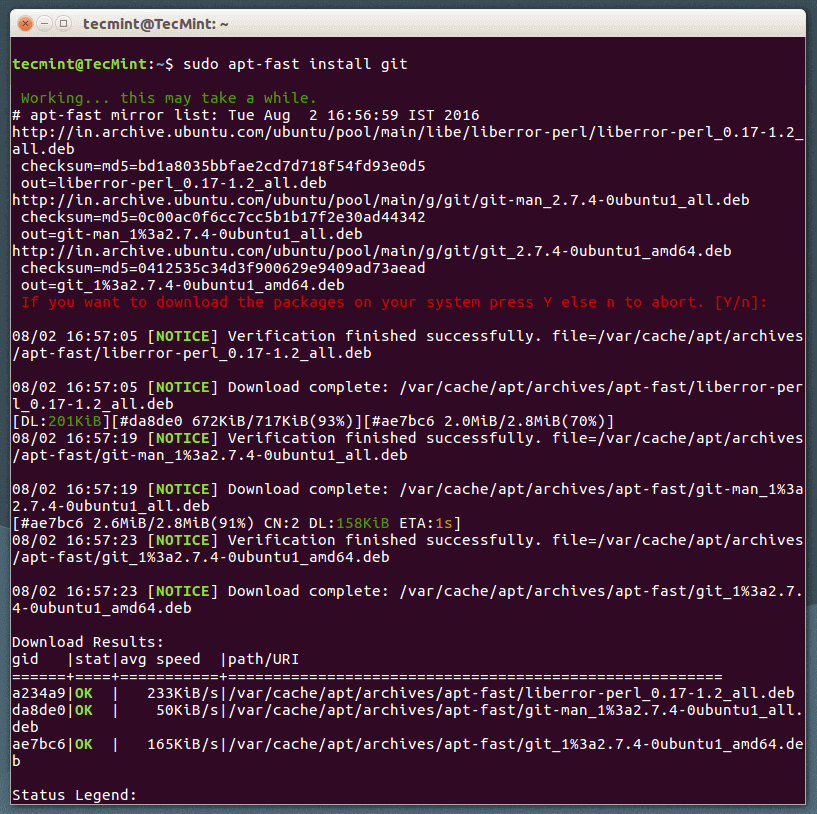
After downloading the git package, you will again be asked to install it by entering Yes/Y and press Enter to proceed with the installation process.
Updating Packages
Similarly, for updating packages, use:
sudo apt-fast update sudo apt-fast upgrade OR sudo apt-fast dist-update
In case a downloading process stops or breaks, run the command below:
sudo apt-fast clean
Removing Packages
For package removal, ‘apt-fast‘ works just like ‘apt‘:
sudo apt-fast remove git
For more information, visit the apt-fast Github repository.
Conclusion
Here, we reviewed a powerful shell-script front-end for apt, apt-get, and aptitude that helps you to boost APT download speeds while installing packages on your Debian-based systems such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and many more.
What is your experience with apt-fast? Do you think it works well for you? Then give us your thoughts plus any other questions you would like to ask, via the feedback form below.





Seems like a very convoluted way of using the APT command.
sudo apt-fast dist-upGRADE not UPDATE
I discovered this wrapper about a year ago. Any time I install Linux, I then install this. It should be put into the mainline repos. It is a must have.
@Joe
Yes, i absolutely agree with you, this is a great front-end for apt/apt-get/aptitude for Debian systems. Its efficient and reliable as well, including it in mainline repos would be so useful.
Thanks a lot for very helpful and detailed article, I Just want to know something . See, in windows IDM i can use multithreaded downloading and set threads upto 32 max, so each file to be downloaded gets divided into 32 parts and every thread downloads its part simultaneously.
I want to use apt-fast for the same purpose, can you please guide me, how can i configure concurrent downloading threads or segments in apt-fast configurations ?? is it Max Number Of Connections or something else.
Sorry for my poor communication skills hope you understand what i want to know and help me, thanks a lot again
Regards
@Junaid
Yes, it is the Max Number of Connections
apt-fast uses more than one connection to download a single package, which i suppose is similar to the multithreaded downloading. Therefore, you need to set the Max Number of Connections to achieve something similar.
It cut my update time significantly. Running Mint 17.2 (Mate). Thanks.
@Larry H
Good to know that it worked well for you, thanks for getting back to us.
thank you, I am use Ubuntu 16.04
@Allan
Welcome, above all, thanks for your feedback.