Filelight is a free, open source, simple, easy to use, and cross-platform KDE utility for viewing graphical disk space usage information. It works on Linux distributions and Windows operating systems. It is a disk analyzer that outputs your file system as a set of concentric segmented-rings to help you view disk usage.
Read Also: 10 Useful Commands to Find Disk Usage of Files and Directories
The filelight package is available for installation in most if not all mainstream Linux distributions, you can install it using a package manager as shown.
$ sudo apt install filelight [On Debian/Ubuntu] $ sudo yum install filelight [On CentOS/RHEL] $ sudo dnf install filelight [On Fedora 22+]
Once you have installed fileflight, you can search for it in the system menu, and open it. You will land in the interface below, which shows all the mounted filesystems.
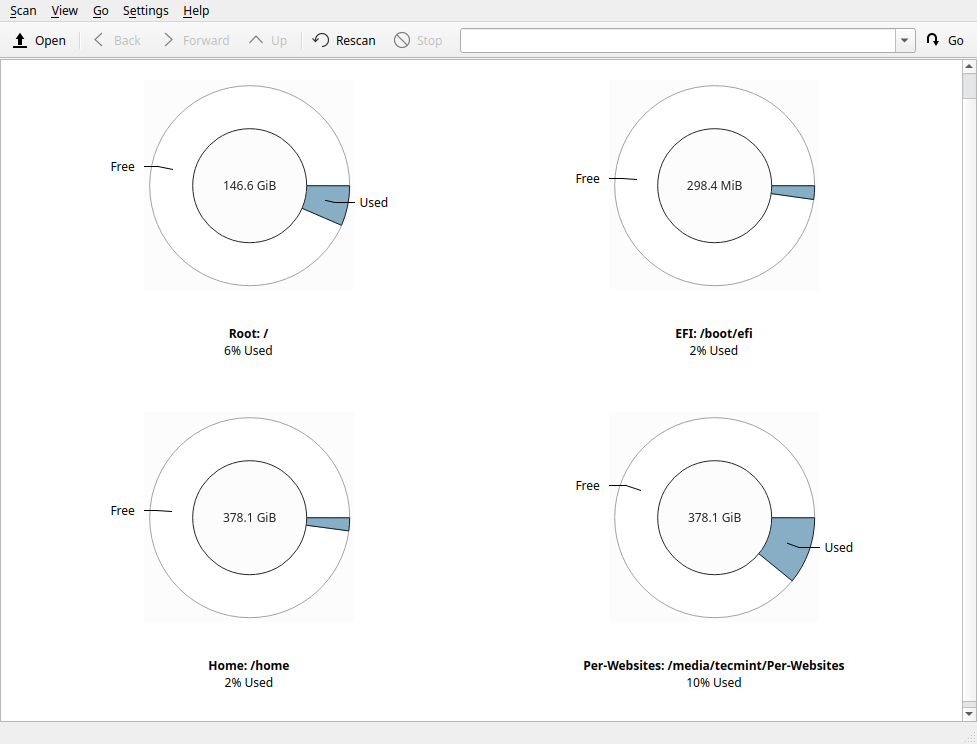
To view a file system in detail, simply click on it. You can move your mouse over the graphical layout to view files and sub-directories under it.
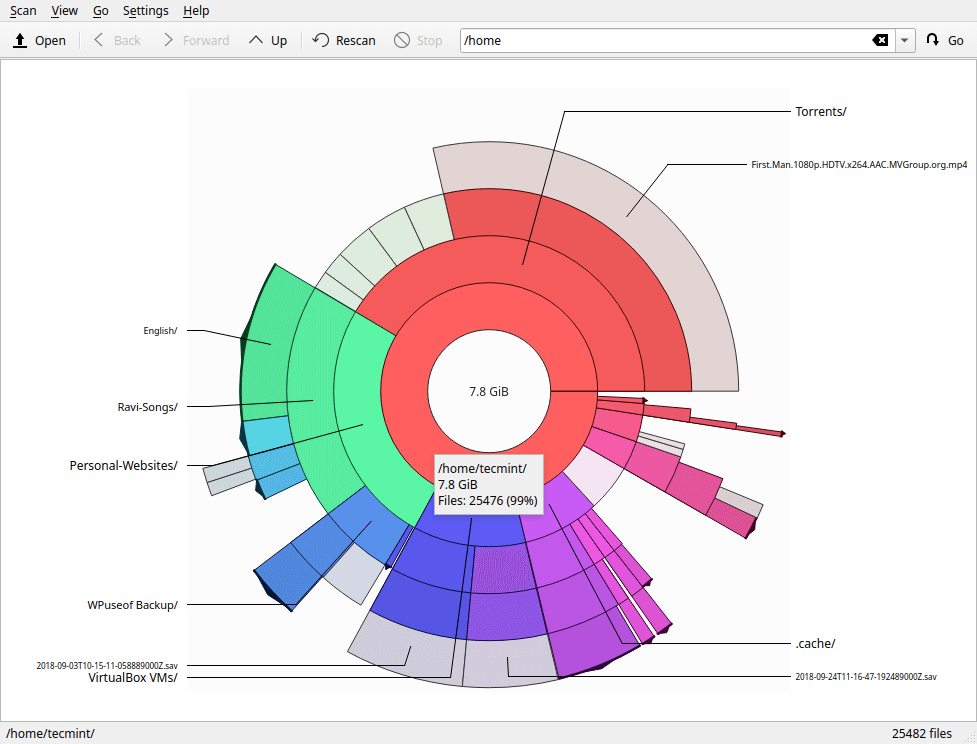
The application also allows you to scan an individual folder/directory to identify hot spots (files and sub-directories occupying the largest space) in it. To do that, go to Scan -> Scan Folder, then select the folder you want to analyze (for example the Downloads folder), and click Choose.
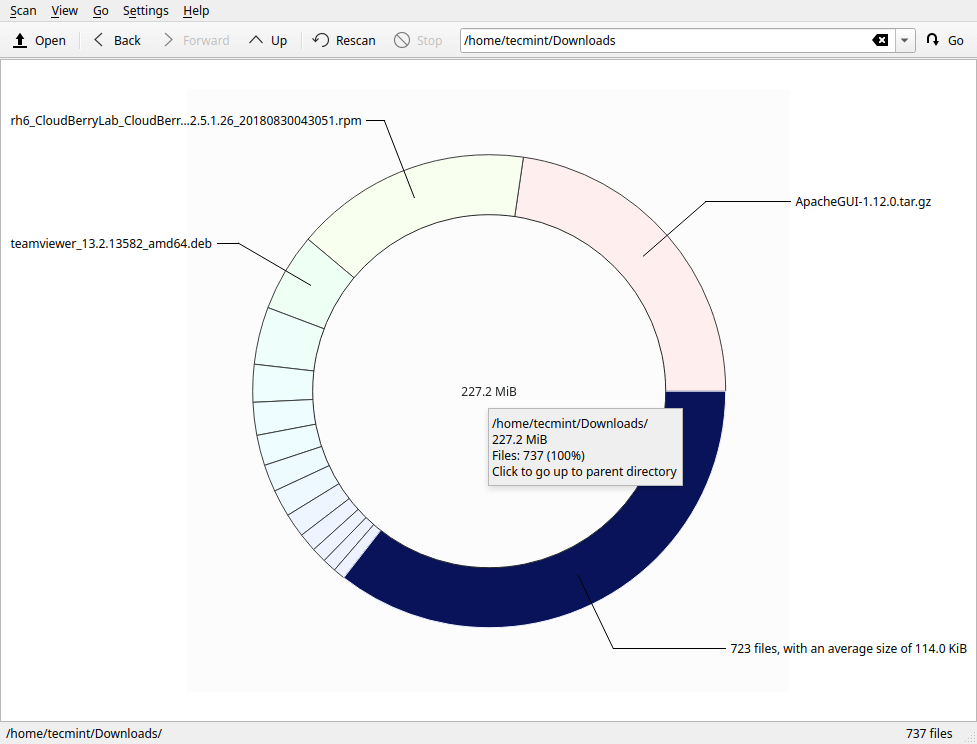
There are many options under Scan; you can choose to Scan your home folder or root folder using the provided options.
Fileflight is also configurable under the Settings menu item. You can select the Toolbars to be shown; configure shortcuts, toolbars and the entire application.
Under the option Configure Fileflight, you can add or remove filesystems to or not to scan by clicking on the Scanning tab. You can also configure its appearance (color scheme, font size etc.) under the Appearance tab.
Fileflight Homepage: https://utils.kde.org/projects/filelight/
That’s all! Fileflight is a simple graphical disk analyzer for Linux systems and Windows operating system. Try it out and share your thoughts with us via the feedback form below.