Each attempt to login to SSH server is tracked and recorded into a log file by the rsyslog daemon in Linux. The most basic mechanism to list all failed SSH logins attempts in Linux is a combination of displaying and filtering the log files with the help of cat command or grep command.
In order to display a list of the failed SSH logins in Linux, issue some of the commands presented in this guide. Make sure that these commands are executed with root privileges.
The most simple command to list all failed SSH logins is the one shown below.
# grep "Failed password" /var/log/auth.log
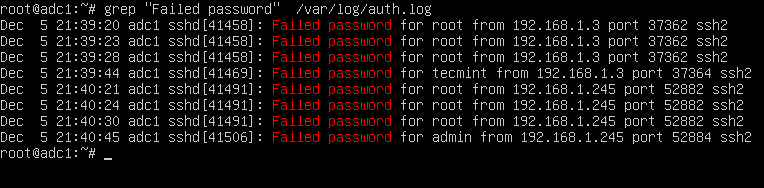
The same result can also be achieved by issuing the cat command.
# cat /var/log/auth.log | grep "Failed password"
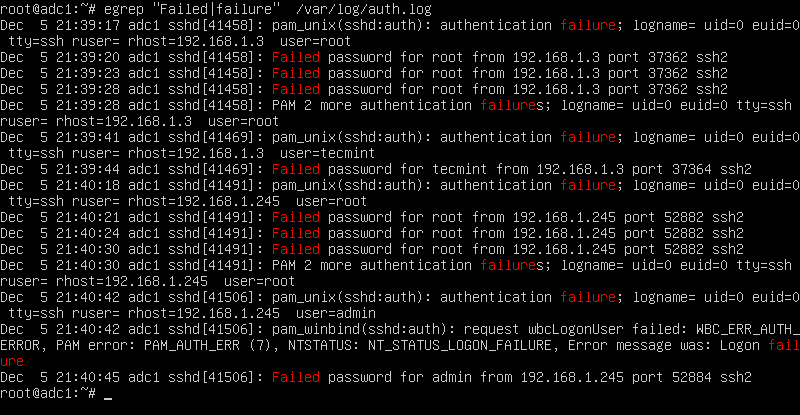
In order to display extra information about the failed SSH logins, issue the command as shown in the below example.
# egrep "Failed|Failure" /var/log/auth.log
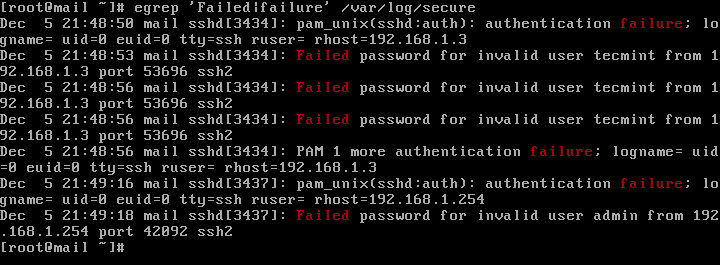
In CentOS or RHEL, the failed SSH sessions are recorded in /var/log/secure file. Issue the above command against this log file to identify failed SSH logins.
# egrep "Failed|Failure" /var/log/secure
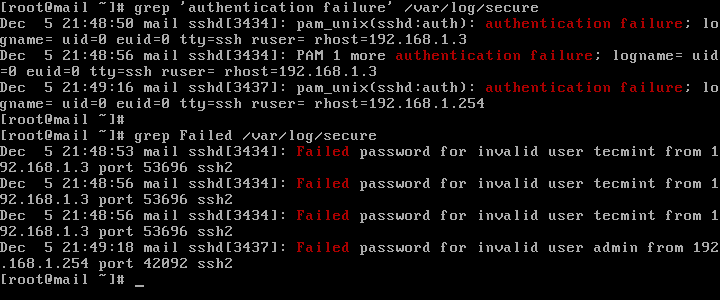
A slightly modified version of the above command to display failed SSH logins in CentOS or RHEL is as follows.
# grep "Failed" /var/log/secure # grep "authentication failure" /var/log/secure
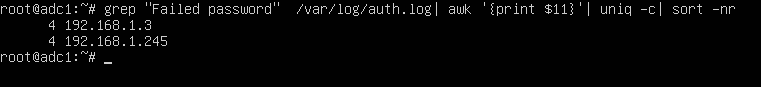
To display a list of all IP addresses that tried and failed to log in to the SSH server alongside the number of failed attempts of each IP address, issue the below command.
# grep "Failed password" /var/log/auth.log | awk ‘{print $11}’ | uniq -c | sort -nr
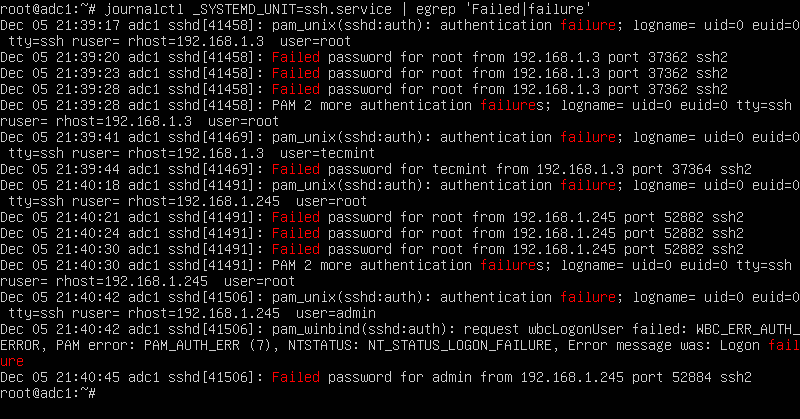
On newer Linux distributions you can query the runtime log file maintained by Systemd daemon via journalctl command. In order to display all failed SSH login attempts you should pipe the result via grep filter, as illustrated in the below command examples.
# journalctl _SYSTEMD_UNIT=ssh.service | egrep "Failed|Failure" # journalctl _SYSTEMD_UNIT=sshd.service | egrep "Failed|Failure" #In RHEL, CentOS
In CentOS or RHEL, replace the SSH daemon unit with sshd.service, as shown in the below command examples.
# journalctl _SYSTEMD_UNIT=sshd.service | grep "failure" # journalctl _SYSTEMD_UNIT=sshd.service | grep "Failed"
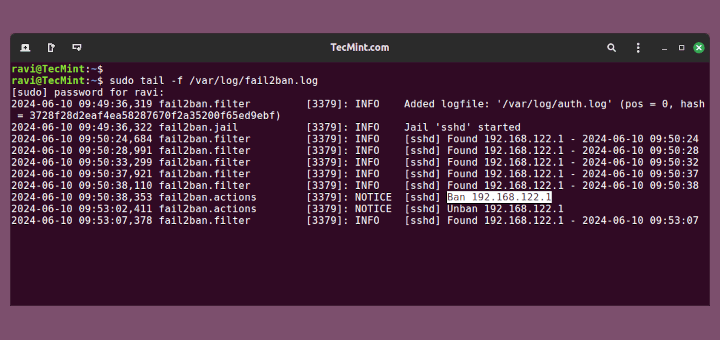
After you’ve identified the IP addresses that frequently hit your SSH server in order to log in to the system with suspicious user accounts or invalid user accounts, you should update your system firewall rules to block the failed SSH attempts IP addresses or use a specialized software, such as fail2ban to manage these attacks.





How can I do with bash script this one? I want to find in the log file failed attempt.
Thank you so much.
Regards
Ziad
Very useful, thanks. Just had my R&D server attacked today bruteforcing the password. Need to read more about fail2ban or other firewall options for Ubuntu..
Very informative article, thanks for share so helpful information
good article
This looks very good stuff. Happy New Year and great job… have very nice day…