Apache web server is one of the most popular and widely used open-source web servers thanks to its stability and reliability. The web server commands a huge market, especially in web hosting platforms.
Be that as it may, you may get a “Forbidden – You don’t have permission to access / on this server” error on your browser after setting up your website. It’s quite a common error and a good chunk of users have experienced it while testing their site. So what is this error?
What Is the 403 Forbidden Error?
Also referred to as the 403 Forbidden error, Apache’s ‘Forbidden Error’ is an error that is displayed on a web page when you are attempting to access a website that’s restricted or forbidden.
It is a standardized HTTP status code indicating that the web server understands the request but is unable to authorize access due to permission issues.
It’s usually splashed on the browser as shown.
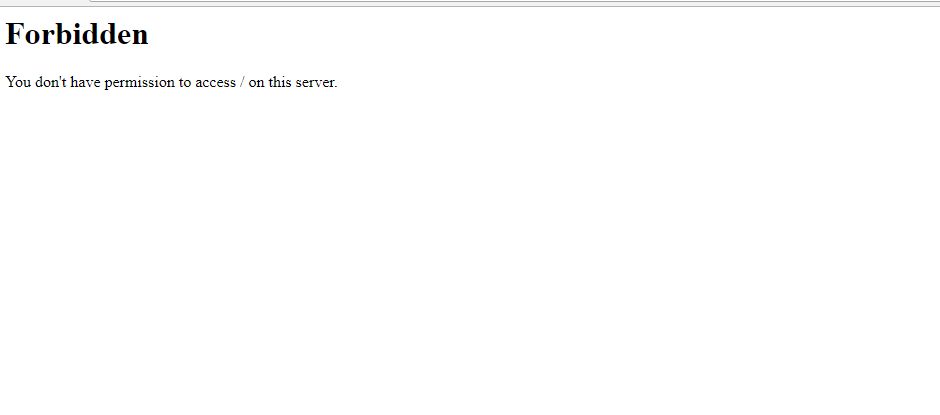
Additionally, the error can manifest in several ways on the browser as indicated below:
- HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden
- Forbidden: You don’t have permission to access [directory] on this server
- 403 Forbidden
- Access Denied You don’t have permission to access
- 403 forbidden requests forbidden by administrative rules
What Causes the 403 Forbidden Error?
The ‘403 Forbidden Error‘ occurs due to the following main reasons:
1. Incorrect File / Directory Permissions
This error can be triggered due to incorrect file/folder permissions on the webroot directory. If the default file permissions are not adjusted to grant users access to the website files, then the chances of this error popping on a web browser are high.
2. Misconfiguration of the Apache Configuration Files
This error can also be attributed to a misconfiguration of one of the Apache configuration files. It could be an incorrect parameter that has been included or missing directives in the configuration file.
3. Misconfiguration of .htaccess File
Another frequent reason for encountering this HTTP response code is a damaged or improperly configured .htaccess file. When this occurs, the 403 Forbidden error typically surfaces after modifying the .htaccess file.
Typically, users can address this by either generating a new .htaccess file or rectifying its configurations.
Fixing the Apache ‘403 Forbidden Error’
If you have encountered this error, here are a few steps that you can take to remedy this.
1. Adjust File Permissions and Ownership of the Webroot Directory
Incorrect file permissions & directory ownership are known to restrict access to website files. So, firstly, be sure to assign the file permissions recursively to the webroot directory as shown.
The webroot directory should always have EXECUTE permissions and the index.html file should have READ permissions.
$ cd /path/to/webroot/directory
$ sudo find . -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
$ sudo find . -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
The above find command is used to find all directories (folders) and files within the current directory (.) and set their permissions to 755 (directories) and 644 (files).
Additionally, adjust the ownership of files and directories to a specific user (tecmint) and group www-data or apache using the chown command as shown.
$ sudo chown -R tecmint:apache .
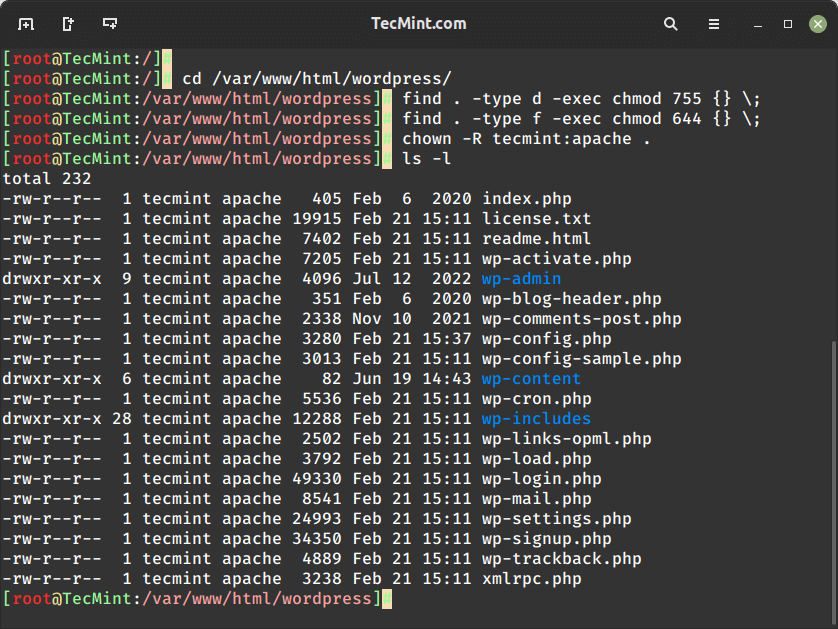
Finally, reload or restart the Apache webserver for the changes to take effect.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2 OR $ sudo systemctl restart httpd
If this does not resolve the issue, proceed to the next step:
2. Adjust Directives in Apache Main Configuration File
If you are on Debian-based Linux or RHEL-based distributions, open the main Apache configuration file, typically named httpd.conf or apache2.conf.
sudo nano /etc/httpd/httpd.conf # For Apache on CentOS/Red Hat sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf # For Apache on Debian/Ubuntu
Locate the <Directory> section that corresponds to the web document root of your website and make sure that the AllowOverride directive is set to "All". This allows .htaccess files to override configuration settings.
<Directory "/var/www/html">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
Replace the path /var/www/html to match the actual path of your website’s document root.
Save and exit and thereafter, restart the Apache.
sudo systemctl restart httpd # For Apache on CentOS/Red Hat sudo systemctl restart apache2 # For Apache on Debian/Ubuntu
. Fix .htaccess File Configuration
If you have an .htaccess file in your web directory, check its configuration. A misconfigured configuration settings or any syntax errors can prevent users from accessing specific web content.
Comment out lines or remove the file temporarily to see if it resolves the problem.
If after trying all these steps you are still getting the error, then please check the configuration of your virtual host files.
We have detailed articles on how you can configure the Apache Virtual host file on:
Resolving the “Forbidden – You don’t have permission to access / on this server” error involves checking and adjusting file permissions, ownership, and server configuration.
I hope that the steps provided have helped you clear the 403 error.





I tried a suggestion in this thread:
AllowOverride None Require all grantedbut it does not cure the exec problem.
There has never been a problem creating a file in /var/www, just running an existing one.
@Colin,
Is SELinux disabled or have the correct context settings on the /var/www directory? Please check, it seems some permission issue…
Hello Ravi,
I’m not sure what you mean by “SELinux“.
Here is an ‘ls -la‘ of /var/www:
Don’t forget the message in /var/log/apache2/error.log is:
“not found” instead of lack of permission seems like a bug, especially as php7.0 works OK.
@Colin,
You are right, it might be a problem with the single-quoted string or the variable in the PHP files…
I can’t help you out, I am not a PHP expert…
I have an allied permissions problem that Stack Exchange can’t solve. Can anyone here help?
I have a fully working raspi3b + apache2 + php5 system on a 32-bit OS.
In a php block there is a simple statement:
The executable MsgToLogger has root ownership and 4755 permissions, and the task is performed fine.
I changed to a raspi4b + apache2 + php7.4 on a 64bit OS.
I get “sh: 1: /var/www/MsgToLogger: not found” in apache/error.log
There is no problem writing a file in /var/www using
file_put_contents($msgfname,$msg);.I have tried putting MsgToLogger in three other places with no luck.
Hello,
I’m still facing the same problem…
Hello, what panel are you using? If you using Aapanel same like me, you go first on “WEBSITE” and open the “CONFIG” on the website you have inside that go to “SITE DIRECTORY” go to “RUNNING DIRECTORY” and just leave it, Blank.
I did all of the above and the error persisted so what I did was edit one of the first lines:
Solution:
You don’t have permission to access /payment/merchants/SATIM/errors_fr.html on this server.
Hi,
I was stuck on 403 forbidden errors on my website. I was searching for a possible solution and came across your article I found this one to be the best article and found the solution to my problem
definitely, a very good article to fix this error. thanks for sharing such detailed information.
keep it up
Hi,
I was stuck on 403 forbidden error at my website. I was searching for a possible solution and I came across your article. I found this one to the best article and found the solution to my problem.
Definitely, a very good article to fix this error. Thanks for sharing such detailed information.
Keep it up.
use this command.
Should this work if one of my sites works and the other give this error?
# 2. Adjust directives in Apache main configuration file solved my problem
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride None Require all grantedThank you, sir.