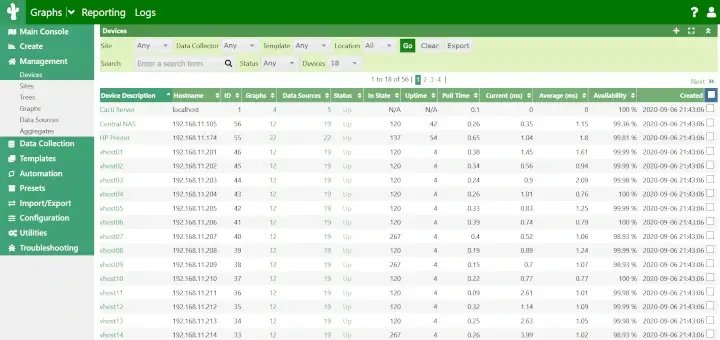
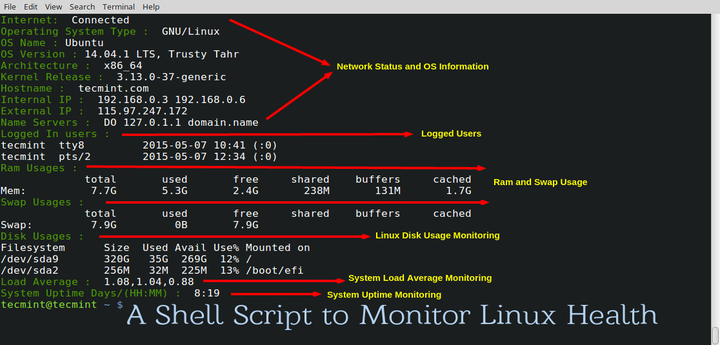
Collectd-web is a web front-end monitoring tool based on RRDtool (Round-Robin Database Tool), which interprets and graphical outputs the data collected by the Collectd service on Linux systems.
Collectd service comes by default with a huge collection of available plug-ins into its default configuration file, some of them being, by default, already activated once you have installed the software package.
Collectd-web CGI scripts which interprets and generates the graphical html page statistics can be simply executed by the Apache CGI gateway with minimal of configurations required on Apache web server side.
However, the graphical web interface with the generated statistics can, also, be executed by the standalone web server offered by Python CGIHTTPServer script that comes pre-installed with the main Git repository.
This tutorial will cover the installation process of Collectd service and Collectd-web interface on RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Ubuntu/Debian based systems with the minimal configurations needed to be done in order to run the services and to enable a Collectd service plug-in.
Please go through the following articles of collectd series.
Step 1: – Install Collectd Service
1. Basically, the Collectd daemon task is to gather and store data statistics on the system that it runs on. The Collectd package can be downloaded and installed from the default Debian based distribution repositories by issuing the following command:
On Ubuntu/Debian
# apt-get install collectd [On Debian based Systems]
On RHEL/CentOS 6.x/5.x
On older RedHat based systems like CentOS/Fedora, you first need to enable epel repository under your system, then you can able to install collectd package from the epel repository.
# yum install collectd
On RHEL/CentOS 7.x
On latest version of RHEL/CentOS 7.x, you can install and enable epel repository from default yum repos as shown below.
# yum install epel-release # yum install collectd
Note: For Fedora users, no need to enable any third party repositories, simple yum to get the collectd package from default yum repositories.
2. Once the package is installed on your system, run the below command in order to start the service.
# service collectd start [On Debian based Systems] # service collectd start [On RHEL/CentOS 6.x/5.x Systems] # systemctl start collectd.service [On RHEL/CentOS 7.x Systems]
Step 2: Install Collectd-Web and Dependencies
3. Before starting to import the Collectd-web Git repository, first you need to assure that Git software package and the following required dependencies are installed on your machine:
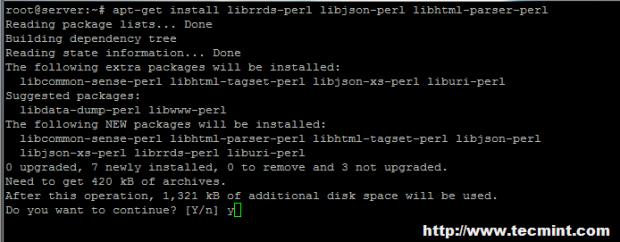
----------------- On Debian / Ubuntu systems ----------------- # apt-get install git # apt-get install librrds-perl libjson-perl libhtml-parser-perl
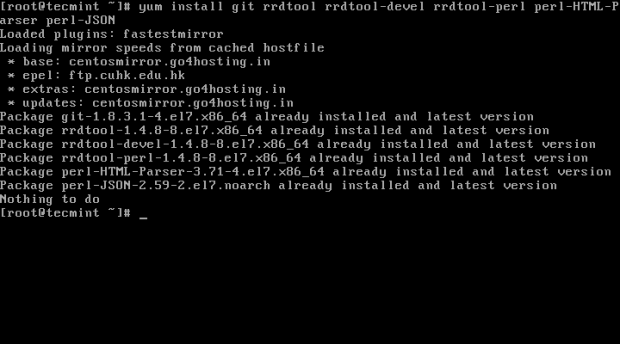
----------------- On RedHat/CentOS/Fedora based systems ----------------- # yum install git # yum install rrdtool rrdtool-devel rrdtool-perl perl-HTML-Parser perl-JSON
Step 3: Import Collectd-Web Git Repository and Modify Standalone Python Server
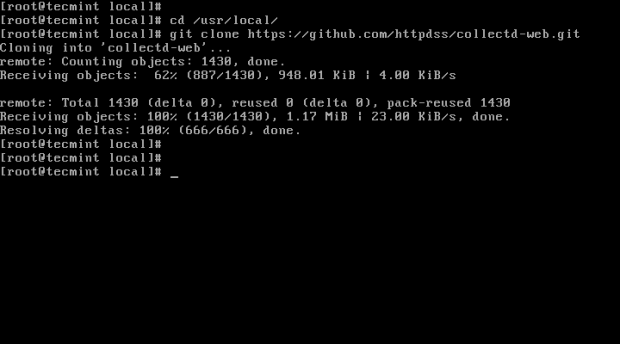
4. On the next step choose and change the directory to a system path from the Linux tree hierarchy where you want to import the Git project (you can use /usr/local/ path), then run the following command to clone Collectd-web git repository:
# cd /usr/local/ # git clone https://github.com/httpdss/collectd-web.git
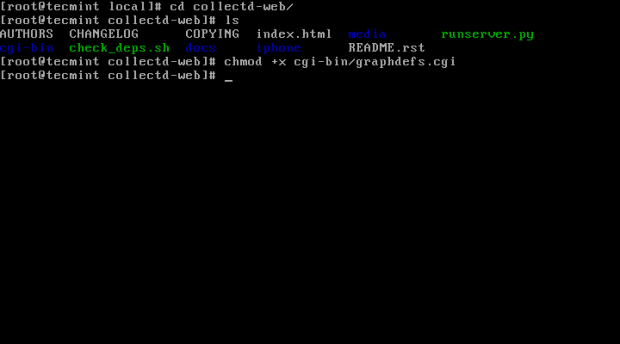
5. Once the Git repository is imported into your system, go ahead and enter the collectd-web directory and list its contents in order to identify the Python server script (runserver.py), which will be modified on the next step. Also, add execution permissions to the following CGI script: graphdefs.cgi.
# cd collectd-web/ # ls # chmod +x cgi-bin/graphdefs.cgi
6. Collectd-web standalone Python server script is configured by default to run and bind only on loopback address (127.0.0.1).
In order to access Collectd-web interface from a remote browser, you need to edit the runserver.py script and change the 127.0.1.1 IP Address to 0.0.0.0, in order to bind on all network interfaces IP Addresses.
If you want to bind only on a specific interface, then use that interface IP Address (not advised to use this option in case your network interface Address is dynamically allocated by a DHCP server). Use the below screenshot as an excerpt on how the final runserver.py script should look like:
# nano runserver.py
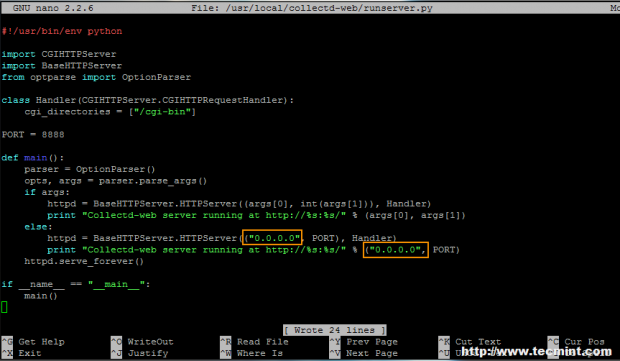
If you want to use another network port than 8888, modify the PORT variable value.
Step 4: Run Python CGI Standalone Server and Browse Collectd-web Interface
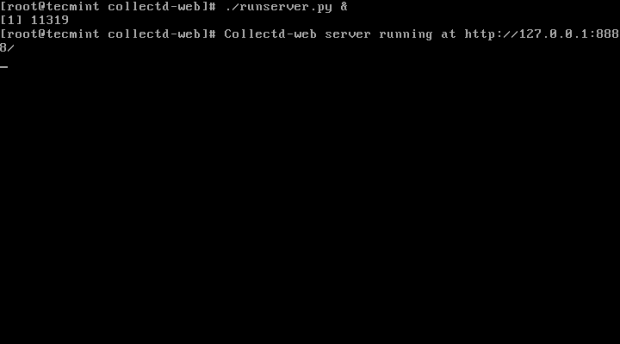
7. After you have modified the standalone Python server script IP Address binding, go ahead and start the server in background by issuing the following command:
# ./runserver.py &
Optional, as an alternate method you can call the Python interpreter to start the server:
# python runserver.py &