MariaDB is an open-source, community-developed relational database management system. It is forked from MySQL and created and maintained by the developers who created MySQL. MariaDB is intended to be highly compatible with MySQL but new features have been added to MariaDB like new storage engines (Aria, ColumnStore, MyRocks).
In this article, we will take a look at the installation and configuration of MariaDB on CentOS 8 Linux.
Step 1: Enable the MariaDB Repository on CentOS 8
Go to the official MariaDB downloads page and select CentOS as the distribution and CentOS 8 as the version and MariaDB 10.5 (stable version) to get the repository.
Once you select the details, you will get MariaDB YUM repository entires. Copy and paste these entries into a file called /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo.
$ sudo vim /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo
# MariaDB 10.5 CentOS repository list - created 2020-12-15 07:13 UTC # http://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/ [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.5/centos8-amd64 module_hotfixes=1 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
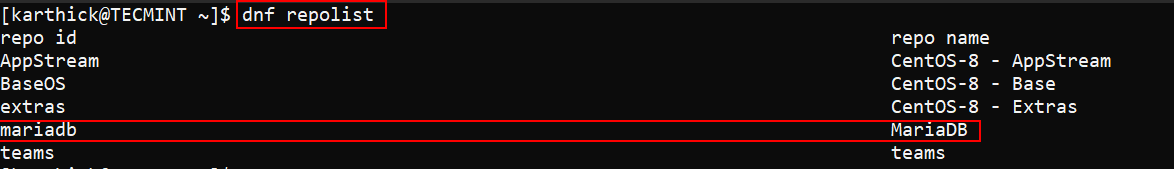
Once the repository file in place, you can verify the repository by running the following command.
$ dnf repolist
Step 2: Installing MariaDB on CentOS 8
Now use the dnf command to install the MariaDB package.
$ sudo dnf install MariaDB-server -y
Next, start the MariaDB service and enable it to autostart during system startup.
$ systemctl start mariadb $ systemctl enable mariadb
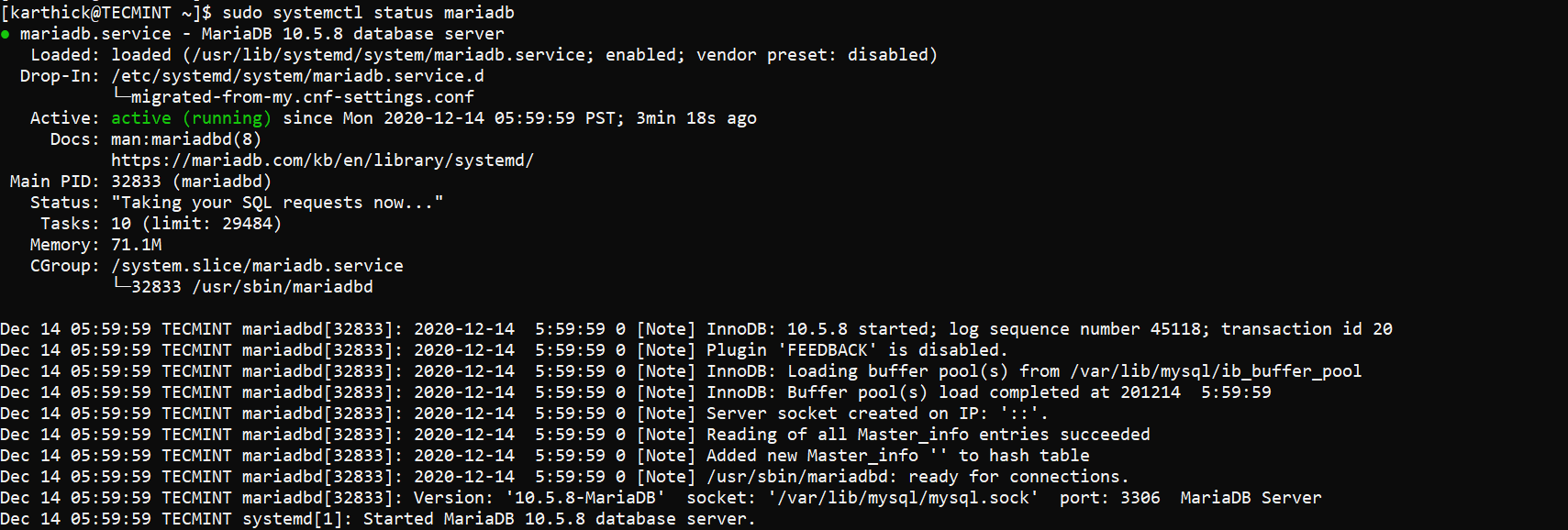
Check the status of the MariaDB service by running the following command.
$ systemctl status mariadb
If you have a firewall enabled, you need to add MariaDB to the firewall rule by running the below command. Once the rule is added, the firewall needs to be reloaded.
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=mysql $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 3: Securing the MariaDB Server on CentOS 8
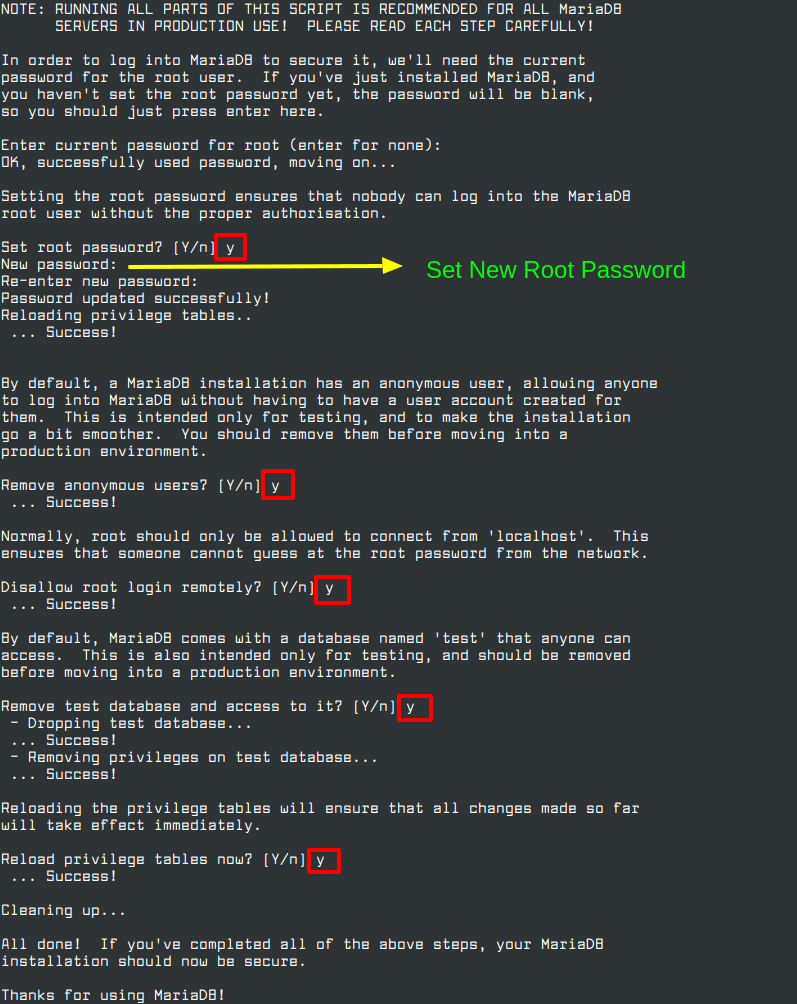
As the last step, we need to run a secure MariaDB installation script. This script takes care of setting up the root password, reloading privileges, removing test databases, disallowing root login.
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
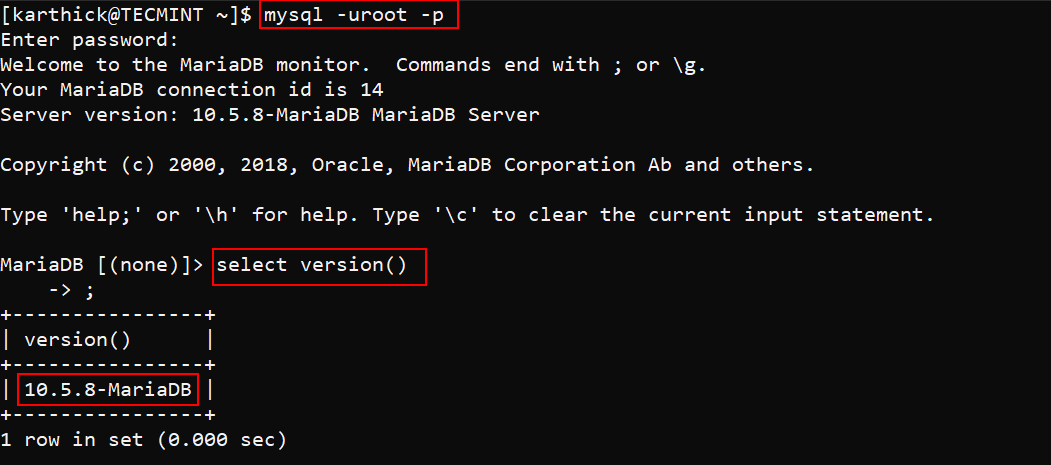
Now connect to MariaDB as the root user and check the version by running the following commands.
$ mysql -uroot -p
That’s it for this article. We have seen how to install and configure MariaDB on CentOS 8 Linux.






Why bother installing MariaDB? CentOS is going away.
@dragonmounth – Yes you are right, still we can use this procedure for RHEL and fedora system.