PgAdmin4 is a easy to use web interface for managing PostgreSQL databases. It can be used on multiple platforms such as Linux, Windows and Mac OS X. In pgAdmin 4 there is migration from bootstrap 3 to bootstrap 4.
In this tutorial we are going to install pgAdmin 4 on a CentOS 7 system.
Note: This tutorial assumes that you already have PostgreSQL 9.2 or above installed on your CentOS 7. For instructions how to install it, you can follow our guide: How to install PostgreSQL 10 on CentOS and Fedora.
How to Install pgAdmin 4 in CentOS 7
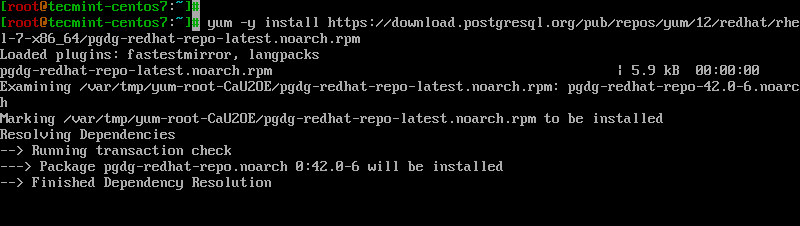
This step should have been completed upon the installation of PostgreSQL, but if you haven’t, you can complete it with:
# yum -y install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/12/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm
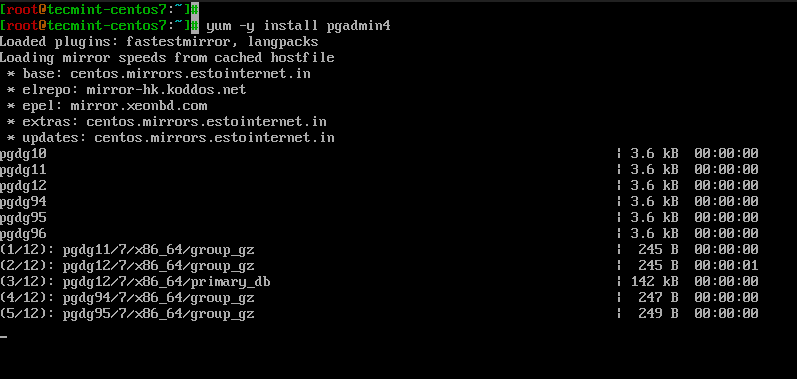
Now you are ready to install pgAdmin with:
# yum -y install pgadmin4
During the installation, due to dependencies, the following two will be installed as well – pgadmin4-web and httpd web server.
How to Configure pgAdmin 4 in CentOS 7
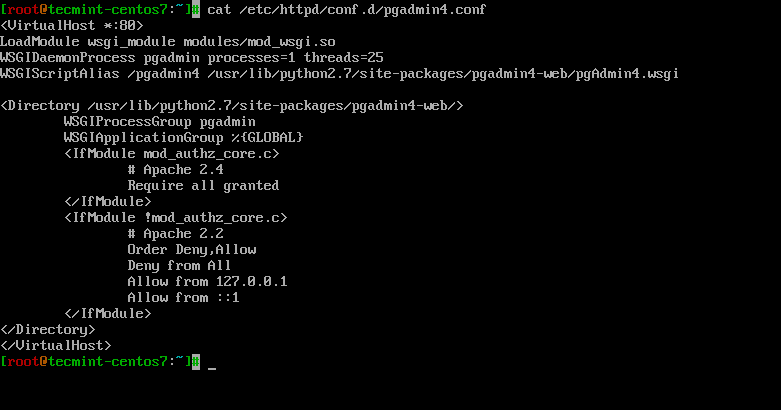
There are few minor configuration changes that need to be done to have pgAdmin4 running. First we will rename the sample conf file from pgadmin4.conf.sample to pgadmin4.conf:
# mv /etc/httpd/conf.d/pgadmin4.conf.sample /etc/httpd/conf.d/pgadmin4.conf # vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/pgadmin4.conf
Adjust the file so it looks like this:
<VirtualHost *:80>
LoadModule wsgi_module modules/mod_wsgi.so
WSGIDaemonProcess pgadmin processes=1 threads=25
WSGIScriptAlias /pgadmin4 /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pgadmin4-web/pgAdmin4.wsgi
<Directory /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pgadmin4-web/>
WSGIProcessGroup pgadmin
WSGIApplicationGroup %{GLOBAL}
<IfModule mod_authz_core.c>
# Apache 2.4
Require all granted
</IfModule>
<IfModule !mod_authz_core.c>
# Apache 2.2
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from 127.0.0.1
Allow from ::1
</IfModule>
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
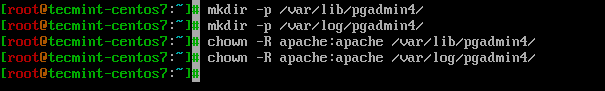
Next we will create logs and lib directories for pgAdmin4 and set their ownership:
# mkdir -p /var/lib/pgadmin4/ # mkdir -p /var/log/pgadmin4/ # chown -R apache:apache /var/lib/pgadmin4 # chown -R apache:apache /var/log/pgadmin4
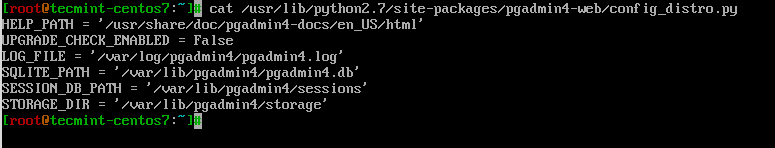
And then we can extend the contents of our config_distro.py.
# vi /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pgadmin4-web/config_distro.py
And add the following lines:
LOG_FILE = '/var/log/pgadmin4/pgadmin4.log' SQLITE_PATH = '/var/lib/pgadmin4/pgadmin4.db' SESSION_DB_PATH = '/var/lib/pgadmin4/sessions' STORAGE_DIR = '/var/lib/pgadmin4/storage'
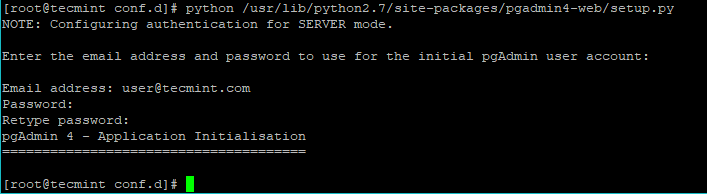
Finally we will create our user account, with which we will authenticate in the web interface. To do this, run:
# python /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pgadmin4-web/setup.py
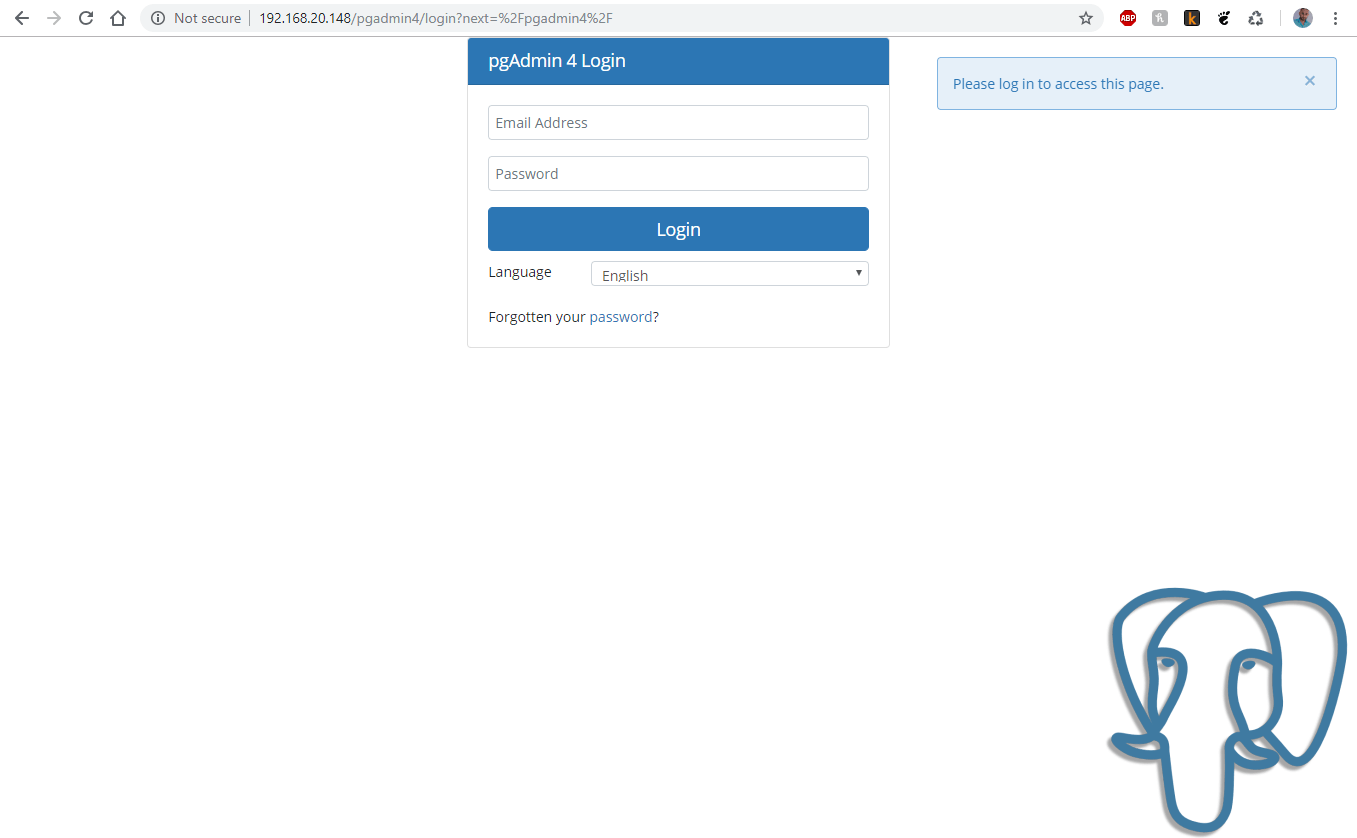
Now you can access your server’s http://ip-address/pgadmin4 or http://localhost/pgadmin4 to reach the pgAdmin4 interface:
If you receive 403 error while accessing PgAdmin4 interface, you need to set the correct SELinux context on the following files.
# chcon -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t /var/log/pgadmin4 -R # chcon -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t /var/lib/pgadmin4 -R
To authenticate, use the email address and password that you have used earlier. Once authenticate, you should see the pgAdmin4 interface:
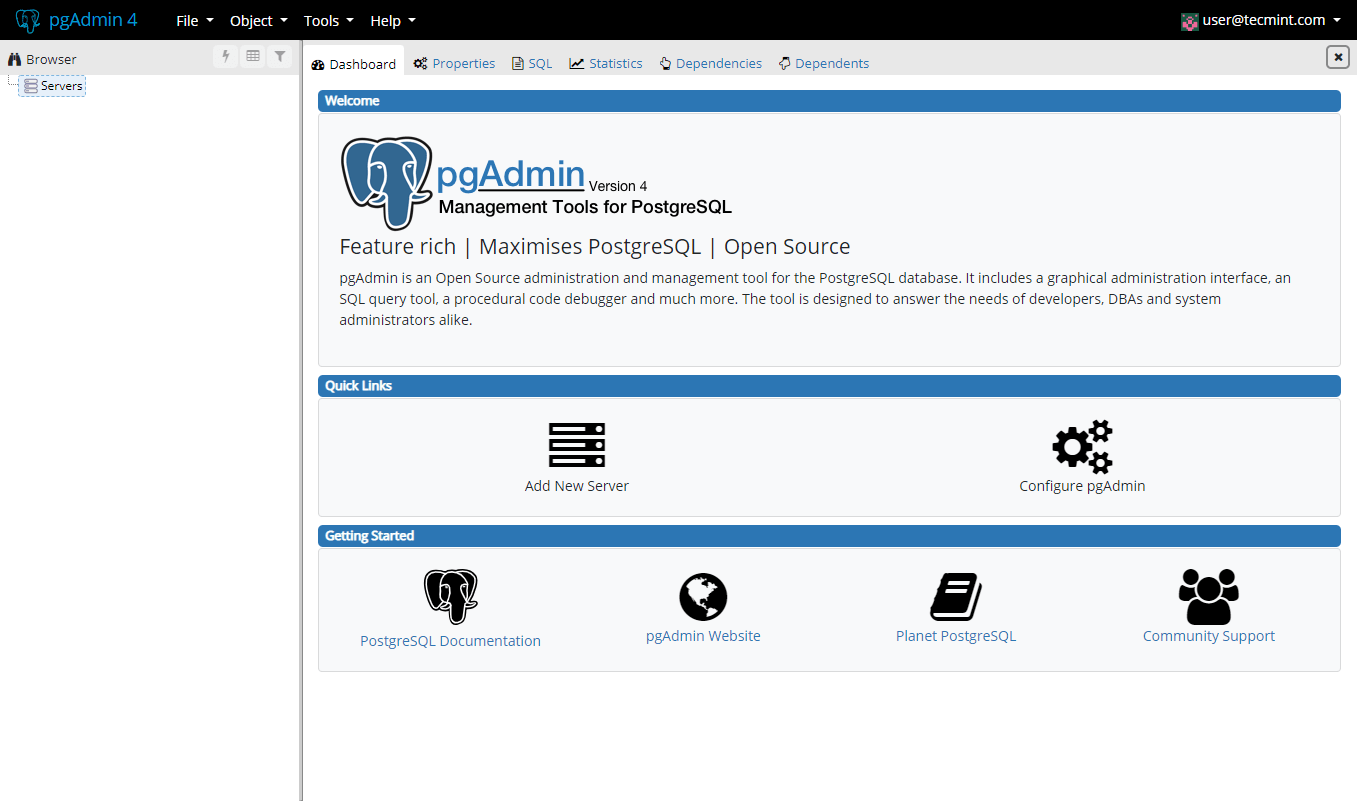
At your first login, you will need to add a new server to manage. Click on “Add New Server”. You will need to configure the PostgresQL connection. In the first tab “General”, enter the following settings:
- Name – give name of the server you are configuring.
- Comment – leave a comment to give description of the instance.
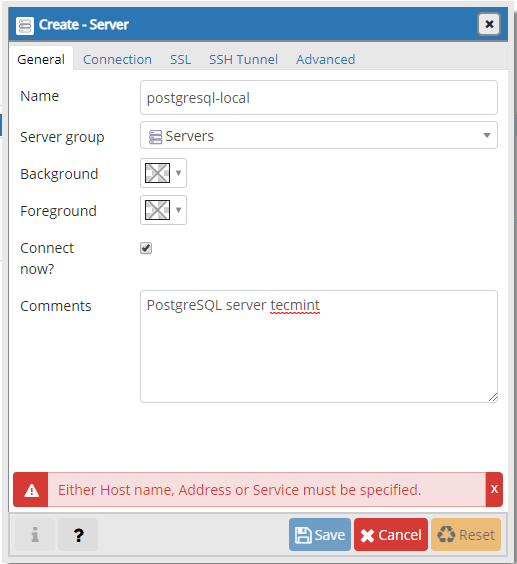
The second tab “Connection” is more important one, as you will have to enter:
- Host – host/IP address of the PostgreSQL instance.
- Port – default port is 5432.
- Maintenance database – this should be postgres.
- Username – the username which will be connecting. You can use postgres user.
- Password – password for the above user.
When you have filled everything, Save the changes. If the connection was successful, you should see the following page:
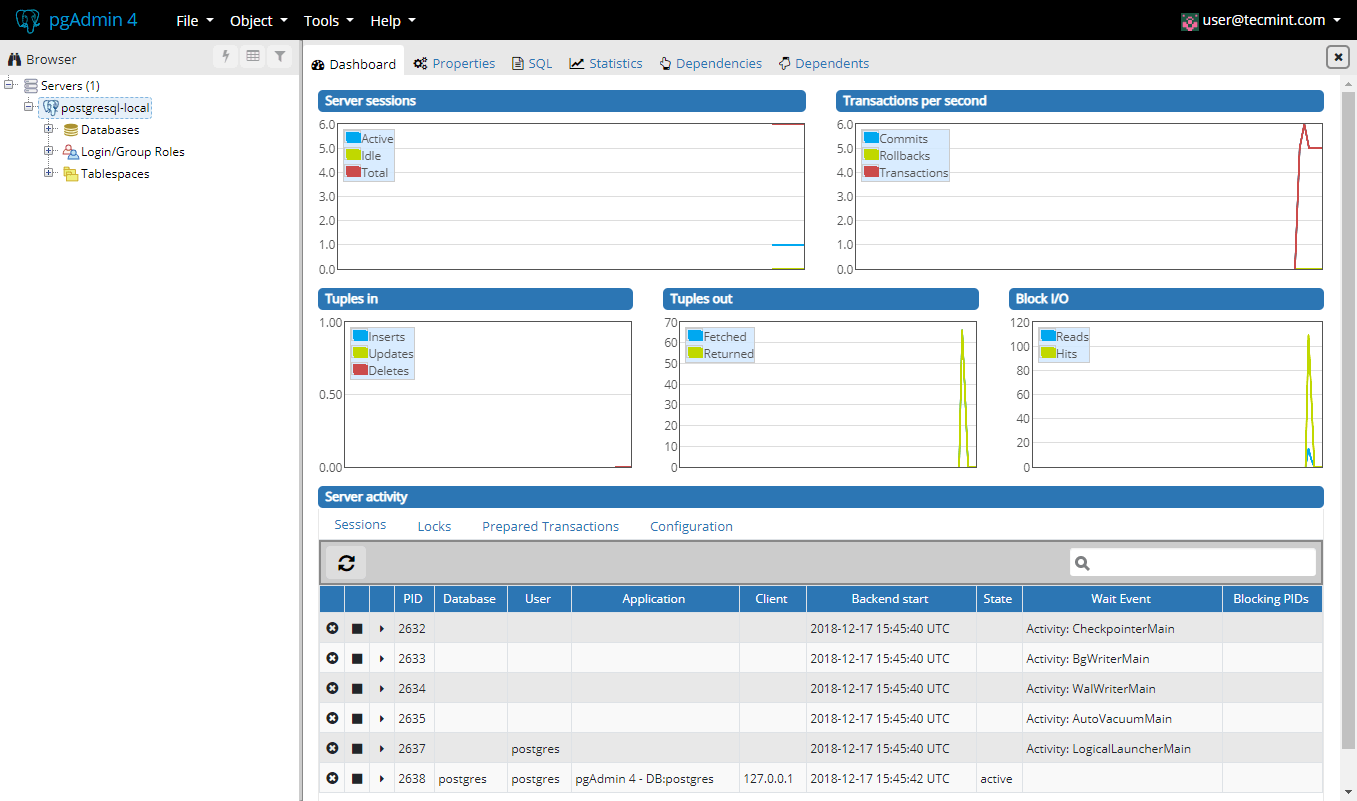
This was it. Your pgAdmin4 installation is complete and you can start managing your PostgreSQL database.