Brief: In this article, you will learn how to install the PostgreSQL 15 database server and pgAdmin 4 in RHEL 9 Linux distribution.
PostgreSQL is a powerful, widely-used, open-source, multi-platform, and advanced object-relational database system known for its proven architecture, reliability, data integrity, robust feature set, and extensibility.
pgAdmin is an advanced, open-source, full-featured, and web-based administration and management tool for the PostgreSQL database server.
Let’s get started…
Step 1: Installing PostgreSQL on RHEL 9
1. First, disable the built-in PostgreSQL module by running the following dnf command.
# dnf -qy module disable postgresql
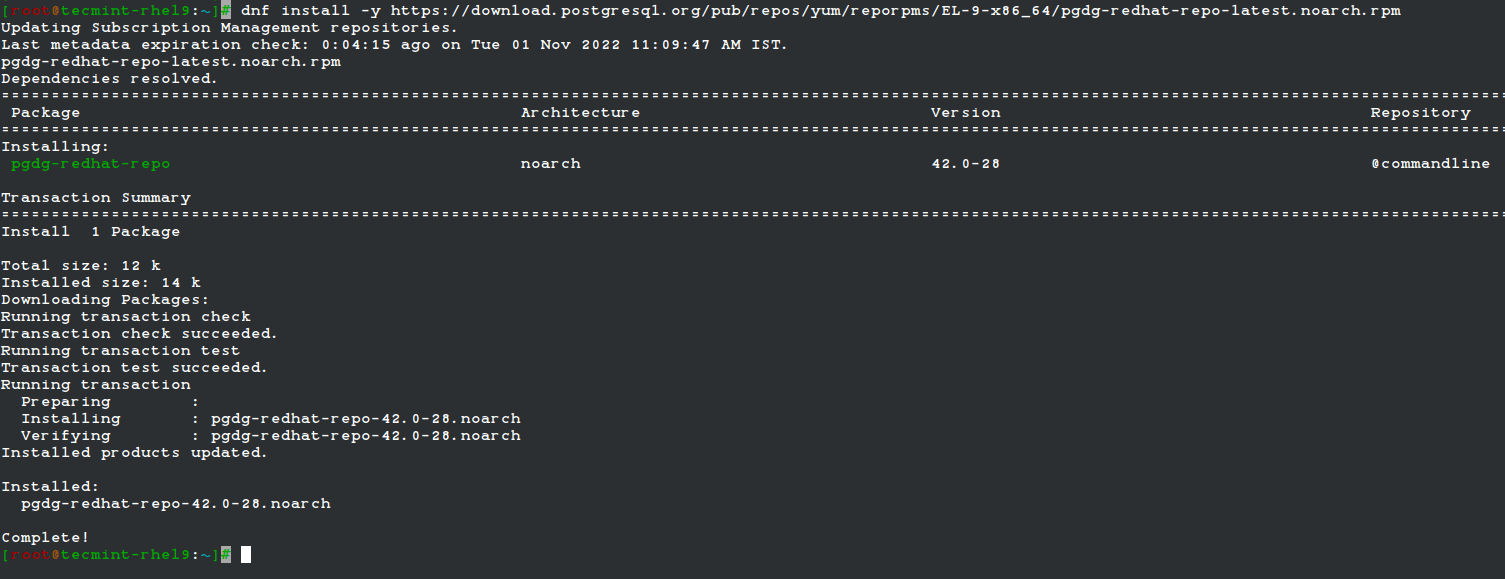
2. Next, enable the official PostgreSQL Yum Repository as shown.
# dnf install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-9-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm
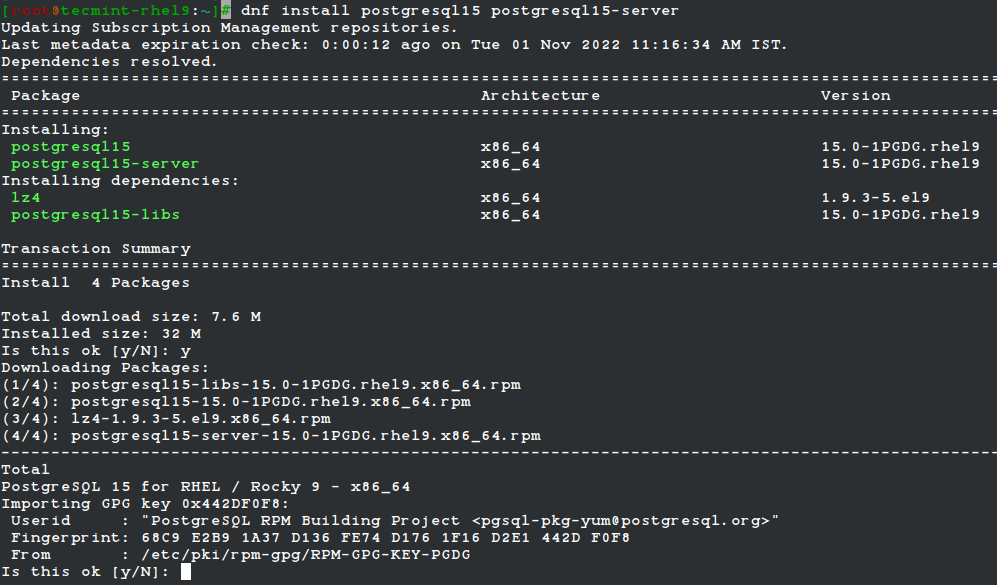
3. Next, install the PostgreSQL 15 server and client packages.
# dnf install -y postgresql15-server
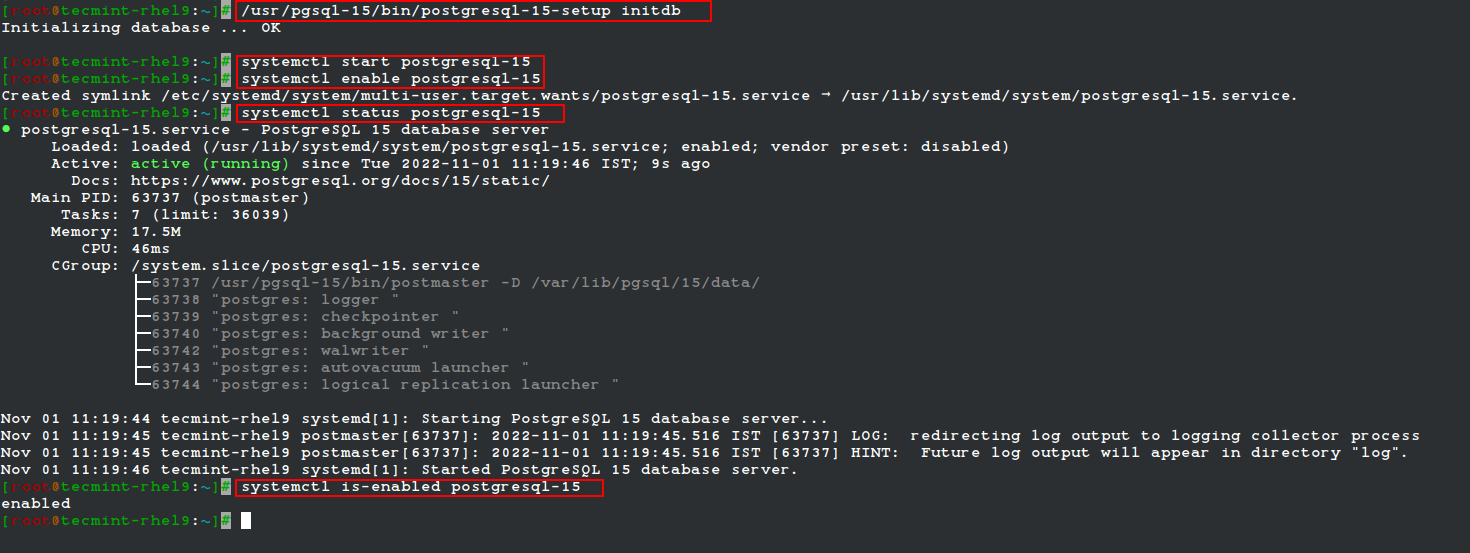
4. Once the installation is complete, initialize the PostgreSQL database, then start the PostgreSQL-15 service and enable it to automatically start at system boot. Then check if the service is up and running, and is enabled as shown.
# /usr/pgsql-15/bin/postgresql-15-setup initdb # systemctl start postgresql-15 # systemctl enable postgresql-15 # systemctl status postgresql-15 # systemctl is-enabled postgresql-15
Step 2: Secure and Configure PostgreSQL Database
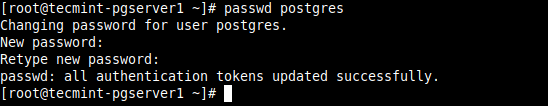
5. Next, secure the Postgres user account and the database administrative user account. Start by creating a password for a Postgres system user account using the passwd utility as shown.
# passwd postgres
6. Then switch to the Postgres system account and create a secure and strong password for PostgreSQL administrative database user/role as follows.
# su - postgres $ psql -c "ALTER USER postgres WITH PASSWORD 'securep@sshere';" $ exit

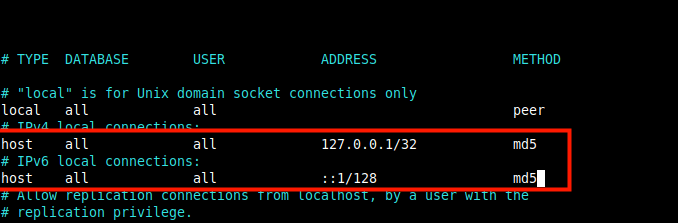
7. Now configure how the Postgres server will authenticate clients such as pgAdmin. The supported authentication methods include password-based authentication which uses one of these methods: md5, crypt, or password.
For this guide, we will configure the md5 authentication method in the file /var/lib/pgsql/15/data/pg_hba.conf.
# vi /var/lib/pgsql/15/data/pg_hba.conf
Find the following lines and change the authentication method to md5 as highlighted in the screenshot.
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5 host all all ::1/128 md5
8. After saving the file, to apply the recent changes in the Postgres configuration, restart the Postgres service.
# systemctl restart postgresql-15
Step 3: Installing pgAdmin4 in RHEL 9
9. Now we will install pgAdmin 4 to manage the PostgreSQL database from the web. First, you need to enable the EPEL and pgAdmin yum repositories which contain some of the dependencies.
# subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-9-$(arch)-rpms # dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm # dnf install -y https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/yum/pgadmin4-redhat-repo-2-1.noarch.rpm
10. Now build a cache for newly installed pgAdmin and EPEL repositories and install pgAdmin using the following commands.
# dnf makecache # yum install pgadmin4
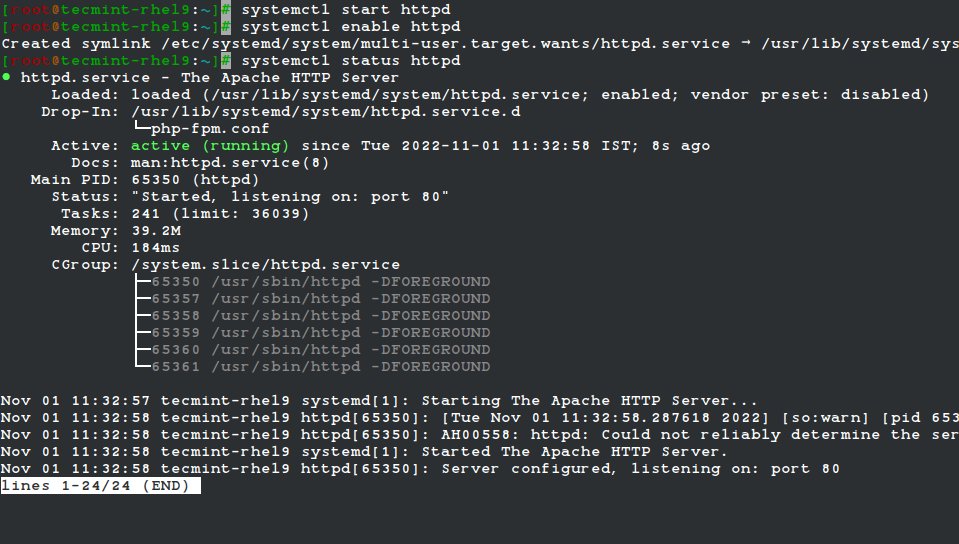
11. Next, start the httpd service and enable it to auto-start at system boot, then check if it is up and running as shown.
# systemctl start httpd # systemctl enable httpd # systemctl status httpd
Step 4: Configuring pgAdmin 4 in RHEL 9
12. The pgadmin4 package comes with a configurable script to configure the pgAdmin web service, which will create a user account used to authenticate in the web interface, configure SELinux policies and Apache webserver to deploy pgAdmin web service.
# /usr/pgadmin4/bin/setup-web.sh
Sample Output
Setting up pgAdmin 4 in web mode on a Redhat-based platform... Creating configuration database... NOTE: Configuring authentication for SERVER mode. Enter the email address and password to use for the initial pgAdmin user account: Email address: [email protected] Password: Retype password: pgAdmin 4 - Application Initialisation ====================================== Creating storage and log directories... Configuring SELinux... The Apache web server is running and must be restarted for the pgAdmin 4 installation to complete. Continue (y/n)? y Apache successfully restarted. You can now start using pgAdmin 4 in web mode at http://127.0.0.1/pgadmin4
13. If you have the firewalld service enabled and running, open ports 80 and 443 in the firewall to allow traffic to the HTTPD web server as shown.
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone public --add-port 80/tcp # firewall-cmd --permanent --zone public --add-port 443/tcp # firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5: Accessing pgAdmin Web Interface
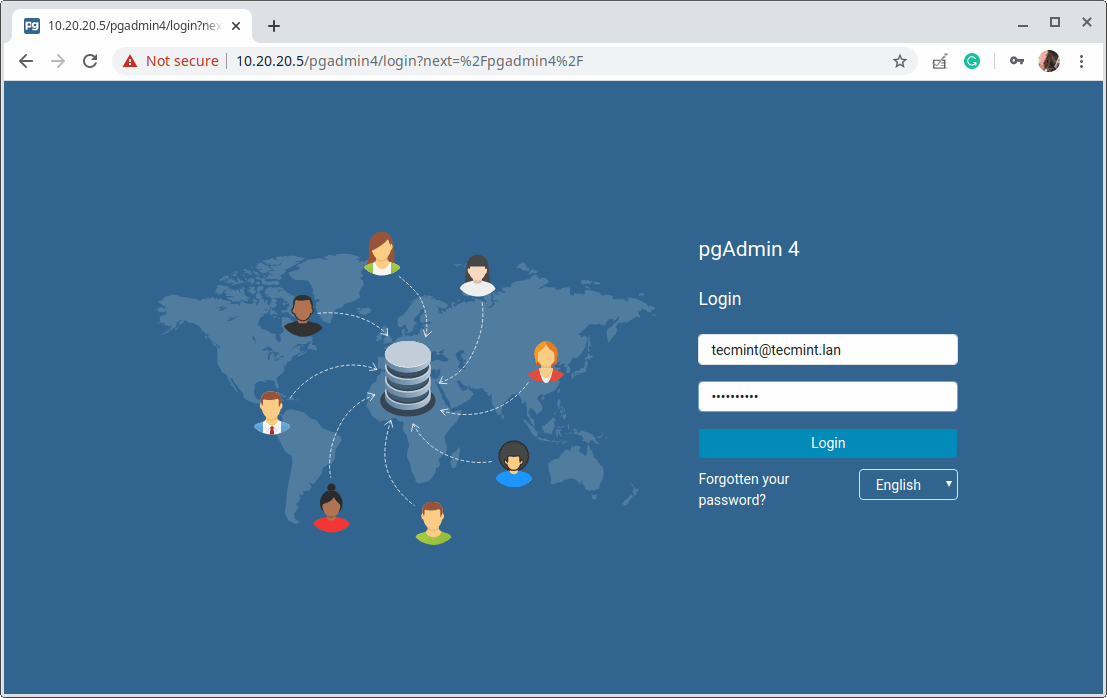
14. To access the pgAdmin web interface, open a browser and navigate using the following URL.
http://SERVER_IP/pgadmin4 OR http://localhost/pgadmin4
Once the login interface loads, use the email address and password you created in step 12 above to log in.
15. Next, add a new server connection by clicking on “Add New Server”.
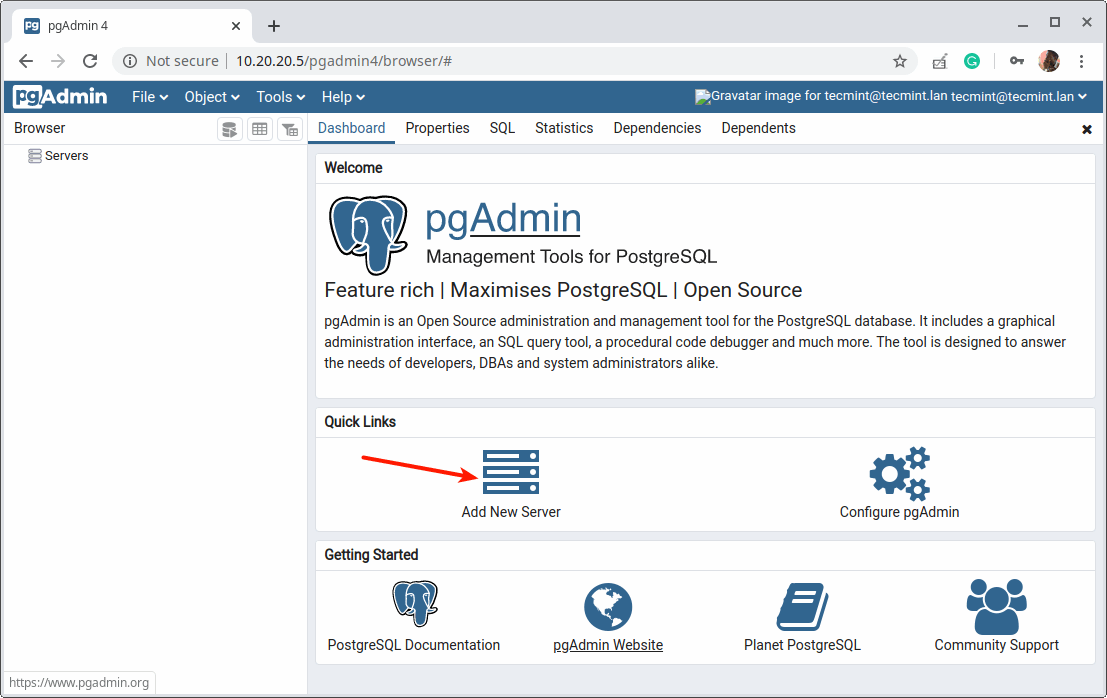
16. Then under the “General” tab, enter the following settings server Name and optionally leave a comment to describe the connection.
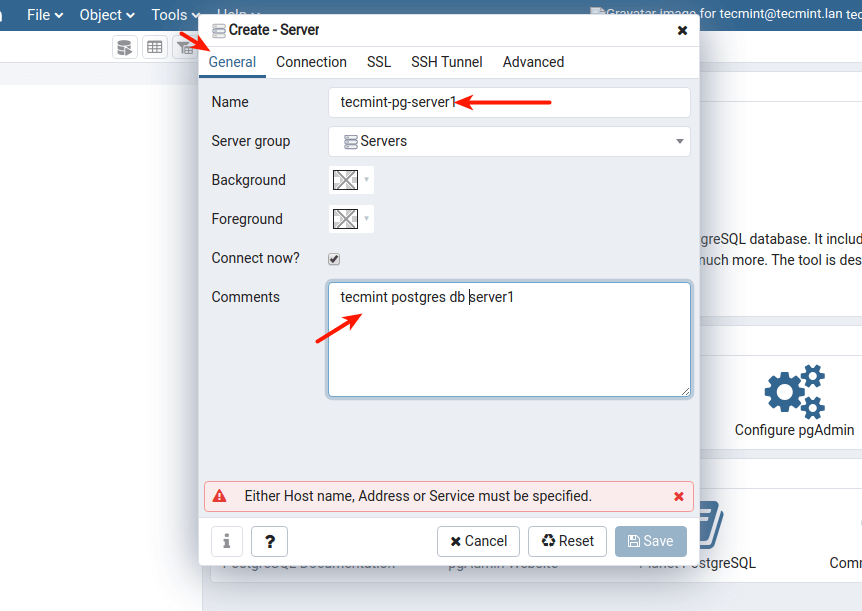
17. Then define the connection profile by filling in the following:
- Host – host/IP address of the PostgreSQL server.
- Port – defaults to 5432.
- Maintenance Database – defaults should be Postgres.
- Username – the database username. You can use Postgres.
- Password – password for the above user.
Then click Save.
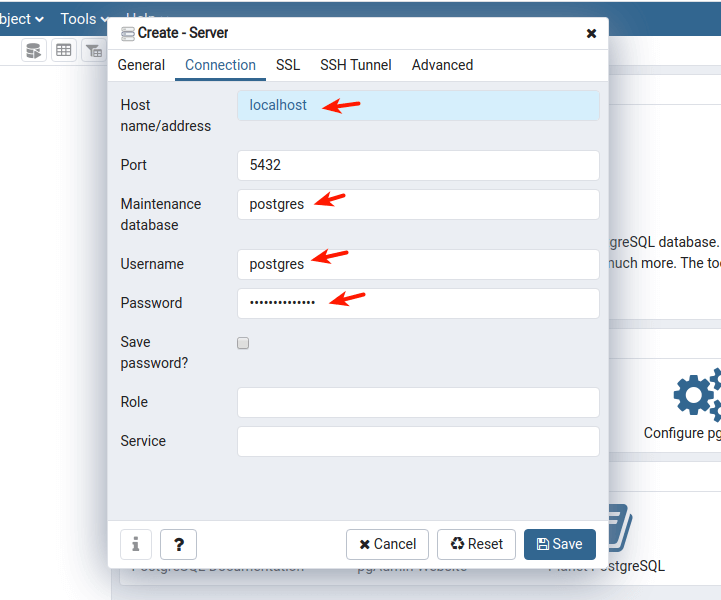
18. The new server should now appear under the list of servers as highlighted in the following screenshot.
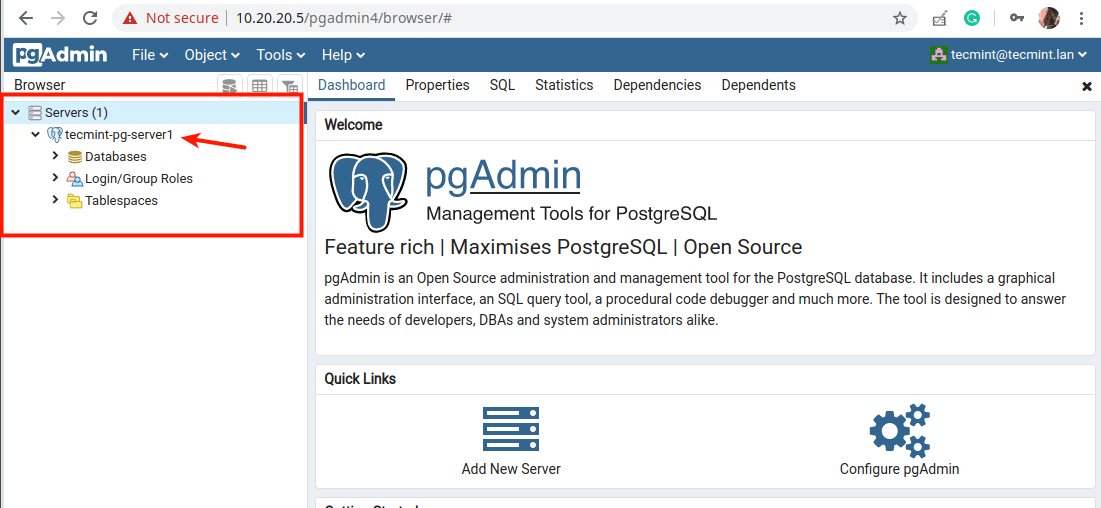
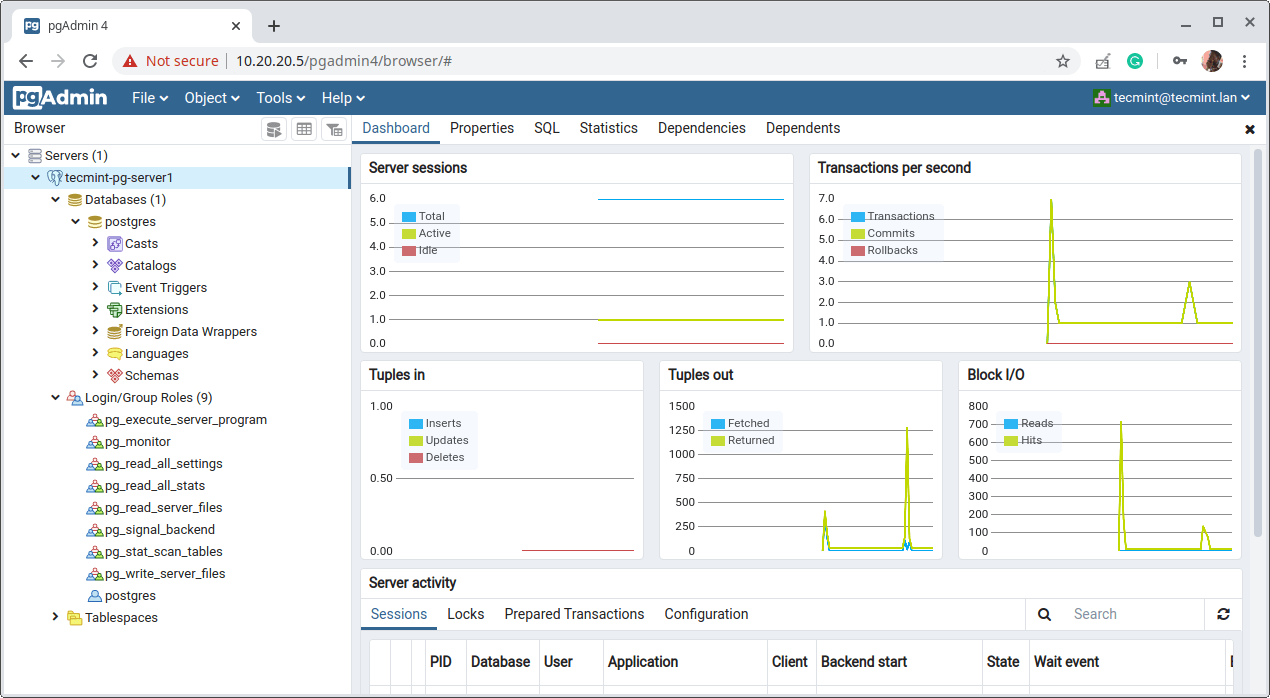
19. When you click on the server name, its attributes should load under the Dashboard as shown in the following screenshot.
There you have it! You have successfully installed Postgresql 15 and pgAdmin 4 in RHEL 9. Reach us via the feedback form below for any thoughts and questions.
You can find more information in the Postgresql 15 documentation and pgAdmin documentation.






This article saved my day. Thanks for the clear instructions.
Aaron,
I forget to click the “notify me” box before hitting send. Adding that now. Thanks in advance for any assistance. I am determined to get this all working. With your help, I am convinced it will be!
Thanks,
T. Miller
Hello Aaron,
As many others have stated, thanks for a great tutorial. I was happily following until Step 3 #9, the second command. Firstly PowerTools created an error. Googled to discover the name changed in 8.3 to “powertools”. Made the change and … magic! But then the “No match for argument: pgadmin 4” error appeared. Googled that and tried many of the things I found that made sense in my environment. NO LUCK. Can’t get past that issue. Any ideas? Happy Easter …
Here is a screen dump:
[root@localhost millert]# dnf –enablerepo=PowerTools install pgadmin4
Error: Unknown repo: ‘PowerTools’
[root@localhost millert]# dnf –enablerepo=powertools install pgadmin4
CentOS Linux 8 – PowerTools 1.1 MB/s | 2.0 MB 00:01
Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux Modular 8 – 613 kB/s | 557 kB 00:00
Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 8 – x86_64 1.3 MB/s | 9.1 MB 00:07
No match for argument: pgadmin4
Error: Unable to find a match: pgadmin4
[root@localhost millert]# dnf install pgadmin4
Last metadata expiration check: 0:03:38 ago on Fri 02 Apr 2021 03:56:39 PM EDT.
No match for argument: pgadmin4
Error: Unable to find a match: pgadmin4
[root@localhost millert]# yum install pgadmin4
Last metadata expiration check: 0:06:25 ago on Fri 02 Apr 2021 03:56:39 PM EDT.
No match for argument: pgadmin4
Error: Unable to find a match: pgadmin4
[root@localhost millert]# sudo yum install pgadmin4
Last metadata expiration check: 0:06:52 ago on Fri 02 Apr 2021 03:56:39 PM EDT.
No match for argument: pgadmin4
Error: Unable to find a match: pgadmin4
[root@localhost millert]#
Thanks, it works for me great. Lets the fun begin.
@Karol
Enjoy! Many thanks for the useful feedback.
Hey Aaron,
Very helpful tutorial, however, I am running to the following error when I try and create the server connection at step #22 – “Unable to connect to server: FATAL: password authentication failed for user ‘Postgres'”
Thanks in advance.
Matt
@Matt
Ensure that you have configured client authentication properly as described in step 2 and entered the correct password for the user postgres.
Thanks, Aaron,
Yes you’re right I went back and fixed the password issue using these commands: https://stackoverflow.com/a/11545725
Great tutorial! I am pretty new to Postgre and your tutorial helped me to install everything without fail!
@WebCochin
We gald to know this. Thanks for the useful feedback.
Hi Aron, thanks for this tutorial was very helpful, sometimes I got an error and I can’t use PgAdmin4 anymore, don’t sure what can be the cause (maybe the reboot) but now when I try to run:
I receive an error:
Internal Server Error
The server encountered an internal error or misconfiguration and was unable to complete your request.
Please contact the server administrator at root@localhost to inform them of the time this error occurred, and the actions you performed just before this error.
More information about this error may be available in the server error log.
I found only two way to solve it but I’m not sure that are the bests:
python3 /usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pgadmin4-web/setup.py” and the other points after that.http://127.0.0.1:5050(keeping the py running).How can I restore the original “process” and use PgAdmin4 by navigating to h
ttp://localhost/pgadmin4?Thank you in advance
Hello Aron, I’ve not yet received any reply from you, please can you give me help? Thank you
@Matt
Did you run this comand:
Ensure that you have, because it creates the pgAdmin4 configuration for HTTPD to enable you access the PgAdmin4 by navigating to
http://localhost/pgadmin4.Alternatively, there was an update for setting up pgadmin4 to run in web mode. After installing gadmin4 or pgadmin4-web, run the web setup script to configure the system to run in web mode:
Hello Aaron, Thanks very much for this tutorial. I am very much new to Linux and Postgres. I have followed your instructions on installing Postgres and pgadmin; I am getting the following error messages below.
I would really appreciate it if you could take a look at it and tell me how to correct it.
[david@centos-nyc ~]$ sudo systemctl start httpd
[sudo] password for david:
Job for httpd.service failed because the control process exited with error code.
See "systemctl status httpd.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.
[david@centos-nyc ~]$ sudo systemctl status httpd.service
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Mon 2020-04-20 09:11:36 EDT; 1min 22s ago
Docs: man:httpd.service(8)
Process: 14737 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/httpd $OPTIONS -DFOREGROUND (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Main PID: 14737 (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Status: "Reading configuration..."
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc httpd[14737]: [Mon Apr 20 09:11:36.045465 2020] [so:warn] [pid 14737:tid 139823543744768] A>
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc httpd[14737]: AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified dom>
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc httpd[14737]: (98)Address already in use: AH00072: make_sock: could not bind to address [::>
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc httpd[14737]: (98)Address already in use: AH00072: make_sock: could not bind to address 0.0>
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc httpd[14737]: no listening sockets available, shutting down
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc httpd[14737]: AH00015: Unable to open logs
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc systemd[1]: httpd.service: Main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc systemd[1]: httpd.service: Failed with result 'exit-code'.
Apr 20 09:11:36 centos-nyc systemd[1]: Failed to start The Apache HTTP Server.
Thanks very much,
Davoo
@David
Is there another web server or service running on port 80 on your serve? According to the status error, HTTPD can’t start because port 80 seems to be in use already.
Run this command to check:
Share the output of the above command. Thanks.
Hello Aaron, Thanks very much for responding. Appears two are running/listening on port 80 and send-Q 128.
I would appreciate your suggestions on how to move forward.
[david@centos-nyc ~]$ ss -tpln
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 5 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:5355 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 32 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 5 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 5 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 5 [::1]:4330 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:5355 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:80 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 5 [::1]:631 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:5432 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6010 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 5 [::1]:44321 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:9090 *:*
Thanks, David
Hello again Aaron, I figured it out! I had nginx active/running, so I had to stop and start it to get working…
Thanks again,
David
Hello Aaron, Do you know of a tutorial site, for beginner, to pick up from you left off for centos 8?
Thanks,
David
@David
Once again, you will get all you need to know about CentOS 8 on this site. Simply use the search feature to look for what you want to read about. If you do not understand anything in any guide, drop us a comment.
@David
Ok, you can’t run two services on the same port. If you want to run NGINX as the primary web server, you need to configure HTTPD to run on a different port e.g port 8080. So when you accessing pgadmin, you add that port in the URL. Thanks.
Thanks. I was trying to install PostgreSQL and pgadmin4 on my CI-Server. I also visited a lot of videos and other how-tos, but nothing worked as well as your how-to does.
It’s really perfect and when following EXACTLY step by step it, for me, guarantees a successful installation. I tried it multiple times on a CentOS8-VM.
@Simon
Good to know that this guide worked for you. We always try our best to create guides that are easy to replicate whether in a test environment or in production. Many thanks for the useful feedback.
Thanks. I was trying to install PostgreSQL on my Linux server, I visited a lot of videos and blogs but your post is perfect!
@fernando
We are glad that this guide helped you out. Many thanks for the useful feedback.
Hi Aaron, thanks for your tutorial it was very helpful, just one step that you need to change in step 15 if you have python3, just you need to use this line “python3 /usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pgadmin4-web/setup.py” to set up the pgadmin4.
@Humbert,
Thanks corrected the command in the article…
You’re welcome for me the tutorial was very useful to me.
Regards.
@Humbert
Many thanks once again for the useful feedback.