Step 2: Installing PowerAdmin to Manage PowerDNS
11. Now we will install PowerAdmin – a friendly web interface designed to manager PowerDNS servers. Since it is written in PHP, we will need to install PHP and a web server (Apache):
# yum install httpd php php-devel php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-mysql php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-mhash gettext

PowerAdmin also requires two PEAR packages:
# yum -y install php-pear-DB php-pear-MDB2-Driver-mysql

You can also refer to the following article for complete instructions how to install LAMP stack in CentOS 7:
Once the install is complete, we will need to start and set Apache to start at system boot:
# systemctl enable httpd.service # systemctl start httpd.service

12. Now that all system requirements for running PowerAdmn are met, we can proceed and download the package. Since the default web directory for Apache is /var/www/html/, we will download the package in there.
# cd /var/www/html/ # wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/poweradmin/poweradmin-2.1.7.tgz # tar xfv poweradmin-2.1.7.tgz

13. Now, we can now start the web installer of PowerAdmin. Simply open:
http://192.168.0.102/poweradmin-2.1.7/install/
This should bring the first step of the installation:
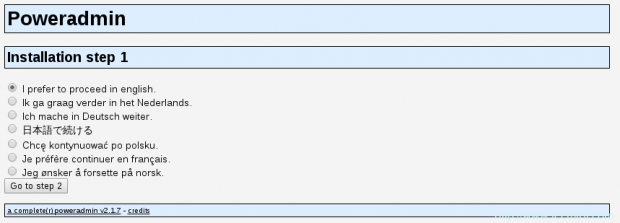
The above page will ask you to choose the language for your PowerAdmin. Select the one you wish to use and click the “Go to step 2” button.
14. The installer will expect you to have a PowerDNS database:
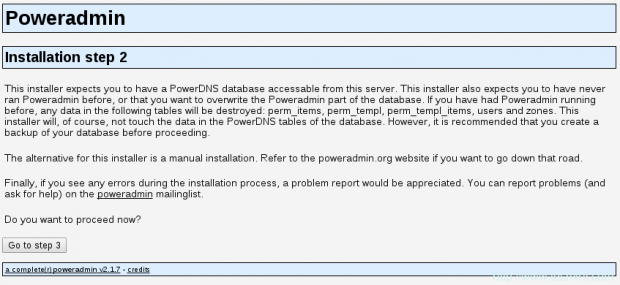
15. Since we already created one, we can proceed to the next step. You will be asked to enter the database details you setup earlier. You will also need to setup Poweradmin administrator password:
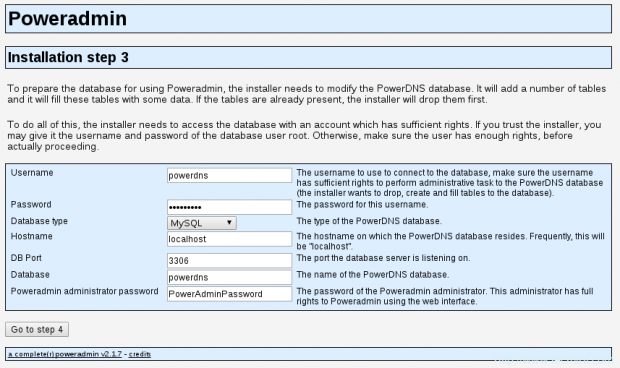
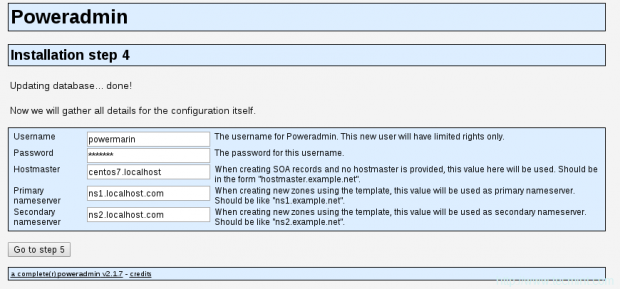
16. Once you have input those, go to step 4. You will create a new user with a limited rights for Poweradmin. The fields that you need to enter here are:
- Username – username for the PowerAdmin.
- Password – password for the above user.
- Hostmaster – When creating SOA records and you have not specified hostmaster, this value will be used.
- Primary nameserver – the value will be used as primary name server when creating new DNS zones.
- Secondary nameserver – the value will be used as primary name server when creating new DNS zones.
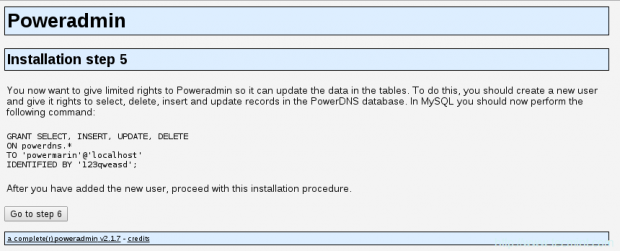
17. On the next step Poweradmin will ask you to create new database user with limited rights on the database tables. It will provide you with the code that you will need to put in a MySQL console:
18. Now open a terminal and run:
# mysql -u root -p
Provide your password and execute the code provided by Poweradmin:
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON powerdns.* TO 'powermarin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123qweasd';

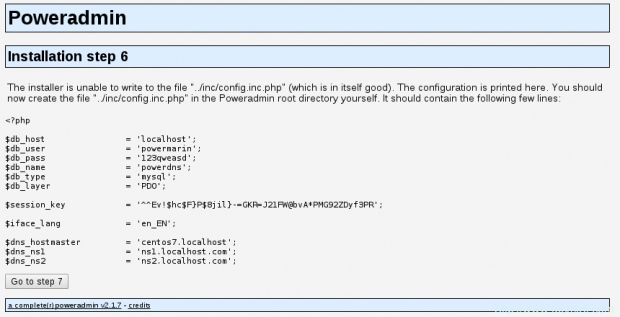
19. Now go back to your browser and proceed to the next step. The installer will attempt to create its configuration file in /var/www/html/poweradmin-2.1.7/inc.
The file name is config.inc.php. In case the script is not able to write that file you can create it manually by copying the text and putting it in above mentioned file:
20. Now go to the last page where you will be informed that the installation is complete and will receive information how to access your Poweradmin install:
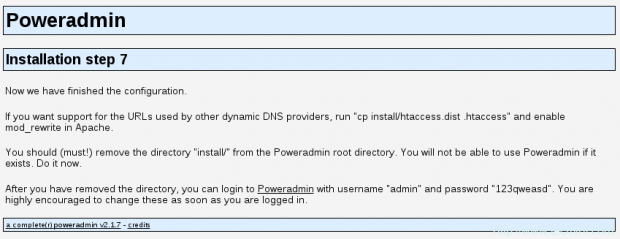
You can enable URLs used by other dynamic DNS providers by running:
# cp install/htaccess.dist .htaccess
For that purpose you will need to have mod_rewrite enabled in Apache’s configuration.
21. Now it is important to remove the “install” folder from Poweradmin’s root directory with the following command:
# rm -fr /var/www/html/poweradmin/install/
After that you can access your poweradmin at:
http://192.168.0.102/poweradmin-2.1.7/

After logging you should see the Poweradmin main page:

At this point your installation is complete and you are now ready to start managing your DNS zones.
Step 3: How to Add, Edit and Delete DNS Zones in PowerDNS
22. To add new master zone, simply click on the “Add master zone”:

On the next page there are few things that you need to fill:
- Domain – domain for which you will be adding the zone.
- Owner – sets the owner of the DNS zone.
- Template – DNS template – leave to none.
- DNSSEC – Donany Name System Security Extensions (optional -check if you need it).
Click the “Add zone” button to add the DNS zone.

Now you can go back to the index page of Poweradmin by clicking the “Index” link. To review all existing DNS zones simply go to “List zones”:

You should now see a list of available DNS zones:

23. To edit an existing DNS zone or add new records click the edit icon:

On the next page you will see the entries for the DNS zone you have chosen:

24. In here to add new DNS zone you will need to set the following information:
- Name – name for the entry. Only add the first part of the domain/subdomain, the rest will be added by Poweradmin.
- Type – choose the record type.
- Priority – priority of the record.
- TTL – Time To Live in seconds.
For the purpose of this article, I will add an A record for subdomain new.example.com that will resolve on IP address 192.168.0.102 with time to live 14400 seconds:

Finally click the “Add record” button.
25. If you wish to delete a DNS zone you can go back to the “List zone” page and click on the “Trash” icon next to the DNS zone which you wish to delete:

Poweradmin will ask you if you are sure you want to delete the DNS zone. Simply click “Yes” to finish the deletion.
For more detailed instructions how to create, edit and delete zones you can refer to Poweradmin’s documentation at:
https://github.com/poweradmin/poweradmin/wiki/Documentation
I hope you have find this article interesting and useful. As always if you have any questions or comments please do not hesitate to submit them in the comment section below.






Excellent article. Unlike anything, I was able to find anywhere else. Thanks so much!
One suggestion I would give to everyone is to determine what PDNS version you have by paying attention to the version number after the yum command. If you are already past that point, run the following command:
Then go to the official website to download the schema that matches the same version that is installed on your system. In my case, I kept using the wrong schema and caused me more frustration than necessary. The schema seems to change between each incremental release and is not forward or backward compatible.
I have error when I connect MySQL with pdns with this databases, for fixed I create the format of databases from the official website of powerdns.
how zone data will replicate on ns1 and ns2 ?
I appreciate to this person but “Username – username for the PowerAdmin.” you have a typo :(
Looks like there was a pdns schema change and some of the tables have changed. powerdns not longer works for me
i tried updating the schema to : https://doc.powerdns.com/md/authoritative/backend-generic-mypgsql/
Hi Ravi,
I installed powerdns and login in to the poweradmin,but my dns is not resolving.
[root@server1 ~]# nslookup server2
;; Got SERVFAIL reply from 192.168.1.17, trying next server
;; Got SERVFAIL reply from 192.168.1.17, trying next server
;; Got SERVFAIL reply from 192.168.1.17, trying next server
Server: 192.168.1.1
Address: 192.168.1.1#53
** server can’t find server2: NXDOMAIN
Hi,
can you plese assist how to upgrade the version from 3.3 to 4.x.
@Sanjay,
Have you tried PowerDNS using default EPEL repository using Yum package manager? if not, try it or compile it from source to get latest version of PowerDNS.
Hi Ravi,
Thanks for your reply,
I have tried with YUM with EPEL repo. I have installed version 3.3. let me try with with source code, or if you with any docs to compile via source code please share.
@Sanjay,
I think you can install latest PowerDNS using official PowerDNS yum repositories, as shown in this documentations here: https://repo.powerdns.com/
I installed powerdns, follow the link https://www.tecmint.com/install-powerdns-poweradmin-mariadb-in-centos-rhel/ .
When I do dig command into self LAN of the pdns I always receive:
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available
anything is default setting… where is the log file?
how can I understand how resolve?
pdns.conf
setuid=pdns
setgid=pdns
launch=bind
launch=gmysql
gmysql-host=localhost
gmysql-user=powerdns
gmysql-password=XXXX
gmysql-dbname=powerdns
recursor=8.8.8.8
from my machine to pdns:
nmap -v -sT 192.168.1.123
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
3306/tcp open mysql
nmap -v -sU 192.168.1.123
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/udp open|filtered domain
; <> DiG 9.8.3-P1 <> gs.mydomain.com @192.168.1.123
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: SERVFAIL, id: 58633
;; flags: qr aa rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;gs.mydomain.com. IN A
;; Query time: 1 msec
;; SERVER: 192.168.1.123#53(192.168.1.123)
;; WHEN: Fri Jul 22 18:15:12 2016
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 31
no firewall, selinux disabled
thanks a lot
I get “Authentication failed! ” error in GUI , Once i launched the GUI, When i try logging in to the GUI with my admin user and password. Can you help.
@Vivan,
Please check your PowerAdmin username and password that you were created on Step 16..
Actually correct way to create tables would be to use: /usr/share/doc/pdns-backend-mysql-3.X.X folder which consists from database schema files. In case you want to deploy powerdns with DNSSEC, schema will be there.
mysql -uroot -p powerdns < /usr/share/doc/pdns-backend-mysql-3.X.X/schema.mysql.sql
Please update your directions:
GRANT ALL ON powerdns.* TO ‘powerdns’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘passWord1’;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MariaDB server version for the right syntax to use near ‘‘passWord1’’ at line 1
@Sirmonkey,
Yes, the apostrophe are mentioned wrongly, corrected in the writeup and thanks for notifying us…