Virtual Networking Computing (VNC) is a kind of remote sharing system that makes it possible to take control of any other computer connected to the internet. Keyboard and mouse clicks can easily transmit from one computer to another. It helps administrators and technical staff to manage their servers and desktops without being to the same location physically.
VNC is an open-source application created in the late 1990s. It is independent and is compatible with Windows and Unix/Linux. This means a normal Windows-based user can interact with Linux based system without any hazel.
[ You might also like: 11 Best Tools to Access Remote Linux Desktop ]
To use VNC you must have a TCP/IP connection and a VNC viewer client to connect to a computer running the VNC server component. The server transmits a duplicate display of a remote computer to the viewer.
This article demonstrates how to install VNC Server using TightVNC a much-enhanced version of an older VNC program, with remote desktop access on RHEL-based Linux distributions and Debian-based distros.
Step 1: Installing the Desktop Environment
If you’ve installed a minimal version of the operating system, which gives only a command-line interface not GUI. Therefore, you need to install a GUI (Graphical User Interface) called GNOME or XFCE desktop which works very well on remote VNC access.
$ sudo dnf groupinstall "Server with GUI" [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] OR $ sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint]
Step 2: Installing TightVNC Server
TightVNC is a remote desktop control software that enables us to connect to remote desktops. To install, use the following yum command as shown below.
$ sudo yum -y install tigervnc-server xorg-x11-fonts-Type1 [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo apt install tightvncserver [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint]
Step 3: Create a Normal VNC User
Create a normal user, that will be used to connect to a remote desktop. For example, I’ve used “tecmint” as a user, you can choose your own username.
$ sudo useradd tecmint OR $ sudo adduser tecmint $ sudo passwd tecmint
Step 4: Set VNC Password for User
First, switch to the user using (su – tecmint) and run ‘vncpasswd‘ to set the VNC password for the user.
Note: This password is for accessing VNC remote desktop, and the password we created in step 3 is for accessing the SSH session.
[root@tecmint ~]# su - tecmint [tecmint@tecmint ~]$ vncpasswd Password: Verify:
The above command asks you to supply a password twice and creates the “.vnc” directory under the user’s home directory with a passwd file inside it. You can check the password file is created, by using the following command.
# ls -l /home/tecmint/.vnc -rw------- 1 tecmint tecmint 8 Jul 14 21:33 passwd
If you are adding another user, just switch to the user and add the vnc password with the vncpasswd command.
Step 5: Configure VNC for Gnome
Here, we will configure TigerVNC to access Gnome using the user configuration settings from the ~/.vnc/config file.
$ vim ~/.vnc/config
Add the following configuration to it.
session=gnome geometry=1920x1200 localhost alwaysshared
The session parameter defines the session you want to access, and the geometry parameter adds the resolution of the VNC desktop.
Now exit from user login and return to root user login.
$ exit
TigerVNC comes with default configuration settings that allow you to map a user to a specific port in the /etc/tigervnc/vncserver.users file:
# vim /etc/tigervnc/vncserver.users
The configuration file uses <display_port>=<username> parameters. In the following example, we are assigning display port :1 to user tecmint.
# This file assigns users to specific VNC display numbers. # The syntax is =. E.g.: # # :2=andrew # :3=lisa :1=tecmint
If you are adding another user, just set the display port to :2 followed by the username.
Step 6: Starting the Tigervnc Server
After making all changes, run the following command to start the VNC server. Before starting the VNC session with a “tecmint” user, let me give you a small intro about Port Numbers and ids.
By Default VNC runs on Port 5900 and ID:0 (which is for the root user). In our scenario, I’ve created tecmint, ravi, Navin, and avishek. So, the ports and id’s are used by these users as follows
User's Port's ID's 5900 root :0 5901 tecmint :1 5902 ravi :2 5903 navin :3 5904 avishek :4
So, here user “tecmint” will get port 5901 and id as :1 and so on. If you’ve created another user says (user5) then he will get port 5905 and id:5 and so on for each user you create.
To start and enable the VNC service for the user assigned to the display port :1, enter:
# systemctl start vncserver@:1 --now # systemctl enable vncserver@:1 --now
You can confirm that the VNC service is successfully started with:
# systemctl status vncserver@:1
To allow VNC access for other users, simply replace 1 with the display port number.
Step 7: Open VNC Ports on Firewall
Open port on iptables, firewalld or ufw, say for the user (tecmint) at 5901.
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 5901 -j ACCEPT OR # firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5901/tcp OR $ sudo ufw allow 5901/tcp
For multiple users, ravi, navin, and avishek. I open ports 5902, 5903, and 5904 respectively.
# iptables -I INPUT 5 -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp -m multiport --dports 5902:5904 -j ACCEPT OR # firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5902-5904/tcp OR $ sudo ufw allow 5901:5910/tcp
Restart Iptables service.
# service iptables save # service iptables restart Or # firewall-cmd --reload # systemctl restart firewalld
Step 8: Download VNC Client
Now go to your Windows or Linux machine and download the VNC Viewer client and install it in your system to access the desktop.
Step 9: Connect to Remote Desktop Using Client
After you installed the VNC Viewer client, open it you’ll get something similar to the below screen. Enter VNC Server IP address along with VNC ID (i.e 1) for user tecmint.
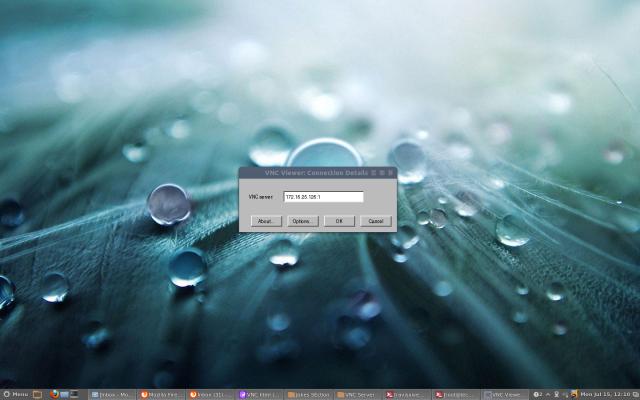
Enter the password that we created with the “vncpasswd” command.
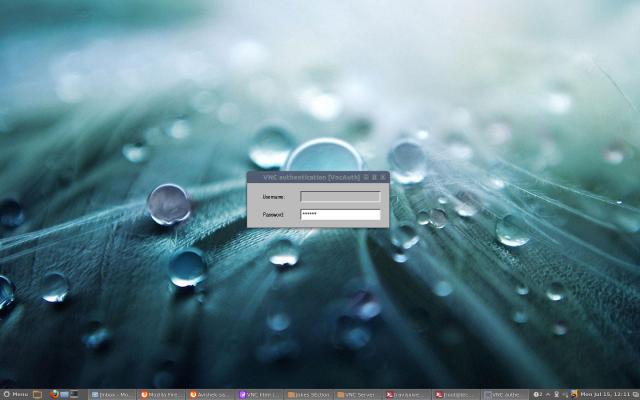
That’s it, you connected to your Remote Desktop.
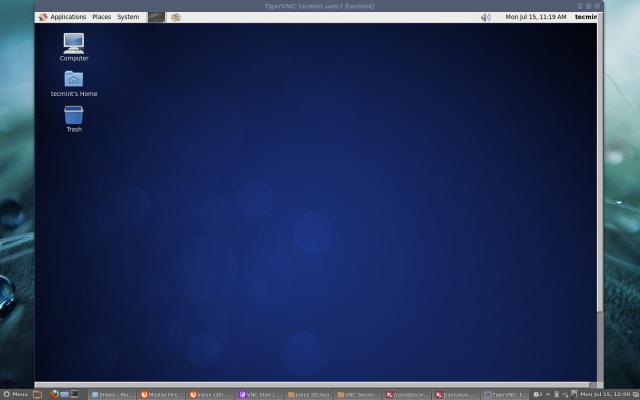
[ You might also like: How to Access Remote VNC Desktop from Web Browser Using TightVNC Java Viewer ]





This article really saved me! I was struggling for a while with setting up remote desktop access via VNC on my Linux machine, and nothing seemed to work. But after following these steps for installing TightVNC, everything fell into place smoothly.
The clarity in the guide made it super easy to follow through, and the extra details about configuring the desktop environment were just what I needed.
Appreciate this article, Ravi! It’s been incredibly useful, and I’ll definitely be using this approach in the future.
Keep it up!
This is not accurate. TightVNC != TigerVNC. TigerVNC is a fork of TightVNC from 2009. Now, TigerVNC has a different feature set than TightVNC. For instance, TigerVNC has encryption & TightVNC has file transfers. Different configurations also.
Why wouldn’t you create an icon on the desktop and/or an entry in the list of programs to be able to click on and the vnc client starts to run and asks for the address of the machine you want to control?
I installed it and don’t see that and I don’t know why. It seems the developers really don’t want people to use it.
Hello Ravi,
I am using fedora 27. In this version /etc/sysconfig/vncservers is replaced by /lib/systemd/system/[email protected].
I just followed https://www.server-world.info/en/note?os=Fedora_27&p=desktop&f=6 this document to set up vncserver in my system. It was working fine till version 25. But now all I get is a blank screen after entering the password.
What could be the reason ? any idea?
@Rahul,
Thanks for updating us about these changes, let me give a try to this TightVNC on my Fedora 28, will get back to you with solution.
any updates on this?
@Rahul,
Sorry for delay, you will see updated article with instructions tomorrow morning without fail..
Hi, thanks for the nice tutorial!
Unfortunately i have some issues.
After following the steps, log in fails from VNC viewer, with error message “the connection was closed unexpectedly”.
Examining the log in /home/my_username/.vnc i notice the lines
gnome-session[11753]: WARNING: Could not connect to ConsoleKit: Failed to connec
t to socket /var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket: No such file or directory
GNOME_KEYRING_SOCKET=/tmp/keyring-44DgDf/socket
SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/keyring-44DgDf/socket.ssh
GNOME_KEYRING_PID=11782
** (gnome-settings-daemon:11785): WARNING **: Connection failed, reconnecting…
….
Any help much appreciated.
Hi Ravi,
I am getting the below error when i am trying to start the vncserver service by /etc/init.d/vncserver start.
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/vncserver start
Starting VNC server: 1:testing xauth: timeout in locking authority file /root/.xauth
Please show me how configure ssh tunnel with VNC with steps
Hi Ravi,
I followed your steps.
it worked fine ….
But my requirement was to configure the multiple vnc clients for the same user. For e.g say user techmint.
So i added entry for the same in /etc/sysconfig/vncservers file as:
VNCSERVERS=”1:techmint 2:techmint”
VNCSERVERARGS[1]=”-geometry 1280×1024″
VNCSERVERARGS[2]=”-geometry 1280×1024″
After restarting the service I am getting black and X as cursor.
Could you help me out???
@Aktar,
I think you can’t create multiple VNC sessions for same user, have you tried with different multiple users? is the VNC sessions worked for all?
Hi Ravi,
Thanks for the reply.
I am able to create multiple VNC sessions for same user and currently I got them working by modifying the xstartup file .
My xstartup file contents are below:
#!/bin/sh
# Uncomment the following two lines for normal desktop:
unset SESSION_MANAGER
exec /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc
gnome-session &
[ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup
[ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources
xsetroot -solid grey
vncconfig -iconic &
#xterm -geometry 80×24+10+10 -ls -title “$VNCDESKTOP Desktop” &
#twm &
my vncservers file content is :
[root@mybox1 ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/vncservers
# The VNCSERVERS variable is a list of display:user pairs.
#
# Uncomment the lines below to start a VNC server on display :2
# as my ‘myusername’ (adjust this to your own). You will also
# need to set a VNC password; run ‘man vncpasswd’ to see how
# to do that.
#
# DO NOT RUN THIS SERVICE if your local area network is
# untrusted! For a secure way of using VNC, see
# .
# Use “-nolisten tcp” to prevent X connections to your VNC server via TCP.
# Use “-nohttpd” to prevent web-based VNC clients connecting.
# Use “-localhost” to prevent remote VNC clients connecting except when
# doing so through a secure tunnel. See the “-via” option in the
# `man vncviewer’ manual page.
# VNCSERVERS=”2:myusername”
# VNCSERVERARGS[2]=”-geometry 800×600 -nolisten tcp -nohttpd -localhost”
VNCSERVERS=”1:user1 2:user1 3:user1 4:user1 5:user1 6:user1″
VNCSERVERARGS[1]=”-geometry 1280×1024″
VNCSERVERARGS[2]=”-geometry 1280×1024″
VNCSERVERARGS[3]=”-geometry 1280×1024″
VNCSERVERARGS[4]=”-geometry 1280×1024″
VNCSERVERARGS[5]=”-geometry 1280×1024″
VNCSERVERARGS[6]=”-geometry 1280×1024″
Now my issue is that I am able to invoke only two sessions for third session it flags below error:
A VNC server is already running as :3
@Aktar,
Thanks for sharing your findings and configuration of both files, hope it will help others who looking for similar problems, about multiple VNC sessions for same users, i really don’t have idea, i need to check and get back to you..
Thanks a lot man, i really like your tutorial, it really makes the installation very easy…
You deserve 100 stars
Hello,
This is not really TightVNC but TigerVNC. I wanted TightVNC to be able to only share one application and not the whole desktop.
Do you know how to do it with TigerVNC ?
Kindly
i have create some video tutorial about this,
your article is my source,
thnk’s a lot
this is my video
http://youtu.be/N2UnYy2kdnk
@Antechno,
Are you taken written permission from us before creating videos from our articles? this is against our copyright violation..I request you to remove article either give proper credit to original article..
hi i did all steps and try start the service get this error
/etc/init.d/vncserver start
plymouth: ply-event-loop.c:493: ply_event_loop_new: Assertion `loop->epoll_fd >=
0′ failed.
/etc/init.d/functions: line 543: 28173 Aborted /bin/plymouth –d
etails
system: centos6.4
please help sending me crazy
Thanks for great efforts. It working great. Can you tell us how to uninstall it properly?
Above steps seems to be quite complicated. I would recommend using a RHUB remote support servers for remotely accessing computers. It is easy to use.
hi
my problem is in step 5
when i try to open commend : /etc/init.d/vncserver start
this error showing :
Starting VNC server: no displays configured [FAILED]
on centos-6-x86
Please configure display in vnc configuration..
I have the same issue”no displays configured [FAILED]”. So could you tell the step to configure Display in VNC Configuration?
Thanks
Just do step 6 before you do step 5.
Worked for me thanks!! :)
after “/etc/init.d/vncserver start” vncserver listen in 127.0.0.1:5902
how to specify vncserver listen ip.
Oh Boy ! ***************************************************************
Close but no cigar…
@ Ravi
1st, at the end of step 5, you write:
“Once, it created, set a desktop resolution in xstartup file. For this, you must stop running VNC service.”
The at the beginning of step 6 you go:
Open file “/etc/sysconfig/vncservers” file your choice of editor. Here I’m using “nano” editor. Create new VNC Session for “tecmint” with below command. where “-geomerty” is used define desktop resolution.
??? Ambiguous file references ???
In xstartup in the user’s home directory or in /etc/sysconfig/vncservers do we add the Resolution setting code ?
2nd, This is ok for sysint and iptables. If, like the gentlemen named Matheis, as of the date of publication of this article, one would be using an advance distribution like Fedora 18, out Jan 15 2013 this article is already old school.
With systemd and firewalld, most of this nice try does not work.
MotherDawg
Aka: NetWeezurd
Hey my fedora too required me to tweak around the systemd. Could you create a page with how to set up vnc with config files under systemd
I have installed VNC as per above tutorial
now Vnc viewer is asking for session password after keeping the server in idel conditins for some time..when i entered the login password its not working
kindly suggest what can be done
Hi. Thank you for your posting.
I’m now using CentOS6.5.
/etc/init.d/vncserver start
Error: bad escape code: f [FAILED]
I have this error. What is the problem???
thank you.
Hi, thank you for a nice tutorial.
I do my work thru VNC, connecting to a remote server. I often encounter problems though when running some applications, I cannot use my keyboard to input on the GUI, thus I cannot type anything on the fields for the gui of this particular app.
Everything works fine on a simple linux shell.
Thank you
how to resolve too many security failures vnc server how to check vnc server logs and how check which ip address are connected to vnc server please guide me
Under user’s home directory you will see a .vnc directory where you can see the log file of each vnc session like ‘mymachine.localnet:1.log’. And about checking vnc connection sessions, you can use netstat command to list vnc ports or use ps -fax to check running vnc services.
hi, I have managed to configure the vnc but when I log in there are some files that I can not edit/delete as vncuser, how can I give vnc user root lever access I have tried to do something like: vncserver:0;0…… to give it root access on users file. But now I cant log in to vnc either.
I followed the steps on my centos 6.5 final VPS trying to connect from windows 7 but is says “connection refused (10061)” I also tried telnet from comments above on SSH it says telnet: connect to address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx: Connection refused
can anybody help? Thanks in advanced
Thank you!
im facing connection : Connection time out (10060).
my telnet is working fine..
telnet 172.31.0.212 5901
Trying 172.31.0.212…
Connected to 172.31.0.212.
Escape character is ‘^]’.
RFB 003.008
some one help me out. im having my aws linux machine and accessing it from local machine.
Thanks for this post.
How will you tunnel vnc via ssh?
Thanks
I have been having trouble with this under Fedora since version 18. Under Gnome 3.6 I could set it in forced fallback mode and using the Cinnamon desktop could get it to work. Now with gnome 3.8 there is no fallback mode option. I went all through your setup instructions, with modification for using systemctl to start/stop vncserver, and it all seems to work fine until I enter the VNC password. The remote desktop window opens but says “Oh no! Something has gone wrong. A problem has occurred and the system can’t recover. Please log out and try again.”
I have been searching the web for a solution to this for nearly a year and so far have not had any luck getting it to work. Any ideas?
Thanks,
Dave
I had a messy setup working for Cinnamon under Fedora 18, but got the “Oh no!” again after upgrading to Fedora 19. However now it appears that there is a much simpler solution in Fedora 19. Install tiger-vncserver, copy file [email protected] to vncserver@:1.service and edit to replace the two uses of to the correct user name and add the -geometry and -depth options you want to the vncserver command line, just like you would to use vnc with the Gnome desktop.
Then to make it use Cinnamon, create a script file named ~/.Xclients that contains
#!/bin/bash
exec /usr/bin/cinnamon-session
When the vnc session starts up it runs ~/.Xclients if it exists instead of starting gnome-session.
The cinnamon-session program appears to be new in Fedora 19 and solves the problem.
Thank you so much for this comment. I spent several hours trying to get the same thing to work without any success. Your solution works for me as well and it’s so simple!
On my fresh install Centos 6.4, I had to invert step 5 and 6.
It refuses to start because no resolution was setup.
hi,
this is Imran raini from Mumbai.
I have Linux Server that is Linux 6.0 version
I want to install VNC on that server. please help me
I try to install VNC but it is not install Proper kindly send me step how can install VNC in Linux 6.0 Server.
Best Regards
Mohd Imran Raini
Dear Imran,
The steps are perfect, kindly follow the instructions correctly…