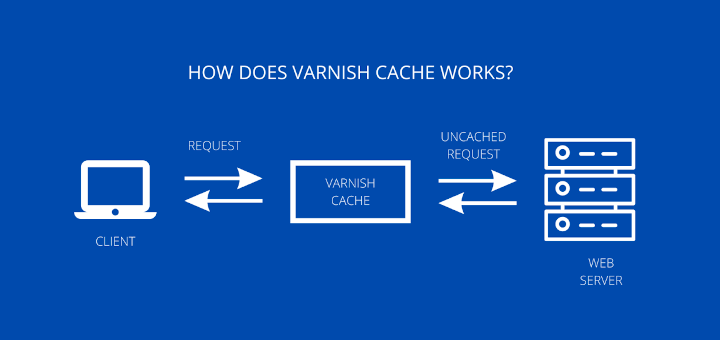
Varnish Cache (also called Varnish) is an open source, HTTP accelerator which stores web pages in memory so web servers don’t have to create the same web page over and over again when requested by a client. You can configure Varnish to work in front of a web server to serve pages in a much faster way thus giving the websites a significant speed up.
In our last article, we have explained how to setup a Varnish Cache for Apache on a Debian and Ubuntu system.
In this article, we will explain how to install and configure Varnish Cache 5 as a front-end to Nginx HTTP server on a Debian and Ubuntu systems.
Requirements:
- A Ubuntu system installed with LEMP Stack
- A Debian system installed with LEMP Stack
- A Debian/Ubuntu system with static IP address
Step 1: Install Varnish Cache on Debian and Ubuntu
1. Unfortunately, there are no pre-compiled packages for latest version of Varnish Cache 5 (i.e 5.1.2 at the time of writing), so you need to build it from its source files as shown below.
Start by installing the dependencies for compiling it from source using the apt command like this.
$ sudo apt install python-docutils libedit-dev libpcre3-dev pkg-config automake libtool autoconf libncurses5-dev libncurses5
2. Now download Varnish and compile it from source as follows.
$ wget https://repo.varnish-cache.org/source/varnish-5.1.2.tar.gz $ tar -zxvf varnish-5.1.2.tar.gz $ cd varnish-5.1.2 $ sh autogen.sh $ sh configure $ make $ sudo make install $ sudo ldconfig
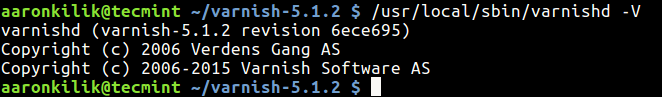
3. After compiling Varnish Cache from source, the main executable will be installed as /usr/local/sbin/varnishd. To confirm that the Varnish installation was successful, run the following command to see the its version.
$ /usr/local/sbin/varnishd -V
Step 2: Configure Nginx to Work With Varnish Cache
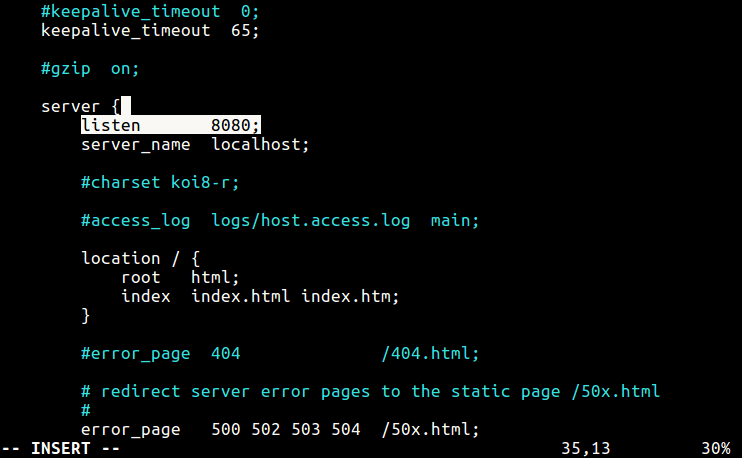
4. Now you need to configure Nginx to work with Varnish Cache. By default Nginx listens on port 80, you need change the default Nginx port to 8080 so it runs behind Varnish caching.
Therefore open the Nginx configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf and find the line listen 80, then change it to listen 8080 as the server block as shown in the screen shot below.
$ sudo vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
5. Once port has been changed, you can restart Nginx services as follows.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
6. Now start Varnish daemon manually by typing following command instead of calling systemctl start varnish, since certain configurations are not in place when its installed from source:
$ sudo /usr/local/sbin/varnishd -a :80 -b localhost:8080

Step 3: Test Varnish Cache on Nginx
7. Finally, test if Varnish cache is enabled and working with the Nginx HTTP server using the cURL command below to view the HTTP header.
$ curl -I http://localhost
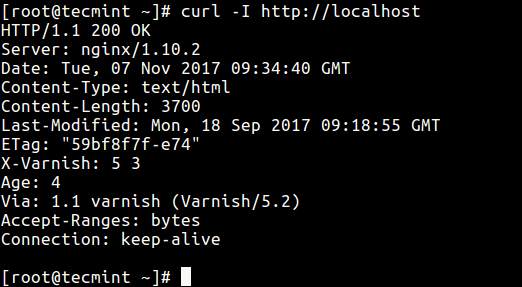
You can find additional information from the Varnish Cache Github Repository: https://github.com/varnishcache/varnish-cache
In this tutorial, we have showed how to setup Varnish Cache 5.1 for Nginx HTTP server on Debian and Ubuntu systems. You can share any thoughts or queries with us via the feedback from below.