VirtualBox is a powerful, free, open-source, feature-rich, high performance and cross-platform x86 and AMD64/Intel64 virtualization software for enterprise and home use. It runs on Linux, Windows, Macintosh, as well as Solaris hosts.
In this article, we will show how to install VirtualBox 6.1 on Fedora 31 distribution using the official yum repository.
Note: If you are using the system as a normal or administrative user, employ the sudo command to gain root privileges to run most if not all the commands in this article.
Downloading VirtualBox Repo on Fedora 31
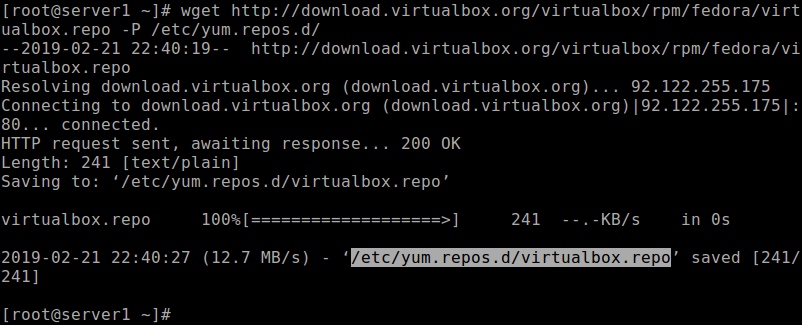
To install VirtualBox on Fedora Linux 30, you first need to download the virtualbox.repo configuration file using the following wget command.
# wget http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/rpm/fedora/virtualbox.repo -P /etc/yum.repos.d/
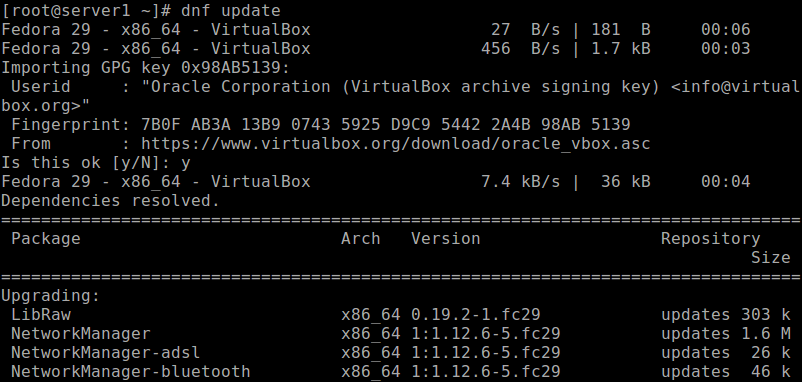
Next, update the installed packages on the system and import the VirtualBox public key by running the following dnf command. This ensures that all system updates are installed and that the system is running the most up-to-date kernel included in the distribution.
# dnf update
Installing Development Tools on Fedora 31
If you want to run the Oracle VM VirtualBox graphical user interfaces (VirtualBox), you need to install Qt and SDL packages. However, if you only want to run VBoxHeadless, the aforementioned packages aren’t required.
In addition, the installer will create kernel modules on the system, therefore you need to install development tools (GNU compiler (GCC), GNU Make (make)) and packages containing header files for your kernel for the build process as well.
# dnf install @development-tools # dnf install kernel-devel kernel-headers dkms qt5-qtx11extras elfutils-libelf-devel zlib-devel
Installing VirtualBox 6.1 on Fedora 31
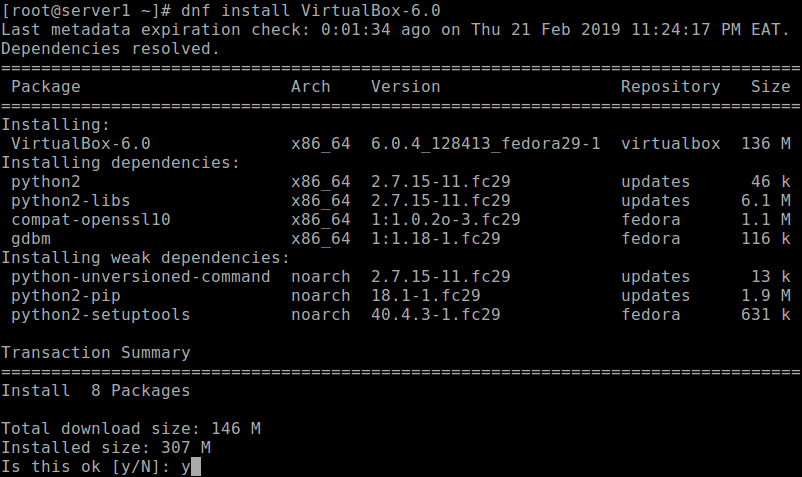
Once the required packages and development tools installed, you can now install VirtualBox 6.0 with the following dnf command.
# dnf install VirtualBox-6.1
During the VirtualBox package installation, the installer created a group called vboxusers, all system users who are going to use USB devices from Oracle VM VirtualBox guests must be a member of that group.
To add a user to that group, use the following usermod command.
# usermod -a -G vboxusers tecmint
At this point, you are ready to start using VirtualBox on your Fedora 31. Search for VirtualBox in the Activities search feature and click on it to launch it.
Alternatively, execute the following command to start VirtualBox from the terminal.
# virtualbox
Read Also: How to Enable USB in VirtualBox
Congratulations! You just installed VirtualBox 6.0 on Fedora 31. If you have any questions or thoughts to share with us, use the feedback form below.




HI,
No need to publish this, but the first line reads: “VirtualBox is a powerful, free, open-source, feature-rich, high performance and cross-platform x86 and AMD64/Intel64 visualization software for enterprise and home use.” One can argue that it VISUALIZES as well, but I guess you mean Virtualize. Thanks for the post.
d.
@degski
Many thanks for pointing this out. True, it should be virtualization instead of a visualization. We will correct this as soon as possible.
This guide works only on computers without having secure boot or having secure boot disabled.
You’ll have to turn USB off, there’s an [new] entry for Fedora 31 in the Wiki, no ifs, buts or maybes. This is new in Fedora 31 and my feeling is, it won’t make Fedora 32, basically, your system is now military-grade secure and military-grade usable at the same time. If you don’t carry 4 stars on your shoulder, it’s overshoot.
/sbin/vboxconfig
vboxdrv.sh: Stopping VirtualBox services.
depmod: WARNING: could not open /lib/modules/4.20.3-200.fc29.x86_64/modules.order: No such file or directory
depmod: WARNING: could not open /lib/modules/4.20.3-200.fc29.x86_64/modules.builtin: No such file or directory
vboxdrv.sh: Starting VirtualBox services.
vboxdrv.sh: Building VirtualBox kernel modules.
vboxdrv.sh: failed: modprobe vboxdrv failed. Please use ‘dmesg’ to find out why.
There were problems setting up VirtualBox. To re-start the set-up process, run
/sbin/vboxconfigas root. If your system is using EFI Secure Boot you may need to sign the
kernel modules (vboxdrv, vboxnetflt, vboxnetadp, vboxpci) before you can load
them. Please see your Linux system’s documentation for more information.