VNC (Virtual Network Computing) is a popular platform for graphical desktop sharing which allows you to remotely access, view and control other computers over a network such as the Internet.
VNC uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) and works on the client-server principle: a server shares its output (vncserver) and a client (vncviewer) connects to the server. Note that the remote computer must have a desktop environment installed.
In this article, we will explain how to install and configure VNC Remote Access in the latest release of RHEL 8 Desktop edition through a tigervnc-server program.
Requirements:
- RHEL 8 with Minimal Installation
- RHEL 8 with RedHat Subscription Enabled
- RHEL 8 with Static IP Address
Once your RHEL 8 system meets the above-listed requirements, you are ready to set it up as a VNC server.
Step 1: Disabling Wayland Display Manager and Enabling X.org
1. The default Desktop Environment (DE) on RHEL 8 is GNOME which is configured to use Wayland display manager by default. However, Wayland isn’t a remote rendering API like X.org. So, you need to configure your system to use the X.org display manager.
Open the GNOME Display Manager (GDM) configuration file using your favorite command line editor.
# vi /etc/gdm/custom.conf
Then uncomment this line to force the login screen to use Xorg.
WaylandEnable=false
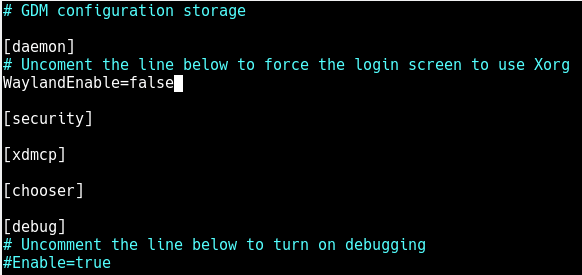
Save the file and close it.
Step 2: Install VNC Server in RHEL 8
2. TigerVNC (Tiger Virtual Network Computing) is an open source, a widely-used system for graphical desktop sharing which allows you to remotely control other computers.
# dnf install tigervnc-server tigervnc-server-module
3. Next, switch to the user you want to run and use the VNC program by setting the user’s VNC server password (which should be at least six characters), as shown.
# su - tecmint $ vncpasswd
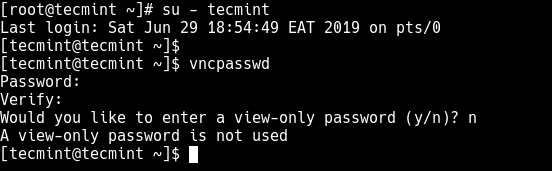
Now switch back to the root account by running the exit command.
$ exit
Step 3 Configure VNC Server in RHEL 8
4. In this step, you have to configure the TigerVNC server to start a display for the above user on the system. Start by creating a configuration file named /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service as follows.
# vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service
Add the following configuration in it (remember to replace tecmint with your actual username).
[Unit] Description=Remote desktop service (VNC) After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking WorkingDirectory=/home/tecmint User=tecmint Group=tecmint PIDFile=/home/tecmint/.vnc/%H%i.pid ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver -autokill %i ExecStop=/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save the file and close it.
Before we move any further, let’s briefly understand how the VNC server listens to requests. By default, VNC uses TCP port 5900+N, where N is the display number. If the display number is 1, then the VNC server will run on display port number 5901. This is the port you have to use while connecting to the server, from the client.
Step 4: Enable VNC Service in RHEL 8
5. To start the VNC service, you need to disable SELinux which is enforcing mode by default on RHEL 8.
# setenforce 0 # sed -i 's/enforcing/disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
6. Now reload the systemd manager configuration to apply the recent changes and then start the VNC service, enable it to auto-start at system boot time and check if it is up and running using the following systemctl commands.
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl start vncserver@:1 # systemctl status vncserver@:1 # systemctl enable vncserver@:1
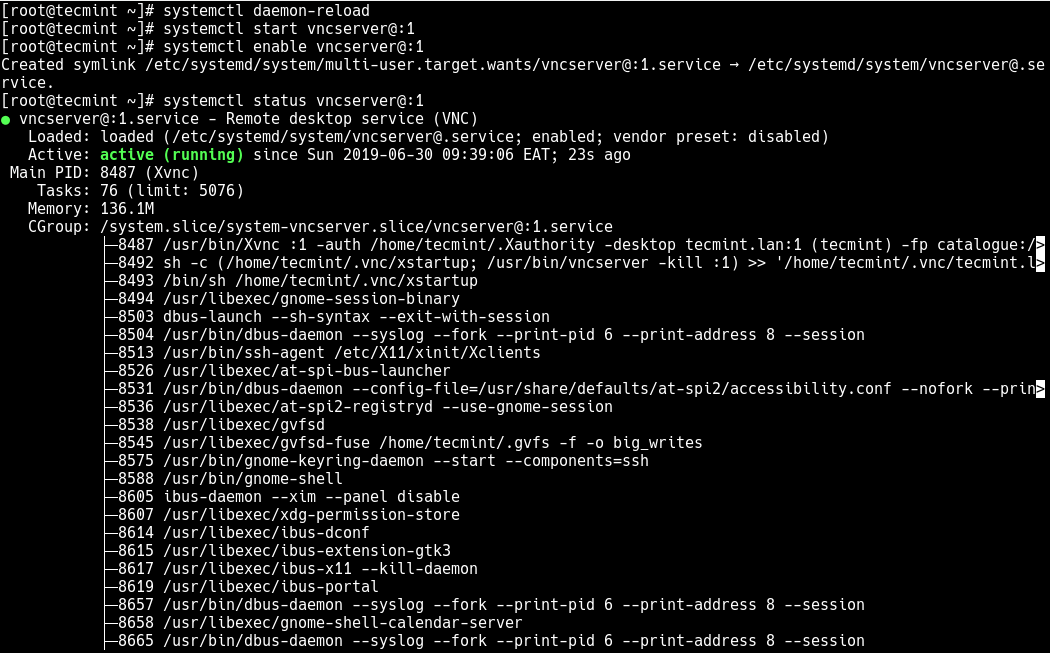
7. At this point, the VNC service is up and running, verify that the VNC server is listening on TCP port 5901 using the netstat command.
# netstat -tlnp
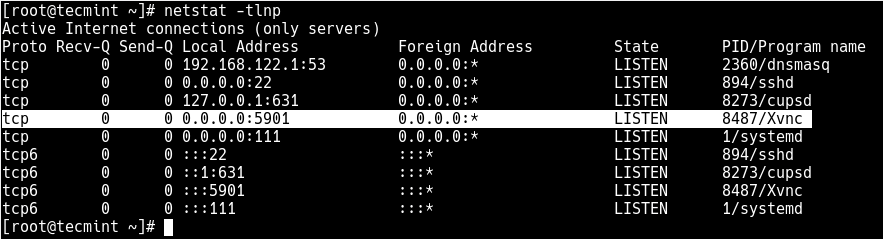
8. Next, open the port 5901 in the system firewall service which is running by default, as shown. This allows access to VNC service from clients.
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5901/tcp # firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5: Connecting to VNC Server via VNC Client
9. Now it is time to look at how to access the VNC server from a client side. VNC is not a secure system by default meaning your connections are not at all encrypted. But you can secure connections from the client to the server using a technique known as SSH tunneling as explained below.
Remember that you need to configure passwordless SSH authentication between the server and the client machine, to increase the trust between the two Linux systems.
Then on Linux client machine, open a terminal window and run the following command to create an SSH tunnel to VNC server (don’t forget to change the path to the identity file (~/.ssh/rhel8) and IP address (192.168.56.110) of the server accordingly):
$ ssh -i ~/.ssh/rhel8 -L 5901:127.0.0.1:5901 -N -f -l tecmint 192.168.56.110
10. After creating the SSH tunnel, you can install vncviewer client such as TigerVNC Viewer on the client machine.
$ sudo apt install tigervnc-viewer #Ubuntu/Debian # yum install tigervnc-viewer #CnetOS/RHEL # yum install tigervnc-viewer #Fedora 22+ $ sudo zypper install tigervnc-viewer #OpenSUSE # pacman -S tigervnc #Arch Linux
11. When the installation is complete, run your VNC client, specify the address localhost:5901 to connect to display 1 as follows.
$ vncviewer localhost:5901 OR $ vncviewer 127.0.0.1:5901
Or else, search and open the VNC client program from the system menu, then enter the address above and then click Connect as shown in the following screenshot.
If the connection is successful, you will be prompted for the VNC login password created earlier on in Step 2, point 3. Provide it and click OK to proceed.
Upon a successful VNC server authentication, you will be presented with the remote RHEL 8 system desktop interface. Click Enter to access the login interface and provide your password to access the desktop.
In this article, we have shown how to install and configure VNC server on RHEL 8. As usual, you can ask questions via the feedback form below.






After connecting to the machine I am getting a black screen!
Follow below steps.
And then do:
Mine failed at pid file is missing:
Nov 17 14:33:48 labdev22 systemd[1]: vncserver@:1.service: Can’t open PID file /root/.vnc/labdev22:1.pid (yet?) afte>
Nov 17 14:33:48 labdev22 systemd[1]: vncserver@:1.service: Failed with result ‘protocol’.
ls /root/.vnc
config passwd xstartup
I am trying to set up vnc for root to use.
systemctl start vncserver@:1
Job for vncserver@:1.service failed because the control process exited with error code.
See “systemctl status vncserver@:1.service” and “journalctl -xe” for details.
How do I correct this error.
Santosh,
Run the following command to find more information about this error.
And yes, the service is active:
# systemctl status vncserver@:1.service ● vncserver@:1.service - Remote desktop service (VNC) Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service; enabled; vendor pres> Active: active (running) since Sun 2020-07-26 10:29:46 BST; 7min ago Process: 1098 ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver -autokill :1 (code=exited, status=> Process: 1068 ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c /usr/bin/vncserver -kill :1 > /dev/null> Main PID: 1115 (Xvnc) Tasks: 196 (limit: 49623) Memory: 575.9M CGroup: /system.slice/system-vncserver.slice/vncserver@:1.service@Peter
The error could be “Failed to import environment: Process org.freedesktop.systemd1 exited with status 1” as stated in your other comment. Allow us to find more about this error.
I also get a blank screen after connecting. Could the error be “Failed to import environment: Process org.freedesktop.systemd1 exited with status 1“?
I got a blank screen too. Couldn’t figure it out with the instruction on the above article. This one worked for me.
OMG. First you don’t disable SELinux. Second, you don’t let vncserver run on 0.0.0.0 if you then want to connect to it via an ssh tunnel. The third vncviewer has a need switch called “via”. Forth, why open port 5901 if connecting via ssh tunnel (in which case only the ssh port needs to be open)?
Thank you, followed it step by step but I’m still tracking the failed>
job for vncserver!:1.service failed because a timeout exceeded.
@Mike
Are you getting any error message from the status o the
vncserver@:1.serviceservice, you can check using:Ok followed the instructions above, but yet I am getting a black screen when I connect. Any ideas?