This tutorial concentrates on how to perform a graphical installation of Red Hat Enterprise or CentOS 7.0 from a remote point in VNC Direct Mode using Anaconda included locally VNC server and how to partition a hard-disk smaller than 2TB with a GPT Partition Table Layout on non-UEFI systems.

In order to access the graphical installation, your remote system that will control the installation process, requires a VNC viewer program installed and running on your machine.
Requirements
- Installation of RHEL 7.0
- Installation of CentOS 7.0
- An VNC client installed on a remote system
Step 1: Boot RHEL/CentOS Media Installer in VNC Mode
1. After the installer bootable media has been created, place your DVD/USB into your system appropriate drive, start the machine, select your bootable media and on the first prompt press TAB key and the boot options should appear.
In order to start b>Anaconda VNC server with a password to restrict access to installation and force your hard-disk smaller than 2TB in size to be partitioned with a GPT valid partition table, append the following options to boot menu command line.
inst.gpt inst.vnc inst.vncpassword=password resolution=1366x768
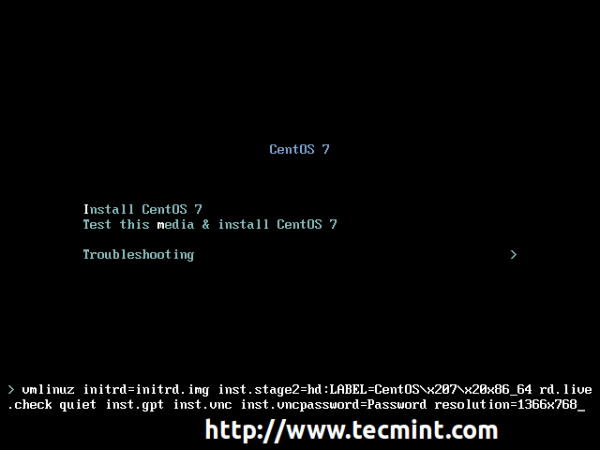
As you can see I’ve added an extra option to force graphical installation resolution to a custom size – replace resolution values with your desired values.
2. Now press Enter key to start the installer and wait until it reaches the message where it shows you the VNC IP Address and Port number to enter, in order to connect, on client side.
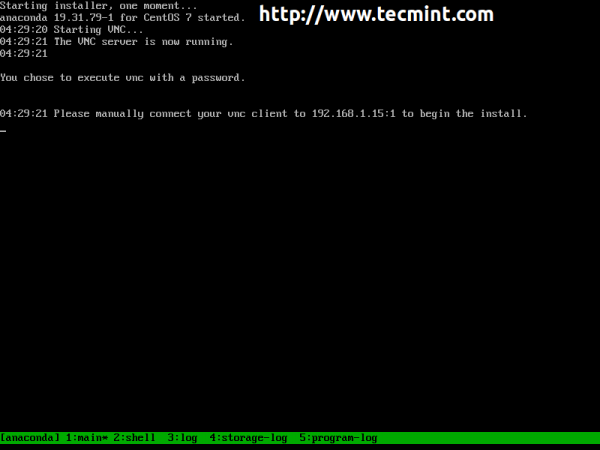
That’s it! Now the installation process is ready to be configured from a remote system using a VNC Client.
Step 2: Configure VNC Clients on Remote Systems
3. As a previously mentioned, in order to be able to perform a VNC installation remote systems requires a running VNC Client. The following VNC clients are available, depending on your Operating System.
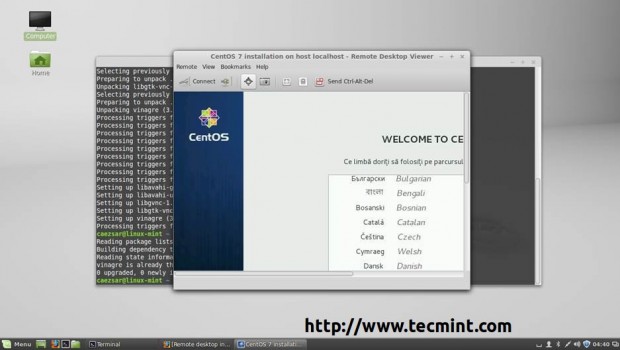
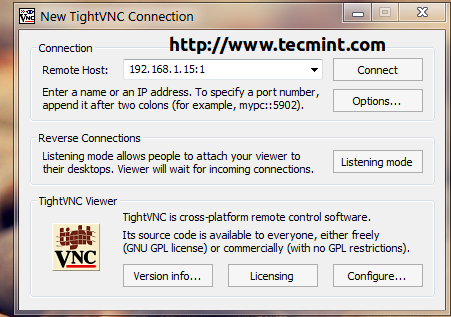
For RHEL/CentOS 7.0 installed with a Graphical User Interface open Remote Desktop Viewer, hit on Connect button and choose VNC for Protocol and add VNC IP Address and Port presented on the system where you perform the installation.
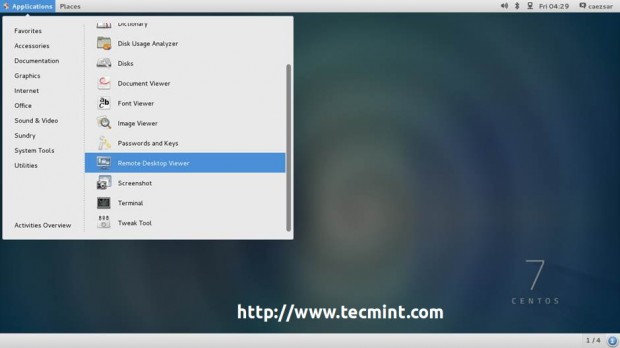
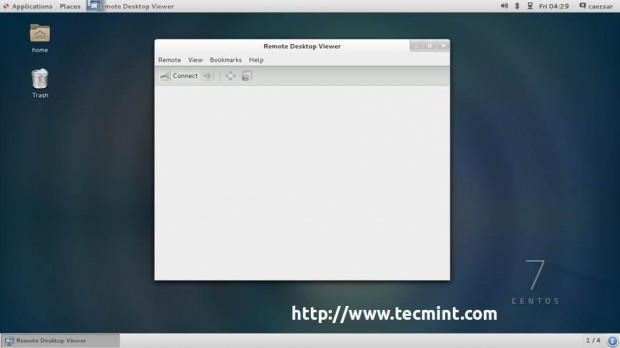
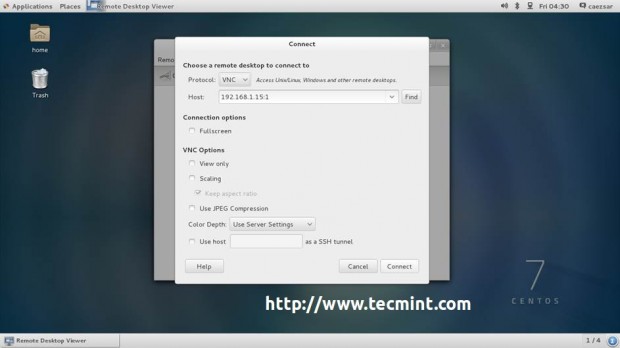
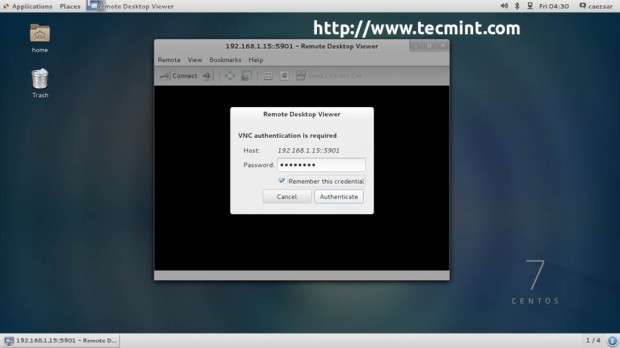
4. After the VNC Client connects to installer, you will be prompted to enter the VNC installer password. Enter the password, hit Authenticate and a new window with CentOS/RHEL Anaconda graphical interface should appear.
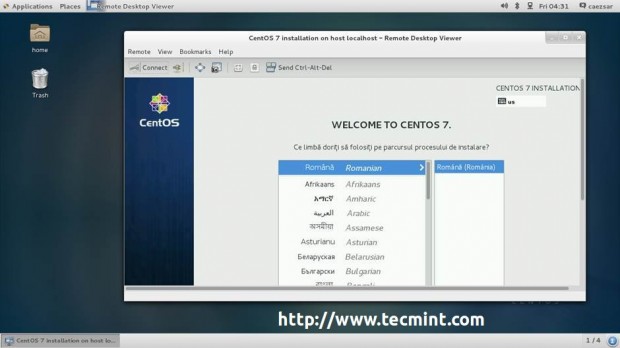
From here, you can continue with the installation process in the same manner as you would do it from a directly connected monitor, using the same procedure as described RHEL/CentOS 7.0 Installation Guide links provide above.
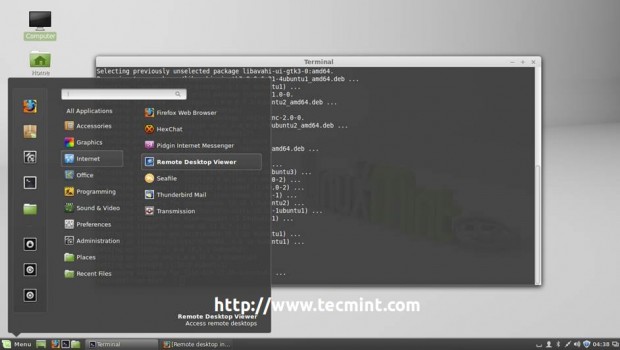
5. For Debian based distributions (Ubuntu, Linux Mint, etc) install Vinagre package for GNOME desktop environment and use the same procedure as explained above.
$ sudo apt-get install vinagre
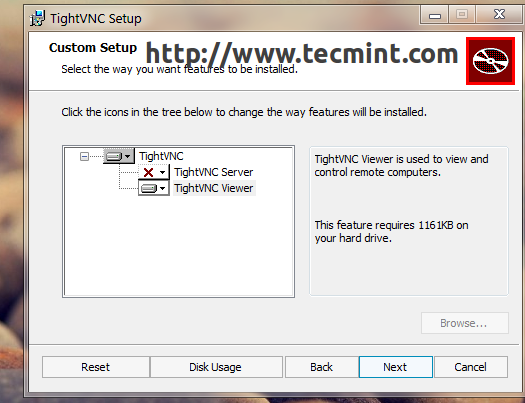
6. For Windows based systems install the TightVNC Viewer program by downloading it using the following link.
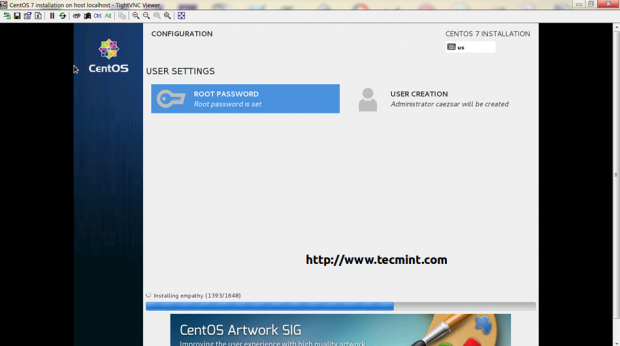
7. If you want to see details about your disk partition layout which now uses GPT on a disk smaller than 2TB, go to Installation Destination, select your disk and the partition table should be visible and a new biosboot partition should be automatically created.
If you opted for Automatically create partitions, in the contrary case you should create one as Standard Partition with Bios Boot as a File System and 1 MB in size on non-UEFI systems.
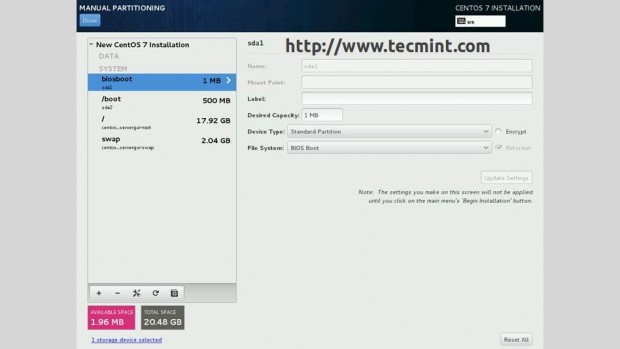
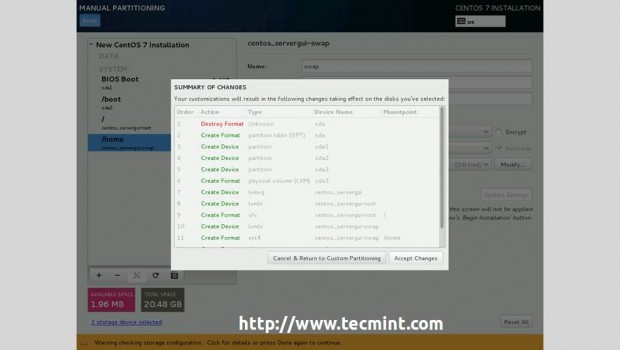
As a last note, if you are planning to use MBR Partition Layout on a disk smaller than 2TB on UEFI based systems, you must initially reformat your hard-disk, and, then create a Standard Partition with EFI System Partition (efi) as File System with a minimal value of 200 MB in size, regardless of your partitioning scheme.






This article assumes you run DHCP.
I see an additional line stating “Attempting to start vncconfig”.
Trying to access via VNC fails. Any ideas?
Try to setup a password for vnc server. It could also mean there’s a problem with your machine NIC!
Unfortunately this does not work for me. I get as far as “Please manually connect your vnc client to [2a00:1f400…]” but when I put in the address in my VNC client, it says “The connection was refused by the host computer”. I can ping the address from my computer.
were you able to solve it?
No …this procedure doesn’t apply for CentOS 6.5.
hey is it same procedure for Centos 6.5