For someone new to Linux, using it can still feel challenging, even with user-friendly distributions like Ubuntu and Mint.
While these distributions simplify many tasks, some manual configuration is often required, but fully harnessing the power of Linux, understanding basic commands is essential.
In Linux, commands are the primary way to interact with the system and allow users to perform tasks, configure settings, and manage the system efficiently.
This guide introduces 60 essential Linux commands, providing a foundation for beginners and a pathway to becoming a skilled system administrator. These commands cover a wide range of functions, from navigating directories and managing files to performing advanced system operations.
Whether you’re just starting out or aiming to deepen your expertise, these commands will help you unlock the full potential of Linux.
Basic Linux Commands and Examples for Newbies
Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, mastering basic Linux commands is essential for navigating and controlling the operating system.
Below are some commonly used Linux commands along with their descriptions and examples:
1. View the Contents of a Directory
The ls command is used to view the files and directories within a specified directory, it can display both visible and hidden files (files starting with . are hidden by default).
Additional options can provide detailed information like file permissions, ownership, size, and modification dates.
ls -la
2. Viewing Blocks, HDD Partition, External HDD
The lsblk command displays information about block devices such as hard drives, partitions, and external drives in a tree-like format.
lsblk
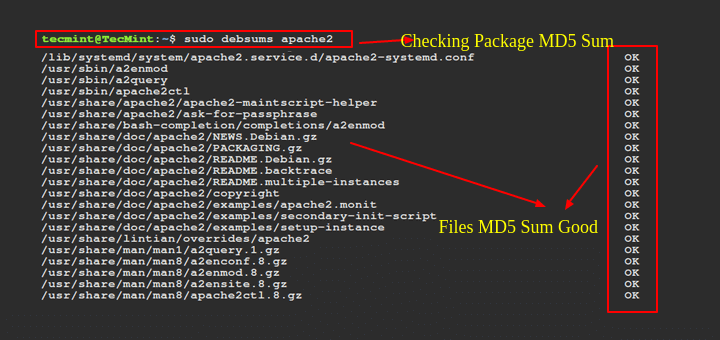
3. Checking the Integrity of Downloaded/Transferred Packages
The sha256sum or md5sum commands generate and verify cryptographic hash values for files, which ensures the file’s integrity after downloading or transferring.
sha256sum file.tar.gz
4. Converting and Copying a File
The dd command is used for low-level file copying and conversion, which is often employed to create bootable USB drives or clone disk images.
dd if=input.img of=output.img bs=4M status=progress
5. Know Your Machine Name, OS, and Kernel
The uname command provides system information, including the kernel version, system architecture, and hostname.
uname -a
6. Viewing History of Commands
The history command lists previously executed commands, allowing you to recall or reuse them.
history
7. Run Commands as Root User
The sudo command allows users to execute commands with administrative privileges. Use sudo -i to switch to a root shell.
sudo -i
8. Make a New Directory
The mkdir command creates a new directory with the specified name in the current location.
mkdir my_folder
9. Create or Update File Timestamps
The touch command creates empty files or updates the timestamp of existing ones.
touch my_file.txt
10. Changing the File Permission
The chmod command changes file permissions, controlling who can read, write, or execute a file.
chmod 644 my_file.txt
11. Change File Ownership
The chown command changes file ownership and group ownership.
sudo chown user:group my_file.txt
12. Install, Update, and Maintain Packages
The apt command manages software packages on Debian-based systems.
sudo apt update && sudo apt install package_name
13. Uncompressing a Tar File
The tar command extracts compressed files.
tar -xvzf file.tar.gz
14. See Current Date, Time, and Calendar
The date and cal commands display the current date, time, and calendar.
date cal
15. Print Contents of a File
The cat command prints the contents of a file to the terminal.
cat my_file.txt
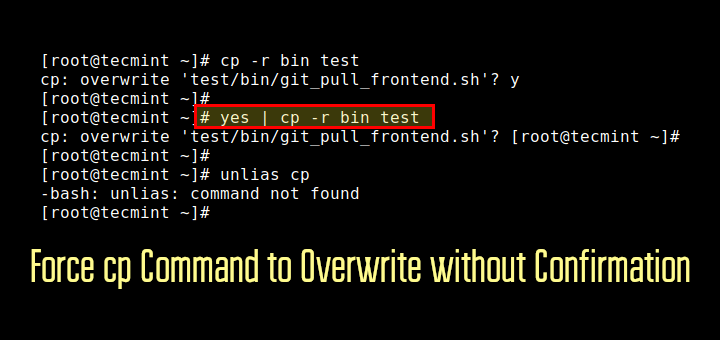
16. Copy and Move Files
The cp and mv commands copy and move files, respectively.
cp source.txt destination.txt mv old_name.txt new_name.txt
17. See the Working Directory for Easy Navigation
The pwd command prints the current directory path.
pwd
18. Change the Working Directory
The cd command navigates between directories.
cd /path/to/directory
Advanced Linux Commands for Intermediate Users
Once you’ve mastered the basic Linux commands, it’s time to dive deeper into more advanced commands that will help you manage and optimize your system more efficiently.
19. Finding a File in a Given Directory
The find command is used to search for files and directories within a specified directory or across the entire file system.
find /path/to/directory -name "filename"
20. Searching a File with the Given Keywords
The grep command is used to search for specific patterns (keywords) within files, which is highly useful when you want to find specific information inside a file or a set of files.
grep "keyword" filename
21. Finding Online Documentation
The man command displays the manual or help documentation for a specific command, which provides detailed information about how to use a command, its options, and its syntax.
man ls
22. List Current Running Processes
The ps command shows a snapshot of the current processes running on your system with details like process IDs (PIDs), memory usage, and CPU usage.
ps aux
To list all processes related to Firefox, using grep to filter the output.
ps aux | grep firefox
23. Kill a Running Process
The kill command is used to terminate a running process by specifying the process ID (PID) of the process you want to terminate.
kill 1234
24. See the Location of Installed Binaries
The which command helps locate the path of executables in your system’s PATH by searching through the directories listed in the PATH environment variable and returns the location of the executable.
which python3
25. Starting, Ending, Restarting a Service
The systemctl command is used to manage system services (also known as daemons) on systems using systemd.
systemctl start service_name systemctl stop service_name systemctl restart service_name
26. Creating and Removing Command Aliases
Aliases are shortcuts for commands, which can save time by reducing the amount of typing and the alias command creates a shortcut, while unalias remove it.
alias shortcut_name='command' unalias shortcut_name
You can create an alias for a command with a custom name.
alias ll='ls -l' unalias ll
This creates an alias ll for the ls -l command, which lists directory contents in a long format.
27. View Disk and Space Usage
The df command shows disk space usage for all mounted file systems by providing information about the total space, used space, and available space.
df -h
28. Removing a File and/or Directory
The rm command is used to remove files and directories. You can use the -r option to remove directories and their contents recursively.
rm filename rm -r directory_name
29. Print/Echo a Custom Output on Standard Output
The echo command is used to print text or the value of a variable to the terminal.
echo "Custom Message"
30. Changing Password in Linux
The passwd command is used to change passwords for the current user or other users (if you are the root user).
passwd username
31. View Printing Queue
The lpq command shows the status of the printing queue, including any pending or completed print jobs.
lpq
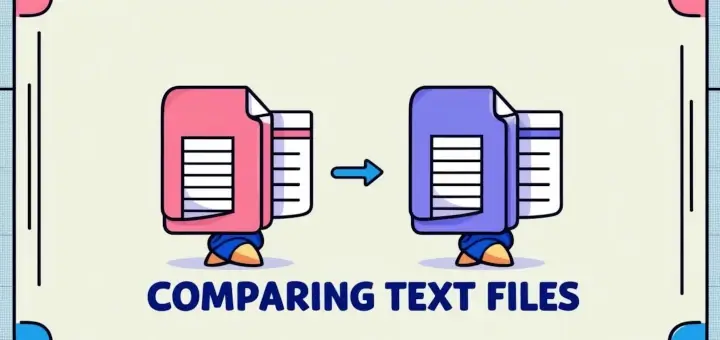
32. Compare Two Files
The diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences between them.
diff file1 file2
33. Download a File, the Linux Way (wget)
The wget command is used to download files from the internet, it supports HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols.
wget https://example.com/file.zip
34. Mount a Block/Partition/External HDD
The mount command is used to attach a block device (e.g., a hard drive or USB drive) to a directory in the filesystem.
mount /dev/sdX /mnt
35. Compile and Run C, C++, and Java Code
To compile and run code in C, C++, and Java, you use the respective compilers and runtimes.
- C:
gccis used to compile C programs.c. - C++:
g++is used to compile C++ programs. - Java:
javacis used to compile Java programs, and java is used to run them.
To compile and run C code:
gcc -o outputfile sourcefile.c ./outputfile
To compile and run C++ code:
g++ -o outputfile sourcefile.cpp ./outputfile
To compile and run Java code:
javac filename.java java filename
Advance Linux Commands for Linux Sysadmins
In the last section of this series, we tried to cover the commands that needed to administer a Linux server.
36. Configuring Network Interface
The ifconfig command is used to allow you to set up, manage, and display network interface parameters, which is typically used to assign IP addresses, configure network interfaces, and troubleshoot network issues.
sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
This command assigns the IP address 192.168.1.100 to the eth0 interface and brings it up.
37. Viewing Custom Network-Related Information
The netstat command provides detailed information about network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, and more.
netstat -tuln
38. Fetching Data with curl
The curl command is used to transfer data from or to a server. It supports various protocols, including HTTP, FTP, and more. You can use it to fetch data from a web server or test server responses.
curl -I https://www.example.com
39. Checking DNS Information
The dig command is a DNS lookup utility that provides detailed information about DNS records, which is commonly used for troubleshooting DNS issues.
dig example.com
40. Knowing Your System Uptime
The uptime command shows how long the system has been running, the number of users logged in, and the system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes.
uptime
41. Broadcast Messages to Logged-in Users
The wall command is used to send messages to all users currently logged into the system.
echo "System Maintenance in 10 minutes" | wall
42. Send Text Messages Directly to a User
The write command allows you to send a message to another logged-in user.
write username
43. Piping Commands Together
You can combine multiple commands using pipes (|) to pass the output of one command to another.
ps aux | grep firefox
44. Seeing the Processes of a CPU
The top command displays a dynamic, real-time view of system processes, including CPU and memory usage.
top
45. Creating a Newly Formatted ext4 Partition
The mkfs.ext4 command is used to create an ext4 file system on a partition.
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
46. Editing Files with vi, emacs, and nano
In Linux, there are several text editors available for editing files directly from the command line. Among the most popular are vi, emacs, and nano.
To edit files with vi:
vi filename.txt
To edit files with emacs:
emacs myfile.txt
To edit files with nano:
nano myfile.txt
47. Copying a Large File/Folder with Progress Bar
The rsync command is used to copy files and directories. With the --progress option, it shows a progress bar.
rsync -avh --progress source_directory/ destination_directory/
48. Check Available Memory
The free command shows the amount of free and used memory in the system.
free -h
49. Backing Up a MySQL Database
The mysqldump command is used to create backups of MySQL databases.
mysqldump -u root -p database_name > backup.sql
50. Generate a Random Password
The openssl command can generate a random password.
openssl rand -base64 12
51. Merge Two Text Files
The cat command can be used to concatenate two text files into one.
cat file1.txt file2.txt > mergedfile.txt
52. List of All the Opened Files
The lsof command lists all open files and the processes that opened them.
lsof
These commands are fundamental tools for system administrators and users to interact with Linux systems efficiently.




Team,
Tecmint is the first link that comes to my mind when I want to refer to anything in Linux, so here I am to ask for help for the best recommendation for setting up user home directories which should be accessible from windows and Linux using Active directory accounts.
More information :
OS: RHEL 7.9
System added to the domain using one identity tool.
where are links to articles, please share
@Sudheer,
Links are already added in the article, please have a close look…
Thanks very much for putting all Linux commands one place for easy learning..
Tecmint is always good for the quality of Information and knowledge sharing on Linux.
@Anil,
Thanks for such kinds words about Tecmint, keep visiting for such quality articles on Linux.
Thank you very much.
The way you have planed your articles is very useful, as you added the screenshots for us to see exactly what is the output of each command typed.
thanks for this guide it has helped me alot
“A Guide from Newbies to System Administrator” should be changed to “A Guide for Newbies from System Administrator” or “A Guide from System Administrator to Newbies”
Content is good :) Thanks.
Very useful guide for beginners.
so how to to resize /Home partation because i give the 235G space in /Home and it was bymistake…..i want my /Home use only 50G and rest of space i want free because of there is no uses to give big amount of space in /Home……so please tell me what to do???
@Khushal,
I already given the link with solution, just go through it..
thanks for wonderful combination of basics commands but i have a one question can you just tell me….in my asterisk server / space is 50G only and /home is 235G so how to transfer /home space to /
reply soon I am waiting
@Khushal,
The best option is to resize your / partition, same question asked by one our reader at our LinuxSay Forum at:
http://linuxsay.com/t/how-to-resize-the-partition-in-ext4-filesystem/1489/12
Try to follow those steps to resize your partition..
sir this not answer of my question….im just asking how to tranfer space /Home to / root disk
@Khushal,
You can’t simply move space from one partition to another, the only way is to resize the partition or use mhddfs tool
Hi,
Thank you so much for this nice article .Very helpful to work on Linux …
Very nice articles, post and even whole web-site. I never seen any website that provide so much information on LINUX. This is BEST. Thank you TECMINT.COM. You guys are on the right way. You guys are helping so many people in the industry.
Keep Posting..Always love to read n follow new posts of TECMINT.com
Happy to know @ Pratik, that my writing helped you. Keep Connected!
Hi Avishek,
This is a really useful article on Linux.
Thank you very much for creating this.
Hope you will provide an article on more advanced Linux commands.
Welcome Vajira, Keep Connected!
tq for a good article! really helpful for me as a beginner in Linux community
Welcome @ halcyon, keep connected for more such post.
Are there specific abbreviations to enter for the codes or should I go to shell and just type what was given and it will show me. I know cd is for change directory. I am trying to study and practice the most common used ones. I know by repetition it will become easier.
@Barbara,
No abbreviations, just open shell and copy/paste the commands from the article and see the results, nothing extra hard work..:)
Brother, it is useful but also something like unsatisfaction i was com to check some commands. kindly send me the just some useful commands
Dear @ Afzal
These are the basic and most useful commands. You may follow the associated link to get more descriptive article. If you finds any missing command we haven’t covered, Poke us.
Keep Connected, Enjoy!
Hello,
Avishek Kumar first of all many many thanks to you,with outer help i can not climb on first step of linux world and i am working on Linux & Cloud.
I always follow your post and Every post in Tecmint that keeps me always update my knowledge.
Thanks a lot
Welcome @ Meraj Hussain.
Keep connected for more such helpful writing.
Your’s comment acknowledged, we are doing fine. Thanks!
Thanks for this Article
Welcome @ Vinoth
Superb tutorial sir
very nice add some more commands n linux tutorial in this site plzzz sir n ha thanx for sharing with us :)
Welcome @ Joshi,
keep connected!
Thank you.
Welcome @ Khoi D. DInh
Hi Avishek,
Its really helped me understand in detail!! Looking forward for more posts.
Thanks
Wonderful to know this @ Kavitha.
Keep connected! Kudos
Dear Avishek,
Its very usefull.
Great work…
Regards,
Veeru.
Thanks @ veerendra for the wonderful feedback!
Dear Avishek and Ravi,
I googled and found tecmint a better source of learning Linux Administration. Please do keep it up to mark and give some detailed information to troubleshoot networks and IP address schema.
Regards,
Aali
Dear Milan,
Thanks for your appreciation.
we are working in all the possible way, to benefit our regular readers.
Keep connected to Tecmint.com.
Thanks for this useful article !!
Awesome work !!!
Small suggestion- Pls ellaborate with mostly used arguements
Dear Hars,
Thanks for your wonderful words.
we welcome your suggestion and will shortly start working on it.
Very helpfull post.
Well the content is for only L1 and L2 level? or it includes L3 As well.
Dear Nasir,
Good to know, it was helpful for you.
There is nothing called L1 and L2.
Its all about increasing your knowledge base, in the right way and feedback of such kind tells the whole story.
these commands r useful 4 me tkx a lot
Welcome @ Vasant Singh
Yes, this information is very helpful. I am an intermediate user of linux, and have used it for almost a year now. I spend around 20% of my time in terminal. Some of these commands, I have never heard of! Thanks very much :-)
Thanks @ cody, for the above nice words
My issue in vacation setup I have postfix with postfix mailadmin setup mails r working fine issue with vacation setup
@ Bharath You have problem in vacation setup is an issue. but Until and Unless you dont provide us the complete details of what is going on, we cant Help you.
hi,
i am going to attend the interview based on Linux position. so they expect basics of Linux from me.i need to prepare Linux from the basic,so sent the suitable link for me
Regards,
tamil
Dear tamil,
we post each of our article, from Knowledge point of view. You can subscribe us and go through each of our post, as well as previous post, to have a lot of Linux/FOSS related knowledge.
This is very very good. Keep on a good work. I follow them all.
THanks @ Marwin :)
It helps a lot on my side!
Happy to know that it was helpful, thanks @ Agatha
Hi,
This is Ziaul Mustafa and i would like to know about linux basic commnads.
so kindly please any link to above my mail id from there i can find easy way to
solve my issue.
Regards,
Ziaul Mustafa
Dear Ziaul Mustafa,
it would be painful for us to send everyone the links and contents.
Please stay connected to us and go through our posts and articles for better and deep understanding of knowledge. If you find any topic not covered by us, please make us know, so that we can help you.
Hope You Understand.
thanks for guidance, this helps alot
Welcome @ John Hunnefield