psacct or acct both are open source utilities for monitoring users’ activities on the Linux system. These utilities run in the background and keep track of each user’s activity on your system as well as what resources are being consumed.
I personally used these tools in our company, we have a development team where our developers continuously work on servers. So, these are the best utilities to keep an eye on them.
These programs provide an excellent way to monitor what users are doing, what commands are they executing, how many resources are being consumed by them, and how long users are active on the system. Another useful feature is, that it gives total resources consumed by services like Apache, MySQL, FTP, SSH, etc.
[ You might also like: How to Monitor Linux Commands Executed by System Users in Real-time ]
I think this is one of the great and most needed utilities for every Linux/Unix System Administrator, who wanted to keep a track of user activities on their servers/systems.
The psacct or acct package provides several features for monitoring process activities.
- ac command prints the statistics of user logins/logouts (connect time) in hours.
- lastcomm command prints the information of previously executed commands of the user.
- accton commands is used to turn on/off process for accounting.
- sa command summarizes information of previously executed commands.
- last and lastb commands show a listing of last logged-in users.
Installing psacct or acct Packages in Linux
psacct and acct both are similar packages and there is not much difference between them, but the psacct package is only available for rpm-based distributions such as RHEL, CentOS, and Fedora, whereas the acct package is available for distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint.
To install the psacct package under rpm-based distributions issue the following yum command.
# yum install psacct
To install the acct package using the apt command under Ubuntu / Debian / Linux Mint.
$ sudo apt install acct
On other Linux distributions, you can install it as shown.
$ sudo apk add psacct [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S acct [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install acct [On OpenSUSE]
Starting psacct or acct service
By default, the psacct service is in disabled mode and you need to start it manually under RHEL-based distributions. Use the following command to check the status of the service.
$ sudo systemctl status psacct
You see the status showing as disabled, so let’s start it manually using the following commands, which will create a /var/account/pacct file.
$ sudo systemctl start psacct $ sudo systemctl enable psacct $ sudo systemctl status psacct
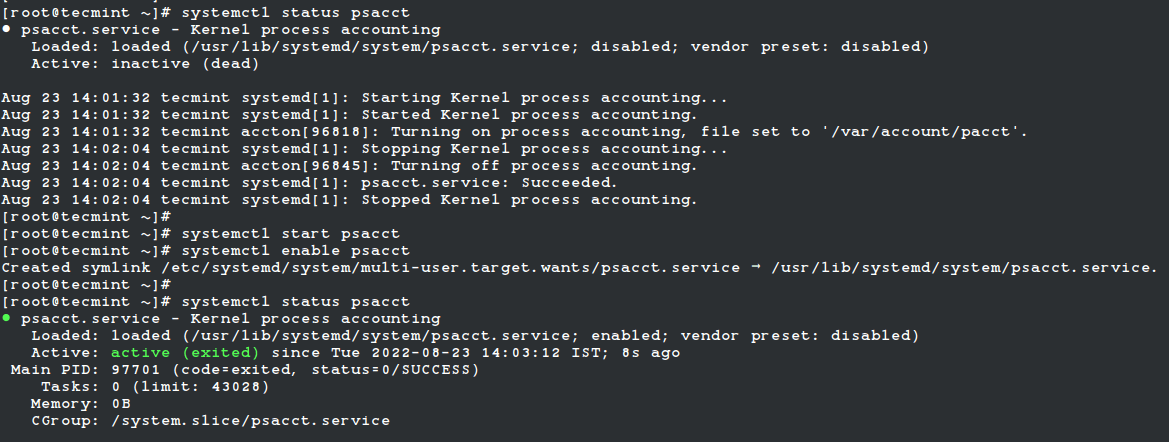
Under Ubuntu, Debian, and Mint service is started automatically, you don’t need to start it again.
Display Statistics of Users Connect Time
ac command without specifying any argument will display total statistics of connect time in hours based on the user logins/logouts from the current wtmp file.
# ac total 11299.15

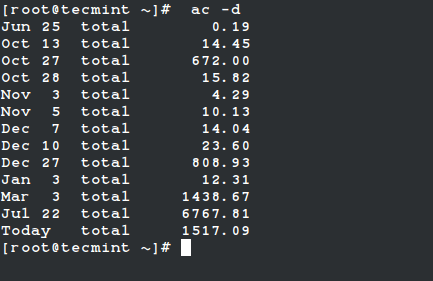
Display Statistics of Linux Users Day-wise
Using the command “ac -d” will print out the total login time in hours by day-wise.
# ac -d Jun 25 total 0.19 Oct 13 total 14.45 Oct 27 total 672.00 Oct 28 total 15.82 Nov 3 total 4.29 Nov 5 total 10.13 Dec 7 total 14.04 Dec 10 total 23.60 Dec 27 total 808.93 Jan 3 total 12.31 Mar 3 total 1438.67 Jul 22 total 6767.81 Today total 1517.09
Display Total Login Time of All Linux Users
Using the command “ac -p” will print the total login time of each Linux user in hours.
# ac -p rockylinux 425.61 tecmint 702.29 root 10171.54 total 11299.44

Display Linux User Login Time
To get the total login statistics time of user “tecmint” in hours, use the command as.
# ac tecmint
total 702.29
Display Day-Wise Login Time of User
The following command will print the day-wise total login time of user “tecmint” in hours.
# ac -d tecmint
Oct 11 total 8.01 Oct 12 total 24.00 Oct 15 total 70.50 Oct 16 total 23.57 Oct 17 total 24.00 Oct 18 total 18.70 Nov 20 total 0.18
Print All Linux Commands Executed by Users
The “sa” command is used to print the summary of commands that were executed by users.
# sa
2 9.86re 0.00cp 2466k sshd*
8 1.05re 0.00cp 1064k man
2 10.08re 0.00cp 2562k sshd
12 0.00re 0.00cp 1298k psacct
2 0.00re 0.00cp 1575k troff
14 0.00re 0.00cp 503k ac
10 0.00re 0.00cp 1264k psacct*
10 0.00re 0.00cp 466k consoletype
9 0.00re 0.00cp 509k sa
8 0.02re 0.00cp 769k udisks-helper-a
6 0.00re 0.00cp 1057k touch
6 0.00re 0.00cp 592k gzip
6 0.00re 0.00cp 465k accton
4 1.05re 0.00cp 1264k sh*
4 0.00re 0.00cp 1264k nroff*
2 1.05re 0.00cp 1264k sh
2 1.05re 0.00cp 1120k less
2 0.00re 0.00cp 1346k groff
2 0.00re 0.00cp 1383k grotty
2 0.00re 0.00cp 1053k mktemp
2 0.00re 0.00cp 1030k iconv
2 0.00re 0.00cp 1023k rm
2 0.00re 0.00cp 1020k cat
2 0.00re 0.00cp 1018k locale
2 0.00re 0.00cp 802k gtbl
Explanation of the above command output:
- 9.86re is a “real-time” as per wall clock minutes
- 0.01cp is a sum of system/user time in cpu minutes
- 2466k is a cpu-time averaged core usage, i.e. 1k units
- sshd command name
Print Linux User Information
To get the information of an individual user, use the options -u.
# sa -u
root 0.00 cpu 465k mem accton root 0.00 cpu 1057k mem touch root 0.00 cpu 1298k mem psacct root 0.00 cpu 466k mem consoletype root 0.00 cpu 1264k mem psacct * root 0.00 cpu 1298k mem psacct root 0.00 cpu 466k mem consoletype root 0.00 cpu 1264k mem psacct * root 0.00 cpu 1298k mem psacct root 0.00 cpu 466k mem consoletype root 0.00 cpu 1264k mem psacct * root 0.00 cpu 465k mem accton root 0.00 cpu 1057k mem touch
Print Number of Linux Processes
This command prints the total number of processes and CPU minutes. If you see a continued increase in these numbers, then it’s time to look into the system about what is happening.
# sa -m
sshd 2 9.86re 0.00cp 2466k root 127 14.29re 0.00cp 909k
Print and Sort Usage by Percentage
The command “sa -c” displays the highest percentage of users.
# sa -c
132 100.00% 24.16re 100.00% 0.01cp 100.00% 923k
2 1.52% 9.86re 40.83% 0.00cp 53.33% 2466k sshd*
8 6.06% 1.05re 4.34% 0.00cp 20.00% 1064k man
2 1.52% 10.08re 41.73% 0.00cp 13.33% 2562k sshd
12 9.09% 0.00re 0.01% 0.00cp 6.67% 1298k psacct
2 1.52% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 6.67% 1575k troff
18 13.64% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 509k sa
14 10.61% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 503k ac
10 7.58% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 1264k psacct*
10 7.58% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 466k consoletype
8 6.06% 0.02re 0.07% 0.00cp 0.00% 769k udisks-helper-a
6 4.55% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 1057k touch
6 4.55% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 592k gzip
6 4.55% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 465k accton
4 3.03% 1.05re 4.34% 0.00cp 0.00% 1264k sh*
4 3.03% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 1264k nroff*
2 1.52% 1.05re 4.34% 0.00cp 0.00% 1264k sh
2 1.52% 1.05re 4.34% 0.00cp 0.00% 1120k less
2 1.52% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 1346k groff
2 1.52% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 1383k grotty
2 1.52% 0.00re 0.00% 0.00cp 0.00% 1053k mktemp
List Last Executed Commands of User
The ‘latcomm‘ command is used to search and display previously executed user command information. You can also search commands of individual usernames. For example, we see commands of the user (tecmint).
# lastcomm tecmint
su tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 ls tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 ls tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 ls tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 bash F tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 id tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 grep tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 grep tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 bash F tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 dircolors tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 bash F tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 tput tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 tty tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 bash F tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 id tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 bash F tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 id tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56
Search Logs for Commands
With the help of the lastcomm command, you will be able to view the individual use of each command.
# lastcomm ls
ls tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 ls tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56 ls tecmint pts/0 0.00 secs Wed Feb 13 15:56
For more information and usage, check out the manual pages of these tools.





I am very new to linux administration.
To audit user activity, I installed and used psacct with the following command:
but I do not get any mention for the command “history” that I ran to test. Is there something I am doing wrong?
Hi,
When I executed lastcomm sdiff command, I could output is popping multiple times instead of a single display, please help me on this?
Hello Ravi,
In our server all users get login in root through SSH. So how I can identify which commands are executed by particular user?
By using “last -F” I got login details in IPADDR & by using “lastcomm” I am getting all executed commands, but still not getting users own history. Please suggest to monitors specific users history in this scenario.
@Sush,
You can find all users commands history under /home/user_name/.bash_history file, you can use find or grep command to list the history of all users..
Hello Ravi,
Thanks for your reply. but here we have only 2 users first login into admin after switch user to root. All our operations team members are working in root administrator account. So in that case I want to found in root only which member have executed the commands in root bash_history.
Hi,
I think you didn’t got my question. Can I repeat?
Hello Ravi,
How to view process logs with it.
@Ravi
Use sa command to view process of user like this:
hello Ravi,
Please i will like to ask a question, the
sa -ucommand does not specify which date the result produced is meant for, is it daily or monthly?Helo ravi,
I installed ‘acct’ in my ubuntu 14.04 ssh server and i can run ‘ac’ command but for the ‘sa’ command gives me this error ” couldnt open file ‘/var/log/account/pacct’: permission denied” anytime i run it, how do i go about this please?
@Damilola,
Try to run it with sudo and see the output..
thank you very much, it worked.
Helo ravi,
the “ac” command only supply information on the present month, is it possible to get information from previous and what command can be used for that?
@Damilola,
Have you tried last and lastb commands to get the last login information?
Hi Ravi,
I intstalled acct in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS last May 19 2016, but when I used ‘ac -d myusername’ it only reflect yesterday and today time consume. Also when I use the ‘lastcomm myusername’ same result it reflect yesterday and today commands use.
Is there something going here? or may I missing something.
Your help is much appreciated.
Thank you!
@Jonathan,
Could you check the ‘history’ and ‘lastlog’ file under /etc directory, you will came to know why it showing results of last day and today..
Hi Ravi Saive, it’s there anyway that the root gives privilege to users to create their own password or to set up their own password so that the root user does not know like in windows. Thanks again for your post. Very good and God bless you.
@Martial,
Yes, you a root can force users to change or set their own password after first login, this can be done by using following command.
Where option “-d0” describes that the password was changed on 1st January 1970, which essentially expires the current password, and force users to change their passwords on the next login.
A very good website. I have been looking for a site like this for a while now to get hands on Linux and I must say this is the bet.
Thanks guys
@Peter,
Thanks for liking our website, we continue to provide such high quality articles for readers like you. Keep visiting
How to join your community…..what is the process of joing community…please tell me…
Thank you
@Atul,
Here is the article, that will help you out to join tecmint community..
https://www.tecmint.com/submit-articles/
thanks for such useful and Excellent article! Keep going :)
how can we know how many task’s(process) are hold by the swap when ram is full.
@prathesh,
Use top to analyze the process and their usage…..
Ravi, thanks for such useful and Excellent article! Keep going :)
thanks, i am using this tools these days , but i found that the information accounted by psacct will reset several days once. do you know how to change it because i want to monitor my computer for a long time. thanks again.
It is possible to give users full sudo access without allowing sudo su… That way all commands will be logged.
Cmnd_Alias SU = /bin/su root, /bin/su – root
Cmnd_Alias FORBIDDEN = /bin/bash, /bin/ksh, /bin/ksh93, /bin/sh, /bin/csh, /bin/tcsh, /bin/zsh, /usr/sbin/pwconv, /usr/sbin/visudo, /usr/bin/crontab
USERS ALL = (ALL) !FORBIDDEN, !SU, ALL
Its good article and very useful. But there are number of sysadmins handling lots of server.
We have done as below:-
1- Disabled first level root access.
2- created individual login for users with sudo access.
User has to login with his individual login ID and he can switch to root prompt through
# sudo su –
Now user becomes root and he has all privileges.
How we can monitor this?
While we can log all that command, which has been fired with sudo. But after the switching to root, not able to identify.
A sudo user can not switch to root. Is this possible??
That’s not possible, if a user knows the root password he will able to login and run commands. But if you would like to trace those commands with date and time of execution, you need to use history command.