8. Configure MySQL query_cache_size
If you have many repetitive queries and your data does not change often – use query cache. People often do not understand the concept behind the query_cache_size and set this value to gigabytes, which can actually cause degradation in the performance.
The reason behind that is the fact that threads need to lock the cache during updates. Usually value of 200-300 MB should be more than enough. If your website is relatively small, you can try giving the value of 64M and increase in time.
You will have to add the following settings in the MySQL configuration file:
query_cache_type = 1 query_cache_limit = 256K query_cache_min_res_unit = 2k query_cache_size = 80M
9. Configure tmp_table_size and max_heap_table_size
Both directives should have the same size and will help you prevent disk writes. The tmp_table_size is the maximum amount of size of internal in-memory tables. In case the limit in question is exceeded the table will be converted to on-disk MyISAM table.
This will affect the database performance. Administrators usually recommend giving 64M for both values for every GB of RAM on the server.
[mysqld] tmp_table_size= 64M max_heap_table_size= 64M
10. Enable MySQL Slow query Logs
Logging slow queries can help you determine issues with your database and help you debug them. This can be easily enabled by adding the following values in your MySQL configuration file:
slow-query-log = 1 slow-query-log-file = /var/lib/mysql/mysql-slow.log long_query_time = 1
The first directive enables the logging of slow queries, while the second one tells MySQL where to store the actual log file. Use long_query_time to define the amount of time that is considered long for MySQL query to be completed.
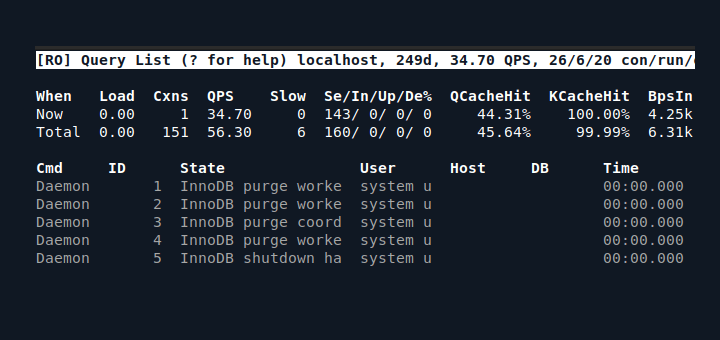
11. Check for MySQL idle Connections
Idle connections consume resources and should be interrupted or refreshed when possible. Such connections are in “sleep” state and usually stay that way for long period of time. To look for idled connections you can run the following command:
# mysqladmin processlist -u root -p | grep “Sleep”
This will show you list of processes that are in sleep state. The event appears when the code is using persistent connection to the database. When using PHP this event can appear when using mysql_pconnect which opens the connection, after that executes queries, removes the authentication and leaves the connection open. This will cause any per-thread buffers to be kept in memory until the thread dies.
The first thing you would do here is to check the code and fix it. If you don’t have access to the code that is being ran, you can change the wait_timeout directive. The default value is 28800 seconds, while you can safely decrease it to something like 60:
wait_timeout=60






Hello ,
I got a dedicated server with the following characteristics.
On Linux server with Centos7 installs and more detailed specifications below.
The problem with this is that I do not know the correct configuration for the error problem 504 Gateway Timeout Error, and I usually have this error on sites.
Someone guides me?
What are the best settings & config for “my.cnf” “nginx.cnf” “php.ini”? Guidance if possible?
thanks .
I have been learning more and more about tuning/hardening from your website when referencing Maria/DB. Thanks for the great presentations and the easy to copy one-liners for my SSH session. Cheers!
I really appreciate your explanation and problem solving methodologies. It’s Awesome article. Thank you very much for the time and effort.
Good job!
Does not work anymore: “Error: mysqlcheck doesn’t support multiple contradicting commands.”
You will have to execute the repair and optimize separately.
Really helpful
Formatted the fs as ext4 then write fstab using ext3. Makes no sense.
“2. Store MySQL Database Data on Separate Partition Note: This setup only works with MySQL, but not with MariaDB.”
Same question as “Asd”, why? Would have been better to include that in the article.
Also, rather than link, I just mounted the second drive at “/var/lib/mysql”.
15. Optimize and Repair is applicable only for tables of myisam storage engine i think so..
At RHEL based systems you should call fdisk with “-c” to disable dos compatible mode which results in proper alignment of your disks.
Nice article :)
This seems to be incorrect/typo. Section 14 has “The tool is called musqltunner”. Should be “mysqltuner”
@Nick,
Corrected that typo….
“2. Store MySQL Database Data on Separate Partition
Note: This setup only works with MySQL, but not with MariaDB.”
Why? And why in 2015 ext3? :)
Excellent, thank you I will review it thoroughly.