mysqladmin is a command-line database administration utility that comes with MySQL/MariaDB server, which is used by Database Administrators to perform some basic MySQL tasks such as setting the root password, changing the root password, monitoring mysql processes, reloading privileges, creating/dropping databases, checking server status, show usage statistic, kill running queries, etc.
The command to use mysqladmin and the general syntax is:
# mysqladmin [options] command [command-arg] [command [command-arg]] ...
If you don’t have MySQL/MariaDB server installed or you are using an older version of the MySQL server, then we recommend you to install or update the MySQL version using the following articles:
In this article, we’ve compiled some very useful ‘mysqladmin‘ commands that are used by system/database administrators in their day-to-day work. You must have MySQL/MariaDB server installed on your system to perform these tasks.
1. How to Set MySQL Root Password
If you have a fresh installation of MySQL/MariaDB server, then it doesn’t require any password to connect it as the root user. To set the MySQL password for the root user, use the following command.
# mysqladmin -u root password YOURNEWPASSWORD
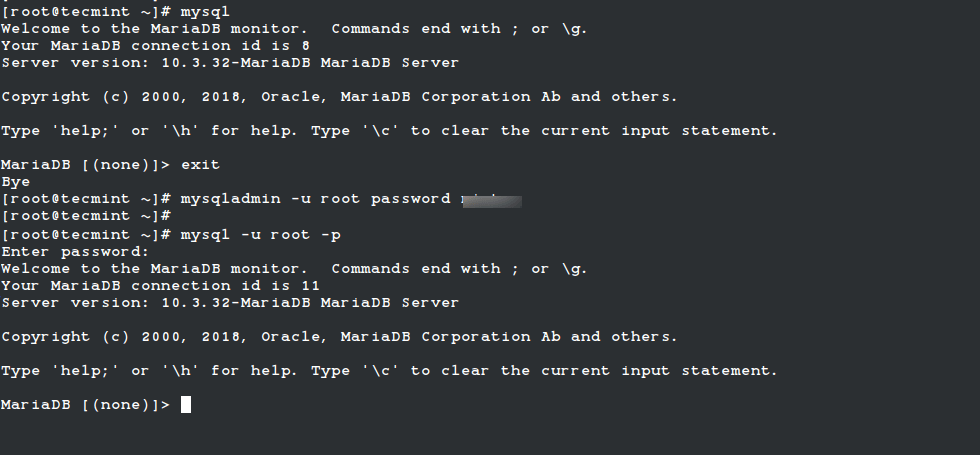
Warning: Setting a new MYSQL password using mysqladmin should be considered vulnerable. On some systems, your password becomes visible to system status programs such as the ps command that may be executed by other users to know the status of active processes on a system.
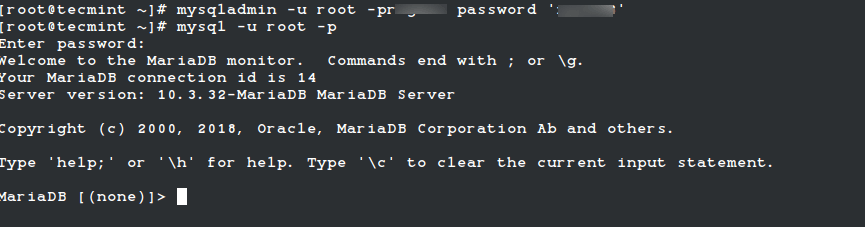
2. How to Change MySQL Root Password
If you would like to change or update the MySQL root password, then you need to type the following command. For example, say your old password is 123456 and you want to change it with a new password say xyz123.
# mysqladmin -u root -p123456 password 'xyz123'
3. How to Check Status of MySQL Server
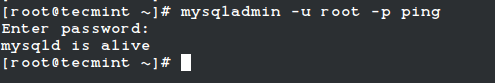
To find out whether the MySQL server is up and running, use the following command.
# mysqladmin -u root -p ping Enter password: mysqld is alive
4. How to Check Which MySQL Version I am Running
The following command shows the MySQL version along with the current running status.
# mysqladmin -u root -p version Enter password: mysqladmin Ver 9.1 Distrib 10.3.32-MariaDB, for Linux on x86_64 Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab, and others. Server version 10.3.32-MariaDB Protocol version 10 Connection Localhost via UNIX socket UNIX socket /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock Uptime: 18 min 6 sec Threads: 6 Questions: 20 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 18 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 11 Queries per second avg: 0.018
5. How to Find Out Current Status of MySQL Server
To find out the current status of the MySQL server, use the following command. The mysqladmin command shows the status of uptime with running threads and queries.
# mysqladmin -u root -p status Enter password: Uptime: 1185 Threads: 6 Questions: 21 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 18 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 11 Queries per second avg: 0.017
6. How to Check MySQL Status Variables and Their Values
To check all the running status of MySQL server variables and values, type the following command. The output would be similar to the one below.
# mysqladmin -u root -p extended-status Enter password: +--------------------------------------------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------------------------------------------+ | Aborted_clients | 0 | | Aborted_connects | 2 | | Access_denied_errors | 2 | | Acl_column_grants | 0 | | Acl_database_grants | 0 | | Acl_function_grants | 0 | | Acl_procedure_grants | 0 | | Acl_package_spec_grants | 0 | | Acl_package_body_grants | 0 | | Acl_proxy_users | 2 | | Acl_role_grants | 0 | | Acl_roles | 0 | | Acl_table_grants | 0 | | Acl_users | 4 | | Aria_pagecache_blocks_not_flushed | 0 | | Aria_pagecache_blocks_unused | 15706 | | Aria_pagecache_blocks_used | 0 | | Aria_pagecache_read_requests | 0 | | Aria_pagecache_reads | 0 | | Aria_pagecache_write_requests | 0 | ...
7. How to see all MySQL server Variables and Values?
To see all the running variables and values of the MySQL server, use the command as follows.
# mysqladmin -u root -p variables Enter password: +--------------------------------------------+-----------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------------------------+-----------------------------+ | auto_increment_increment | 1 | | auto_increment_offset | 1 | | autocommit | ON | | automatic_sp_privileges | ON | | back_log | 50 | | basedir | /usr | | big_tables | OFF | | binlog_cache_size | 32768 | | binlog_direct_non_transactional_updates | OFF | | binlog_format | STATEMENT | | binlog_stmt_cache_size | 32768 | | bulk_insert_buffer_size | 8388608 | | character_set_client | latin1 | | character_set_connection | latin1 | | character_set_database | latin1 | | character_set_filesystem | binary | | character_set_results | latin1 | | character_set_server | latin1 | | character_set_system | utf8 | | character_sets_dir | /usr/share/mysql/charsets/ | | collation_connection | latin1_swedish_ci | +---------------------------------------------------+----------------------+ ...
8. How to Check Active Threads of MySQL Server
The following command will display all the running processes of MySQL database queries.
# mysqladmin -u root -p processlist Enter password: +----+-------------+-----------+----+---------+------+--------------------------+------------------+----------+ | Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | Progress | +----+-------------+-----------+----+---------+------+--------------------------+------------------+----------+ | 2 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB purge coordinator | | 0.000 | | 1 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB purge worker | | 0.000 | | 4 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB purge worker | | 0.000 | | 3 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB purge worker | | 0.000 | | 5 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB shutdown handler | | 0.000 | | 20 | root | localhost | | Query | 0 | Init | show processlist | 0.000 | +----+-------------+-----------+----+---------+------+--------------------------+------------------+----------+
9. How to Create a Database in MySQL Server
To create a new database in the MySQL server, use the command shown below.
# mysqladmin -u root -p create tecmint Enter password: # mysql -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 22 Server version: 10.3.32-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab, and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | tecmint | +--------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.001 sec)
10. How to Drop a Database in MySQL Server
To drop a Database in the MySQL server, use the following command. You will be asked to confirm press ‘y‘.
# mysqladmin -u root -p drop tecmint Enter password: Dropping the database is potentially a very bad thing to do. Any data stored in the database will be destroyed. Do you really want to drop the 'tecmint' database [y/N] y Database "tecmint" dropped
11. How to Reload/Refresh MySQL Privileges?
The reload command tells the server to reload the grant tables and the refresh command flushes all tables and reopens the log files.
# mysqladmin -u root -p reload # mysqladmin -u root -p refresh
12. How to Shutdown MySQL Server Safely
To shutdown the MySQL server safely, type the following command.
mysqladmin -u root -p shutdown Enter password:
You can also use the following commands to start/stop the MySQL server.
# systemctl stop mysqld # systemctl start mysqld Or # systemctl stop mariadb # systemctl start mariadb
13. Some useful MySQL Flush Commands
Following are some useful flush commands with their description.
- flush-hosts: Flush all host information from the host cache.
- flush-tables: Flush all tables.
- flush-threads: Flush all threads cache.
- flush-logs: Flush all information logs.
- flush-privileges: Reload the grant tables (same as reload).
- flush-status: Clear status variables.
Let’s check out these commands.
# mysqladmin -u root -p flush-hosts # mysqladmin -u root -p flush-tables # mysqladmin -u root -p flush-threads # mysqladmin -u root -p flush-logs # mysqladmin -u root -p flush-privileges # mysqladmin -u root -p flush-status
14. How to kill Sleeping MySQL Client Process?
Use the following command to identify the sleeping MySQL client process.
# mysqladmin -u root -p processlist Enter password: +----+------+-----------+----+---------+------+-------+------------------+ | Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | +----+------+-----------+----+---------+------+-------+------------------+ | 5 | root | localhost | | Sleep | 14 | | | | 8 | root | localhost | | Query | 0 | | show processlist | +----+------+-----------+----+---------+------+-------+------------------+
Now, run the following command with kill and process ID as shown below.
# mysqladmin -u root -p kill 5 Enter password: +----+------+-----------+----+---------+------+-------+------------------+ | Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | +----+------+-----------+----+---------+------+-------+------------------+ | 12 | root | localhost | | Query | 0 | | show processlist | +----+------+-----------+----+---------+------+-------+------------------+
If you like to kill multiple processes, then pass the process ids with commas separated as shown below.
# mysqladmin -u root -p kill 5,10
15. How to Run Multiple mysqladmin Commands Together
If you would like to execute multiple ‘mysqladmin‘ commands together, then the command would be like this.
# mysqladmin -u root -p processlist status version Enter password: +----+-------------+-----------+----+---------+------+--------------------------+------------------+----------+ | Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | Progress | +----+-------------+-----------+----+---------+------+--------------------------+------------------+----------+ | 1 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB purge worker | | 0.000 | | 2 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB purge coordinator | | 0.000 | | 4 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB purge worker | | 0.000 | | 3 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB purge worker | | 0.000 | | 5 | system user | | | Daemon | | InnoDB shutdown handler | | 0.000 | | 9 | root | localhost | | Query | 0 | Init | show processlist | 0.000 | +----+-------------+-----------+----+---------+------+--------------------------+------------------+----------+ Uptime: 173 Threads: 6 Questions: 4 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 18 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 11 Queries per second avg: 0.023 mysqladmin Ver 9.1 Distrib 10.3.32-MariaDB, for Linux on x86_64 Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab, and others. Server version 10.3.32-MariaDB Protocol version 10 Connection Localhost via UNIX socket UNIX socket /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock Uptime: 2 min 53 sec Threads: 6 Questions: 4 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 18 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 11 Queries per second avg: 0.023
16. How to Connect Remote Mysql Server
To connect to the remote MySQL server, use the -h (host) with the IP Address of the remote machine.
# mysqladmin -h 172.16.25.126 -u root -p
17. How to Execute Command on Remote MySQL Server
Let’s say you would like to see the status of the remote MySQL server, then the command would be.
# mysqladmin -h 172.16.25.126 -u root -p status
18. How to Start/Stop MySQL Replication on a Slave Server
To start/stop MySQL replication on the slave server, use the following commands.
# mysqladmin -u root -p start-slave # mysqladmin -u root -p stop-slave
19. How to Store MySQL Server Debug Information to Logs
It tells the server to write debug information about locks in use, used memory, and query usage to the MySQL log file including information about the event scheduler.
# mysqladmin -u root -p debug Enter password:
20. How to View mysqladmin Options and Usage
To find out more options and usage of the myslqadmin command use the help command as shown below. It will display a list of available options.
# mysqladmin --help
We have tried our best to include almost all of the ‘mysqladmin‘ commands with their examples in this article, If still, we’ve missed anything, please do let us know via comments, and don’t forget to share with your friends.





Can you guide me on mysql certification
@Varun,
Check the this link for MySQL certification: https://www.mysql.com/certification/
Hi Ravi Saive,
Nice article, can you share the list of available free ” Open Source Platform called Linux” for hosting my J2EE web applications, am very much interested on it.
@Sairam,
Thanks for finding this article useful, but Linux is free and all softwares and OS’s are free to download and use..
Hello Mr. Ravi Saive..
Thanks for this useful article. very nice article..
Please keep posting..
@Divya,
Thanks for finding my article useful, keep connected to tecmint for such more articles..
Please, whoever edited this post didn’t understand how to use an apostrophe. Plurals do not use apostrophes.
Hi Friend,my name Arun Sharma working as IT support engineer in MNC company. I want to move now in Linux platform that certificate done by me in2009 with version 5. Could you please guide me for Linux interview and career in Linux what i need to done. Because of i am working as troubleshooter with all platform, but now move to only one Linux.
So please guide from where i will start for Linux admin and its interview
@Arun,
If you are keen into Linux platform for the job purpose, I suggest you to take RedHat Certification in RHEL 7 version, because this certification is specially designed for newbies who want to make mark in Linux world. We’ve written a preparation for the Red Hat certification here, you go through it https://www.tecmint.com/red-hat-rhcsa-rhce-exam-certification-book/
Great collections!
Great list. Thank you !
I got server from digital ocean and using Ubuntu 14. Mysql automatically stops. Till i restart my site showing database connectivity error. I can’t able to figure out the issue. Can you tell me ?
@Shankar,
Ubuntu is a buggy OS, never use Ubuntu.. go for CentOS with MySQL…
Thank you. From next time i will choose cent os.
very helpful…. thanx
Hi Its very useful for beginners like me… -:)
Thanks!
Really HelpFul!
Great going!
hi.
I am confused.
I wanted to show all the databases i’ve made excluding all those default mysql DBs (e.g information_schema, mysql etc.)
Please help.
SELECT table_schema, table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema NOT IN ( ‘information_schema’, ‘performance_schema’, ‘mysql’ );
http://dba.stackexchange.com/questions/93919/mysql-list-databases-with-tables/93928#93928
Hello Ravi Saive, you are doing a great job.
can you help me? I have centos running mysql server and playing a game that I wrote, but I change a table record in the database.
I stop the game and then restart the game and the change did nothing, but
If it restart my machine then the change takes place.
How can I not restart the machine and give a command in root to make the change take place.
If you have any questions please e-mail me.. thanks
Thank you,
Tom
Dear please help me to connect oracle database with MySQL database on Linux platform. I shall be very thankful to you
my official email address is “[email protected]”
Hi Ravi,
Thanks, Its really help full post….
Regards,
Surya
Hi Ravi,
How to identify a sleeping process/ connection?
Regards,
Nithya
SELECT * FROM information_schema.processlist WHERE Command = ‘Sleep’
Ravi,
Thanks for useful information.
I want to automatically re-start mysql service daily at specified time, pls suggest how to achieive it. Thanks..
Use a Cron to achieve such task, for example, to start mysql daily at around 9:30am put the following entry in your crontab file.
HI Ravi,
Can we get how many memory and cpu load taken each mysql process .
Regards,
Shufil
Use Mtop (MySQL Database Monitoring) Tool to monitor cpu and load of each mysql process.
Hi,
Can you please tell me how to unlock the tables in linux mysql and how to recover the mysql crashed tables
I am waiting for your reply sir,
How to change database name in mysql ubuntu ex: db1 to db2
First, dump the old database using ‘mysqldump’ command and then create a new database and then dump the old data into new database. For example, follow the commands.
Hi,
Can you please share the script for monitoring the CPU/Memory/IO usage for the MySQL Process alone in the Linux OS.
Thanks,
Mohanraj Jayaraman
Please use the search form at the right top corner to search for the MySQL monitoring articles.
Hi,
am learning MySQL DBA, am a beginner…..when am practicing i received below message…but the database exist there and i deleted it by using drop DDL command…!
Is there any other things to do after creating a database by using mysqladmin…please clarify me…!
Note: This is test machine, no root password assigned…!
mysql> show databases;
+——————–+
| Database |
+——————–+
| information_schema |
| bakshu |
| bumper |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+——————–+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> exit
Bye
[root@host-7-89 ~]# mysqladmin -u root drop bumber
Dropping the database is potentially a very bad thing to do.
Any data stored in the database will be destroyed.
Do you really want to drop the ‘bumber’ database [y/N] y
mysqladmin: DROP DATABASE bumber failed;
error: ‘Can’t drop database ‘bumber’; database doesn’t exist’
[root@host-7-89 ~]# mysql -u root
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 11
Server version: 5.5.14 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type ‘help;’ or ‘\h’ for help. Type ‘\c’ to clear the current input statement.
mysql> drop database bumper;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> show databases;
+——————–+
| Database |
+——————–+
| information_schema |
| bakshu |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+——————–+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Thanks a lot Dear Ravi Saive for your valuable “20 MySQL (Mysqladmin) Commands for Database Administration in Linux”.
As i’m new to mysql , helped me a lot for the basic understanding of mysql usage. Now got confidence Dear.
Hi Ravi,
Thanks for this article.
Could you please share some knowledge on MySQL replication.
Already covered that MySQL replication, use our search form to look for articles.
Hi Sir,
Very very thanks… Great
Thanks a lot Mr. Ravi Saive, very informative and in simple understandable language. Must say apart from good tech knowledge you also have great writing skills. keep it up
Fantastic work
hI..,
Realy its very useful and simply path queries to creating the commands..
Let me show you another list of useful admin commands;
http://zaboilab.com/mysql-tool-box/queries-to-see-rapidly-what-your-mysql-is-doing-now
Here you can find something to check performance events too.
HI ,
I am beginner to mysql database administration .these commands are really help full for me .
can any body tell me how to create a replica of the database in the mysql.
Thanks in Advance.
You can easily create and replicate your MySQL databases using MySQL-Slave replication guide.
Thanks for another informative website. The place else could I am getting that type of info written in such a perfect means? I have a challenge that I’m simply now working on, and I’ve been on the glance out for such information.
Great collection of MySQL commands, thanks for sharing.
Useful commands for every admin !
Hi there,
Nice post, I guess it will be a good start point to beginner on MySQL admin.
keep writing.
the list duplicates no. 4
@Tierno,
No, there is no duplicate. I have checked.
Small typo at #18
# mysqladmin -u root -p start-slve
should be
# mysqladmin -u root -p start-slave
@Alex,
Corrected now.. thanks..