Abbreviated as nmcli, the network manager command-line interface is a nifty and easy to use tool that saves you lots of time when you need to configure an IP address.
Read Also: How to Configure IP Network with ‘nmtui’ Graphical Tool
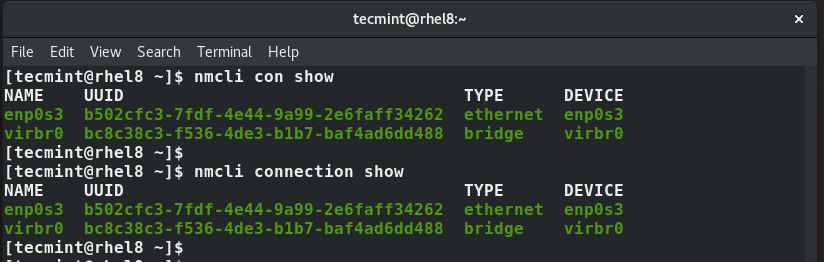
To display all the active network interfaces on your Linux system execute the command.
$ nmcli connection show OR $ nmcli con show
Note that con is the truncated form of connection and you will still end up with the same result as shown.
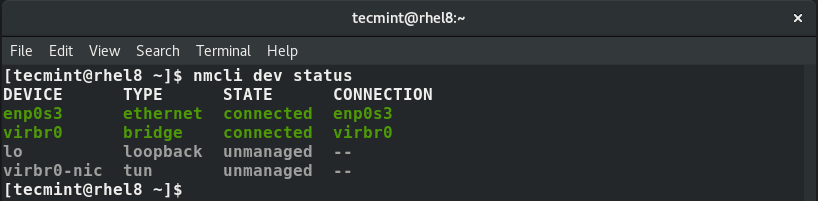
Also, you can run the command below to display both active and inactive interfaces.
$ nmcli dev status
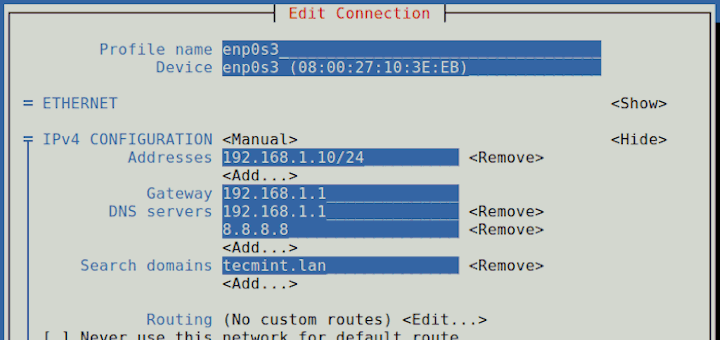
Set Static IP Address Using nmcli Tool
Using nmcli tool, you can modify a network interface to use a static IP address. In this example, we will modify the network interface enps03 to use a static IP.
But first, let’s check the IP address using IP command.
$ ip addr
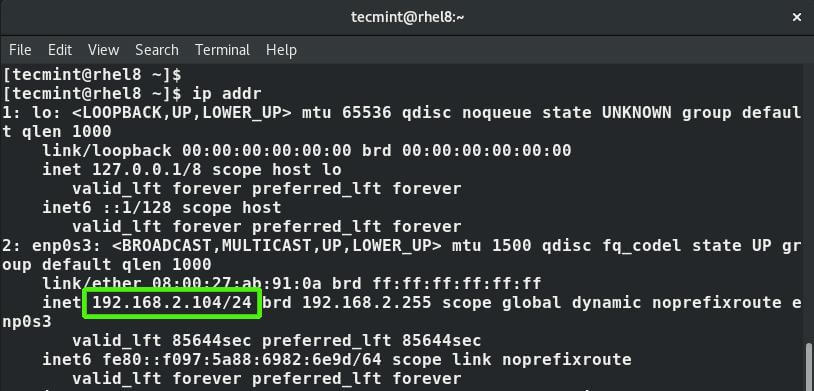
The current IP address is 192.168.2.104 with a CIDR of /24. We are going to configure a static IP with the following values:
IP address: 192.168.2.20/24 Default gateway: 192.168.2.1 Preferred DNS: 8.8.8.8 IP addressing static
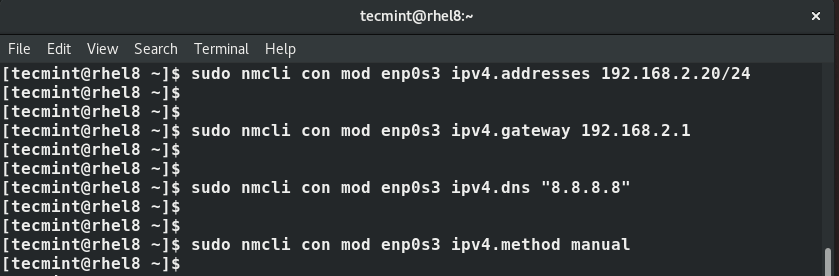
First, run the command below to set up the IP address.
$ nmcli con mod enps03 ipv4.addresses 192.168.2.20/24
Next, configure the default gateway as shown:
$ nmcli con mod enps03 ipv4.gateway 192.168.2.1
Then set up the DNS server:
$ nmcli con mod enps03 ipv4.dns “8.8.8.8”
Next , change the addressing from DHCP to static.
$ nmcli con mod enps03 ipv4.method manual
To save the changes, run the command
$ nmcli con up enps03
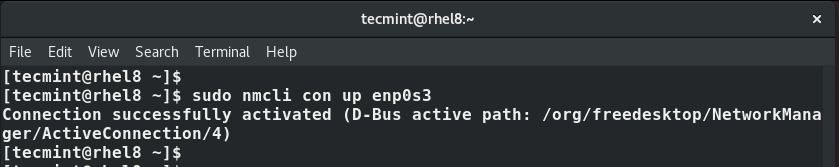
The changes will be written to /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enps03 file.
To confirm the IP, once again run the command:
$ ip addr enps03
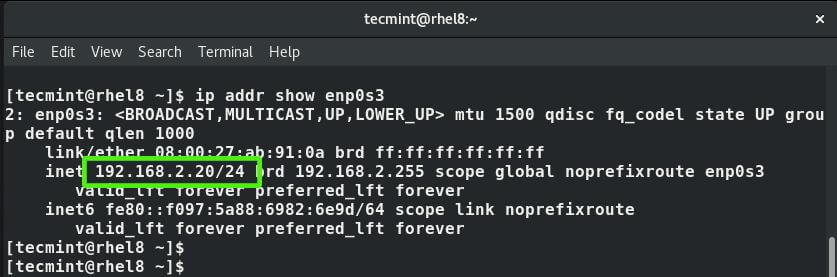
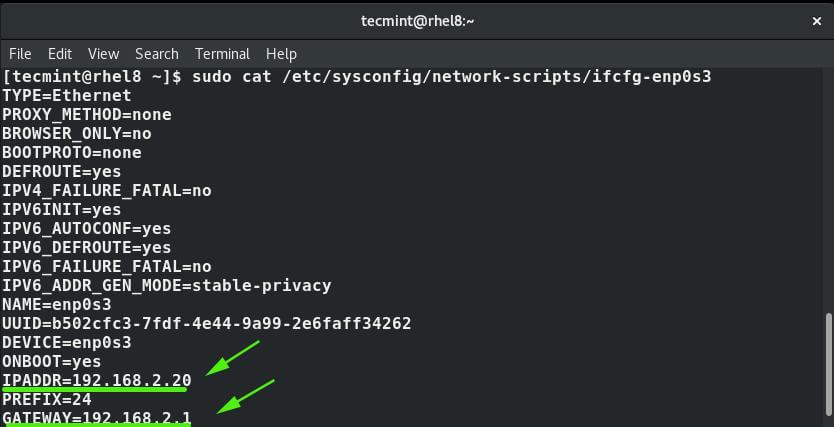
Additionally, you can view the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enps03 file using cat command.
$ cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enps03
And this concludes this guide on configuring network connection using ‘nmcli’ command-line tool on Linux. We hope you found this guide helpful.

Hello from the future!
I have set up a Raspberry Pi 4 with Debian/Raspberry Pi OS Bookworm and realized it wasn’t running dhcpcd. I looked everywhere for hours for help and this page explained it sooo well.
THANK YOU!
The following path is wrongly given in the following command.
The correct location is:
@Mohit,
Thanks for notifying the error, corrected the command in the article.
Nice article that explains the use of “nmcli” quite well. However, it seems that “nmcli” is not a universal Linux command. I run PCLinusOS and when I try to use “nmcli“, I get “no such command error“. Where and how “nmcli” can be obtained was never mentioned in the article.
@Dragonmouth,
The nmcli package comes pre-installed on most of the latest Linux distributions because it is part of NetworkManager…
Would that be “most Linux distributions” using systemd? I seem to recall that the Network Manager requires systemd to run.
PCLinuxOS is one of the more popular Linux distros, not some esoteric or “one and gone” distro. NMCLI is not installed by default and it is not in the repositories. No matter how good nmcli may be, it is not worth switching distros for. Especially if I have to put up with systemd to use it.
@Dragonmouth,
Most of today’s latest Linux distributions using systemd to manage networks and services. I really don’t have any idea about PCLinuxOS, I never used it, but will surely give a try on my VM. If nmcli not installed, I think you can install it using a package manager.