In this guide, we are going to look at how to use a script and scriptreplay commands in Linux that can help you to record commands and their output printed on your terminal during a given session.
The history command is a great command-line utility that helps users to store previous commands used, though it does not store the output of a command.
Therefore the script command comes in handy to provide you a powerful functionality that helps you to record everything that is printed on your terminal to a log_file.
You can then refer to this file later on in case you want to view the output of a command in history from the log_file.
You can also replay commands that you recorded using the scriptreplay command by using timing information.
How to Record a Terminal in Linux?
If you want to create a typescript (record of a terminal session) in Linux, you can use the script command which starts a new shell session and records everything displayed on the terminal, including input and output, to the specified filename.
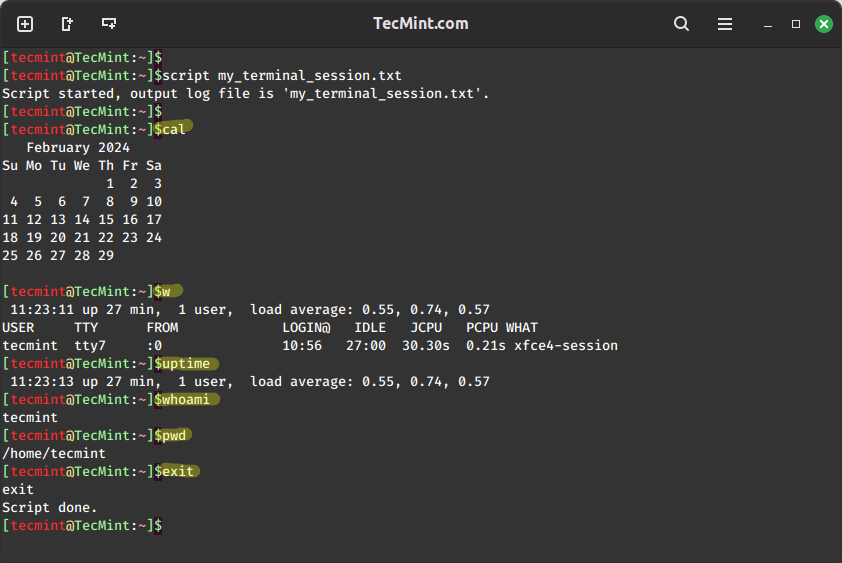
script my_terminal_session.txt
After running the script command, you will see the terminal prompt, where you can run various commands and your terminal session will be recorded to the “my_terminal_session.txt” file.
Now try to execute a few commands to allow the script to record executed commands on the terminal.
cal w uptime whoami pwd
To stop recording, simply type exit or press Ctrl+D.
exit
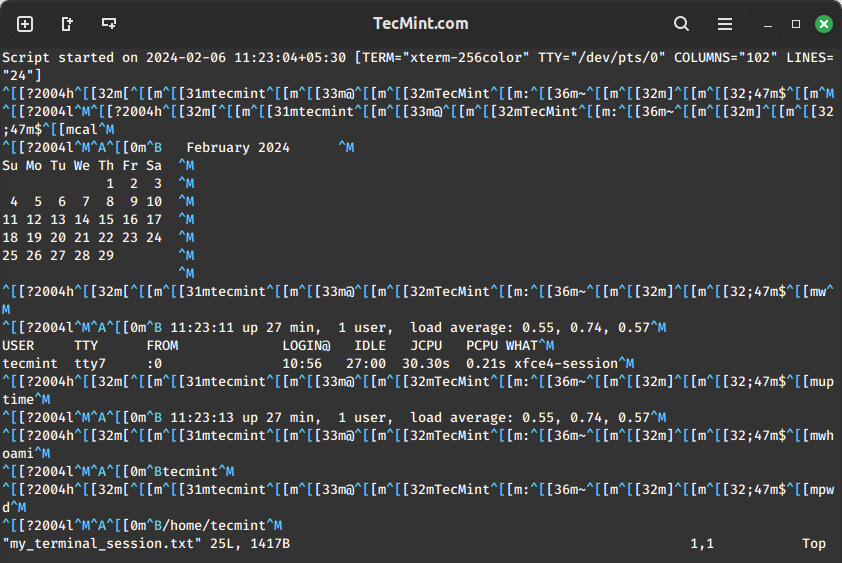
Now try to view the log file ‘my_terminal_session.txt‘ for all recorded commands, while you view the log you realize that the script also stores line feeds and backspaces.
vi my_terminal_session.txt
You may use the -a option to append the log file or typescript, retaining the prior contents.
script -a my_terminal_session.txt vi my_terminal_session.txt
To log the results of a single command other than an interactive shell session, use the -c option.
script -c 'hostname' script.log
If you want the script to run in a quiet mode then you can use the -q option. You will not see a message that shows the script is starting or exiting.
script -c 'who' -q script.log
To set timing information to standard error or a file use the --timing option. The timing information is useful when you want to re-display the output stored in the log_file.
Let us start the script and run the following commands w, uptime, and cal to be recorded.
script --timing=time.txt script.log
You can view the script.log and time.txt file for the timing command above.
vi script.log
Now view the time.txt file.
vi time.txt
The time.txt file has two columns, the first column shows how much time has elapsed since the last display and the second column, shows the number of characters that have been displayed this time around.
Use the man page and --help to seek more options and help in using the script command-line utility.
How to Replay Recorded Terminal Session in Linux?
The scriptreplay command helps to replay information in your log_file recorded by the script command.
The timing information is defined by the -timing=file option used with the script command and the file in this case is script.log which was used with the script command.
scriptreplay --timing=time.txt script.log
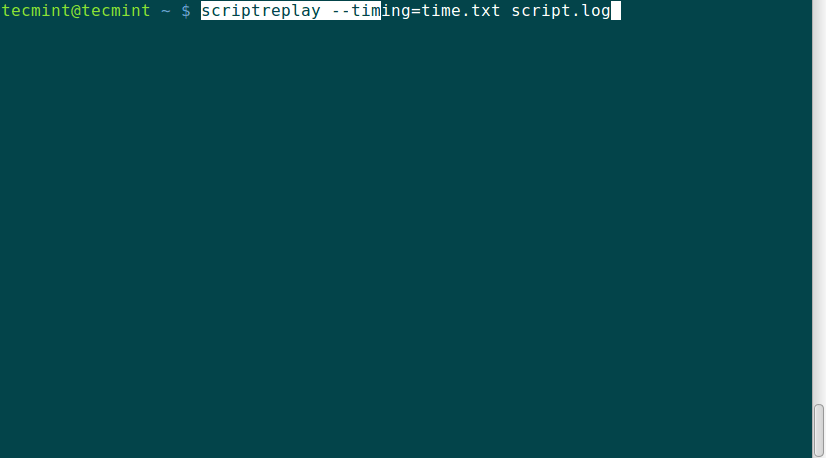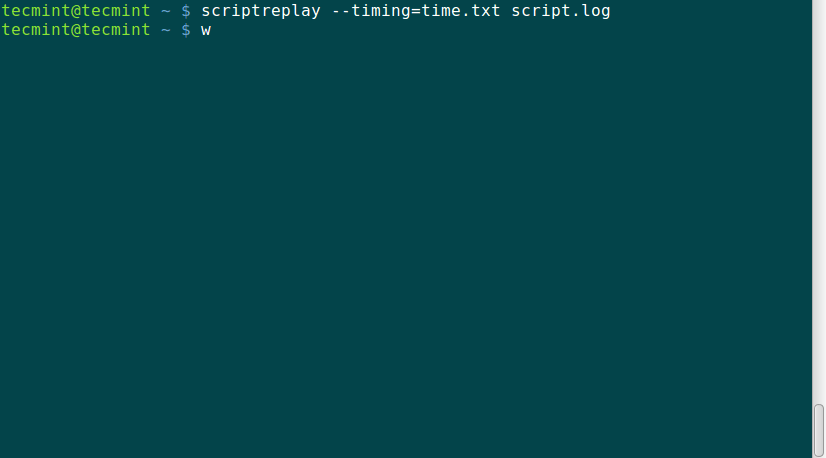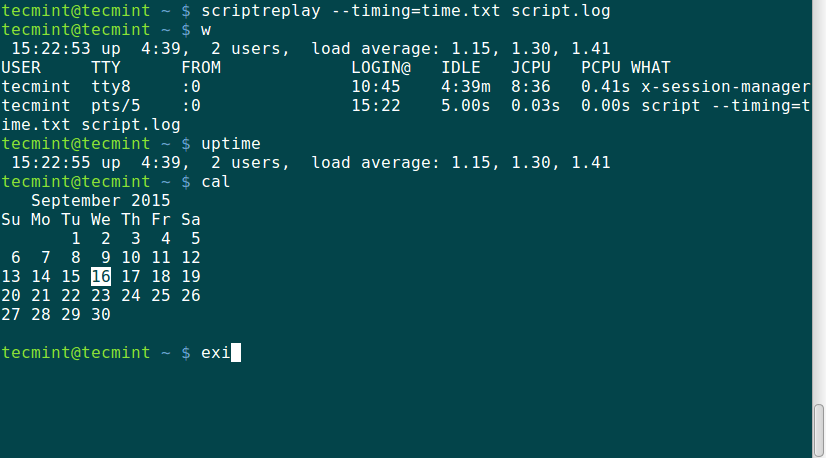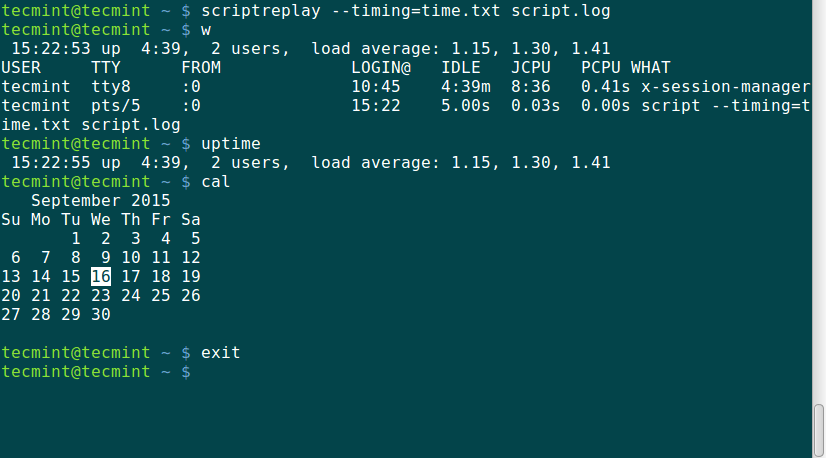
When the log_file is replayed using the timing information, the commands recorded are run and their output is displayed at the same time the original output was displayed while being recorded.
Summary
These two commands, script and scriptreplay easy to use and help a lot when you need to run the same batch of commands several times.
They help a lot in managing servers that have only a command-line interface for interaction with your system. Hope this guide was useful and if you have anything to add or face a challenge while using them, do not hesitate to post a comment.