As someone with over 10 years of experience working with Linux systems, I can say that setting up a reverse proxy with Nginx is one of the most common and efficient ways to handle traffic to your web applications.
A reverse proxy acts as an intermediary server that forwards client requests to the appropriate backend server, and it’s an essential tool for load balancing, security, and performance.
In this guide, I will walk you through the steps to configure Nginx as a reverse proxy on Ubuntu 24.04, along with an example of hosting a simple web application behind Nginx.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure that you have the following:
- Ubuntu 24.04 server up and running (you can use a VPS or a physical server).
- Root or sudo privileges to perform system administration tasks.
- A sample web application running on a backend server (we will use a basic
Node.jsapp for this example). - Basic knowledge of Linux commands and networking concepts.
Step 1: Install Nginx on Ubuntu 24.04
First, we need to install the Nginx web server from the default Ubuntu repositories using the following command.
sudo apt update sudo apt install nginx
Once the installation is complete, you can check the status of Nginx to ensure it’s running:
sudo systemctl status nginx
If Nginx is not running, start it with the command:
sudo systemctl start nginx
To make sure Nginx starts automatically on boot:
sudo systemctl enable nginx
If you have a UFW firewall enabled on your server, make sure that HTTP (port 80) traffic is allowed.
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full' sudo ufw enable
Step 2: Set Up Your Backend Web Application
In this example, we’ll use a simple Node.js application as our backend server, which will listen on port 3000.
First, install Node.js and npm on your server:
sudo apt install nodejs npm
Now, let’s create a simple Node.js web application:
sudo mkdir /var/www/myapp cd /var/www/myapp
Initialize the Node.js app:
sudo npm init -y
Install Express, a simple web framework for Node.js:
sudo npm install express
Create an app.js file inside the /var/www/myapp directory with the following content:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, this is a backend app!');
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`App running on http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Start your Node.js application.
sudo node app.js
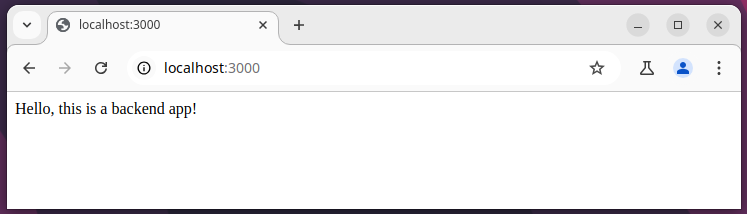
Your backend web application is now running on http://localhost:3000 and you can verify this by navigating to the folloiwng address in your browser, and you should see the “Hello, this is a backend app!” message.
http://your-server-ip:3000
Step 3: Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy
Now, let’s configure Nginx to forward requests from the outside world to the Node.js backend running on port 3000.
First, create a new configuration file in the sites-available directory:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/myapp
In the new file, add the following configuration to tell Nginx to forward incoming HTTP requests to the backend server running on port 3000:
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain_or_ip; location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:3000; # Forward requests to your backend server proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade'; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade; } }
After saving the configuration, create a symbolic link to the sites-enabled directory to enable this configuration:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/myapp /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
It’s important to make sure that there are no syntax errors before restarting Nginx:
sudo nginx -t sudo systemctl restart nginx
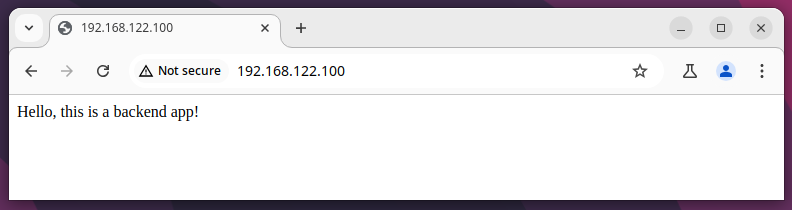
Now, open your browser and navigate to your server’s public IP address or domain (e.g., http://your-server-ip or http://your_domain).
You should see the message “Hello, this is a backend app!“, which means Nginx is successfully forwarding requests to your backend Node.js application.
For secure connections, you can configure SSL with Let’s Encrypt.
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx sudo certbot --nginx -d your_domain_or_ip
Conclusion
In this guide, we configured Nginx as a reverse proxy to forward HTTP requests to a backend Node.js web application running on localhost:3000 on an Ubuntu 24.04 server.
By following these steps, you’ve learned the basic concepts of reverse proxying with Nginx and how to host a simple web application behind Nginx. With this setup, you can easily expand it to more complex applications and scale your infrastructure as needed.