In this article of the RHCSA series, we will start with a brief revision of what happens from the moment you press the Power button to turn on your RHEL 9 server until you are presented with the login screen in a command line interface.
Please note that:
- the same basic principles apply, with perhaps minor modifications, to other Linux distributions as well, and
- the following description is not intended to represent an exhaustive explanation of the boot process, but only the fundamentals.
Linux Boot Process
1. The POST (Power On Self Test) initializes and performs hardware checks.
2. When the POST finishes, the system control is passed to the first stage boot loader, which is stored on either the boot sector of one of the hard disks (for older systems using BIOS and MBR), or a dedicated (U)EFI partition.
3. The first stage boot loader then loads the second stage boot loader, most usually GRUB (GRand Unified Boot Loader), which resides inside /boot, which in turn loads the kernel and the initial RAM-based file system (also known as initramfs, which contains programs and binary files that perform the necessary actions needed to ultimately mount the actual root filesystem).
4. We are presented with a splash screen that allows us to choose an operating system and kernel to boot:
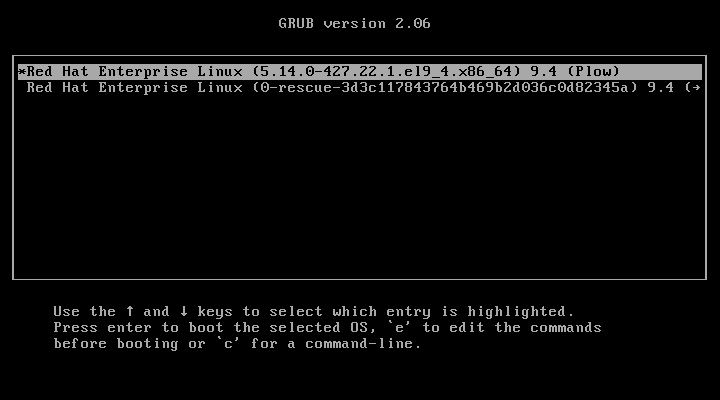
5. The kernel sets up the hardware attached to the system and once the root filesystem has been mounted, launches the process with PID 1, which in turn will initialize other processes and present us with a login prompt.

Note: That if we wish to do so at a later time, we can examine the specifics of this process using the dmesg command and filter its output using the tools that we have explained in previous articles of this series.
ps -o ppid,pid,uname,comm --ppid=1
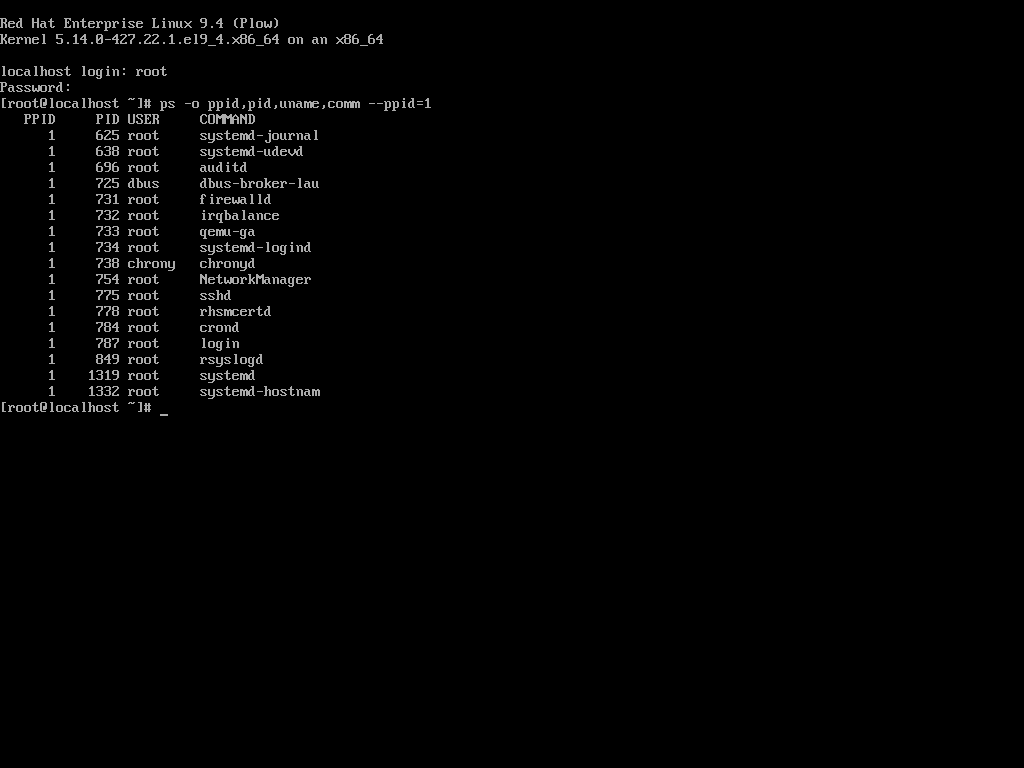
In the example above, we used the well-known ps command to display a list of current processes whose parent process (or in other words, the process that started them) is systemd (the system and service manager that most modern Linux distributions have switched to) during system startup:
Remember that the -o flag (short for --format) allows you to present the output of ps in a customized format to suit your needs using the keywords specified in the STANDARD FORMAT SPECIFIERS section in man ps.
man ps
Another case in which you will want to define the output of ps instead of going with the default is when you need to find processes that are causing a significant CPU and/or memory load and sort them accordingly:
ps aux --sort=+pcpu # Sort by %CPU (ascending) ps aux --sort=-pcpu # Sort by %CPU (descending) ps aux --sort=+pmem # Sort by %MEM (ascending) ps aux --sort=-pmem # Sort by %MEM (descending) ps aux --sort=+pcpu,-pmem # Combine sort by %CPU (ascending) and %MEM (descending)
An Introduction to SystemD
Few decisions in the Linux world have caused more controversies than the adoption of systemd by major Linux distributions. Systemd’s advocates name as its main advantages the following facts:
Systemd allows more processing to be done in parallel during system startup (as opposed to older SysVinit, which always tends to be slower because it starts processes one by one, checks, if one depends on another, and then waits for daemons to launch so more services, can start).
It works as a dynamic resource management in a running system. Thus, services are started when needed (to avoid consuming system resources if they are not being used) instead of being launched without a valid reason during boot.
Backwards compatibility with SysVinit scripts.
Systemd is controlled by the systemctl utility. If you come from a SysVinit background, chances are you will be familiar with:
- the service tool, which -in those older systems- was used to manage SysVinit scripts, and
- the chkconfig utility, which served the purpose of updating and querying runlevel information for system services.
- shutdown, which you must have used several times to either restart or halt a running system.
The following table shows the similarities between the use of these legacy tools and systemctl:
| Legacy tool | Systemctl equivalent | Description |
| service name start | systemctl start name | Start name (where name is a service) |
| service name stop | systemctl stop name | Stop name |
| service name condrestart | systemctl try-restart name | Restart name (if it’s already running) |
| service name restart | systemctl restart name | Restarts name |
| service name reload | systemctl reload name | Reloads the configuration for the name |
| service name status | systemctl status name | Displays the current status of a name |
| service –status-all | systemctl | Displays the status of all current services |
| chkconfig name on | systemctl enable name | Enable the name to run on startup as specified in the unit file (the file to which the symlink points). The process of enabling or disabling a service to start automatically on boot consists in adding or removing symbolic links inside the /etc/systemd/system directory. |
| chkconfig name off | systemctl disable name | Disables name to run on startup as specified in the unit file (the file to which the symlink points) |
| chkconfig –list name | systemctl is-enabled name | Verify whether the name (a specific service) is currently enabled |
| chkconfig –list | systemctl –type=service | Displays all services and tells whether they are enabled or disabled |
| shutdown -h now | systemctl poweroff | Power off the machine (halt) |
| shutdown -r now | systemctl reboot | Reboot the system |
Systemd also introduced the concepts of units (which can be either a service, a mount point, a device, or a network socket) and targets (which is how systemd manages to start several related processes at the same time and can be considered -though not equal- as the equivalent of runlevels in SysVinit-based systems.
Linux Process Management
Other tasks related to process management include, but may not be limited to, the ability to:
1. Manage Process Resource Usage with Priority in Linux
This is accomplished through the renice utility, which alters the scheduling priority of one or more running processes.
In simple terms, the scheduling priority is a feature that allows the kernel (present in versions => 2.6) to allocate system resources as per the assigned execution priority (aka niceness, in a range from -20 through 19) of a given process.
The basic syntax of renice is as follows:
renice [-n] priority [-gpu] identifier
In the generic command above, the first argument is the priority value to be used, whereas the other argument can be interpreted as process IDs (which is the default setting), process group IDs, user IDs, or user names.
A normal user (other than root) can only modify the scheduling priority of a process he or she owns, and only increase the niceness level (which means taking up fewer system resources).
ps -efl | grep top | grep -v grep
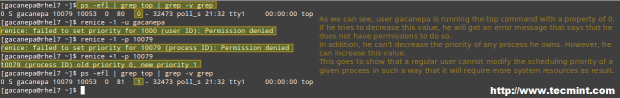
2. Terminate Running Processes in Linux
In more precise terms, killing a process entitles sending it a signal to either finish its execution gracefully (SIGTERM=15) or immediately (SIGKILL=9) through the kill or pkill commands.
The difference between these two tools is that the former is used to terminate a specific process or a process group altogether, while the latter allows you to do the same based on name and other attributes.
In addition, pkill comes bundled with pgrep, which shows you the PIDs that will be affected should pkill be used.
For example, before running:
pkill -u gacanepa
It may be useful to view at a glance which are the PIDs owned by gacanepa:
pgrep -l -u gacanepa
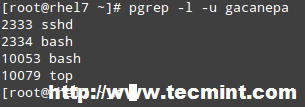
By default, both kill and pkill send the SIGTERM signal to the process. As we mentioned above, this signal can be ignored (while the process finishes its execution or for good), so when you seriously need to stop a running process with a valid reason, you will need to specify the SIGKILL signal on the command line:
kill -9 identifier # Kill a process or a process group kill -s SIGNAL identifier # Idem pkill -s SIGNAL identifier # Kill a process by name or other attributes
Conclusion
In this article, we have explained the basics of the boot process in a RHEL 9 system and analyzed some of the tools that are available to help you with managing processes using common utilities and system-specific commands.
Note that this list is not intended to cover all the bells and whistles of this topic, so feel free to add your own preferred tools and commands to this article using the comment form below. Questions and other comments are also welcome.
For comprehensive RHCSA exam preparation, we have created a comprehensive ebook titled ‘RHCSA Exam Study Guide‘, covering all the objectives with practical examples.







Great article, but due to my little understanding of operating systems, let me ask this…are the terms processes and services one and the same thing in this context? I know some processes at times serve other processes but is this why they are called services too?
Those terms are often used interchangeably. However, there is a subtle difference. Refer to this link for further reading: http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/263979/service-vs-process.
Great article, thank you very much
@Marie,
You’re welcome! Please help us spread the word by sharing this and our other articles in your social network profiles :).
Very well explained. All my doubts are now clear.
@Nikhil,
I’m glad to hear that. Thank you for your comment!
hello. thanks for the article. I want to ask something. If now the management process is handled by systemctl, it means we can’t use the “service” based commands anymore?
@Rizal,
systemd is supposed to support backward compatibility with -at least- some sysvinit-based well-known commands, but trust me, that doesn’t always seem to be the case. Moving forward, all of us who have become used to service-based commands will have to learn the systemd-based ones (systemctl and all that). The effort is well worth it, though.
VERY GOOD
@Praduman,
I’m glad you enjoyed the article! And thanks for commenting.