Mounting NFS Network Shares
To show the list of NFS shares available in your server, you can use the showmount command with the -e option, followed by the machine name or its IP address. This tool is included in the nfs-utils package:
# yum update && yum install nfs-utils
Then do:
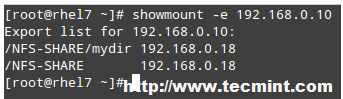
# showmount -e 192.168.0.10
and you will get a list of the available NFS shares on 192.168.0.10:
To mount NFS network shares on the local client using the command line on demand, use the following syntax:
# mount -t nfs -o [options] remote_host:/remote/directory /local/directory
which, in our case, translates to:
# mount -t nfs 192.168.0.10:/NFS-SHARE /mnt/nfs
If you get the following error message: “Job for rpc-statd.service failed. See “systemctl status rpc-statd.service” and “journalctl -xn” for details.”, make sure the rpcbind service is enabled and started in your system first:
# systemctl enable rpcbind.socket # systemctl restart rpcbind.service
and then reboot. That should do the trick and you will be able to mount your NFS share as explained earlier. If you need to mount the NFS share automatically on system boot, add a valid entry to the /etc/fstab file:
remote_host:/remote/directory /local/directory nfs options 0 0
The variables remote_host, /remote/directory, /local/directory, and options (which is optional) are the same ones used when manually mounting an NFS share from the command line. As per our previous example:
192.168.0.10:/NFS-SHARE /mnt/nfs nfs defaults 0 0
Mounting CIFS (Samba) Network Shares
Samba represents the tool of choice to make a network share available in a network with *nix and Windows machines. To show the Samba shares that are available, use the smbclient command with the -L flag, followed by the machine name or its IP address. This tool is included in the samba-client package:
You will be prompted for root’s password in the remote host:
# smbclient -L 192.168.0.10

To mount Samba network shares on the local client you will need to install first the cifs-utils package:
# yum update && yum install cifs-utils
Then use the following syntax on the command line:
# mount -t cifs -o credentials=/path/to/credentials/file //remote_host/samba_share /local/directory
which, in our case, translates to:
# mount -t cifs -o credentials=~/.smbcredentials //192.168.0.10/gacanepa /mnt/samba
where smbcredentials:
username=gacanepa password=XXXXXX
is a hidden file inside root’s home (/root/) with permissions set to 600, so that no one else but the owner of the file can read or write to it.
Please note that the samba_share is the name of the Samba share as returned by smbclient -L remote_host as shown above.
Now, if you need the Samba share to be available automatically on system boot, add a valid entry to the /etc/fstab file as follows:
//remote_host:/samba_share /local/directory cifs options 0 0
The variables remote_host, /samba_share, /local/directory, and options (which is optional) are the same ones used when manually mounting a Samba share from the command line. Following the definitions given in our previous example:
//192.168.0.10/gacanepa /mnt/samba cifs credentials=/root/smbcredentials,defaults 0 0
Conclusion
In this article we have explained how to set up ACLs in Linux, and discussed how to mount CIFS and NFS network shares in a RHEL 7 client.
I recommend you to practice these concepts and even mix them (go ahead and try to set ACLs in mounted network shares) until you feel comfortable. If you have questions or comments feel free to use the form below to contact us anytime. Also, feel free to share this article through your social networks.







And I am wondering why this has covered before editing /etc/exports & smb.conf. RHCE certification is not only for experienced people, many freshers do it as well. I need to recommend the series for newbies, please get it corrected.
@Neeraj,
The answer is simple. The RHCSA objective related to this article reads as follows: “Mount and unmount CIFS and NFS network file systems”. It does NOT require a candidate to SET UP a CIFS or NFS share. That objective is covered as part of the RHCE exam.
I was referring to:
Prerequisites
Before proceeding further, please make sure you have a Samba server and a NFS server available (note that NFSv2 is no longer supported in RHEL 7).
@Neeraj,
I see your point – but that’s the way it is. Maybe you should contact RH directly and ask for their feedback on the ordering on contents.
Anyway, I’ll tell you my experience with the Linux Foundation certifications. With the LFCS exam, one of the required competencies is that you know how to mount a NFS share. You are NOT required to know how to SET it up – just mount it.
I understand then, even LDAP authentication from the client side needs to be done in RHCE though I don’t know the configuration of Linux DC. Hopefully, would be done today or tomorrow.
Waiting for my 4 more training and certifications to be completed. Once I would be a certified architect then will contact them again. I didn’t get satisfactory answers in the past at one go, even when my tickets were escalated to the top most level.
Small mistake, in set permission for gacanepa user you probably committed.
I think should be full path to file testfile.txt not only directory.
PS.
Thanks for that another article.