A computer hostname represents a unique name that gets assigned to a computer in a network in order to uniquely identify that computer in that specific network. A computer hostname can be set to any name you like, but you should keep in mind the following rules:
- hostnames can contain letters (from a to z).
- hostnames can contain digits (from 0 to 9).
- hostnames can contain only the hyphen character
( – )as a special character. - hostnames can contain the dot special character
( . ). - hostnames can contain a combination of all three rules but must start and end with a letter or a number.
- hostnames letters are case-insensitive.
- hostnames must contain between 2 and 63 characters long.
- hostnames should be descriptive (to ease identifying the computer purpose, location, geographical area, etc on the network).
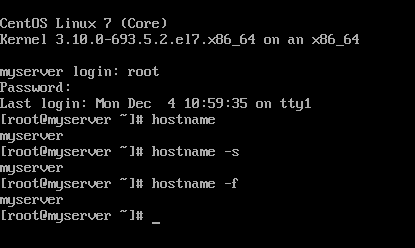
In order to display a computer name in CentOS 7/8 and RHEL 7/8 systems via console, issue the following command. The -s flag displayed the computer short name (hostname only) and the -f flag displays the computer FQDN in the network (only if the computer is a part of a domain or realm and the FQDN is set).
# hostname # hostname -s # hostname -f
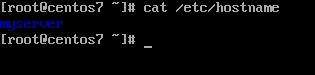
You can also display a Linux system hostname by inspecting the content of /etc/hostname file using the cat command.
# cat /etc/hostname
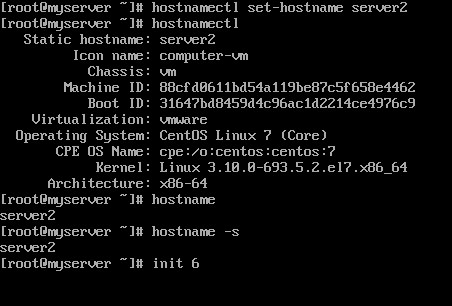
In order to change or set a CentOS 7/8 machine hostname, use the hostnamectl command as shown in the below command excerpt.
# hostnamectl set-hostname your-new-hostname
In addition to hostname command, you can also use hostnamectl command to display a Linux machine hostname.
# hostnamectl
In order to apply the new hostname, a system reboot is required, issue one of the below commands in order to reboot a CentOS 7 machine.
# init 6 # systemctl reboot # shutdown -r
A second method to set up a CentOS 7/8 machine hostname is to manually edit the /etc/hostname file and type your new hostname. Also, a system reboot is necessary in order to apply the new machine name.
# vi /etc/hostname
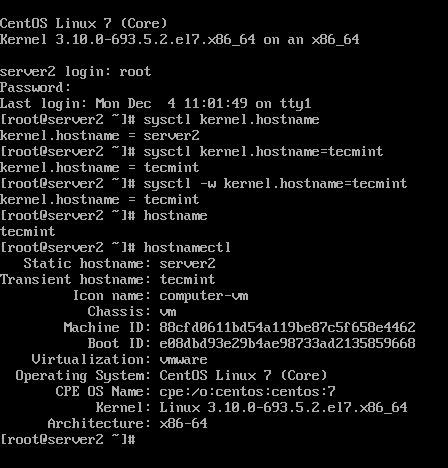
A third method that can be used to change a CentOS 7/8 machine hostname is by using the Linux sysctl interface. However, using this method to change machine name results in setting-up the machine transient hostname.
The transient hostname is a special hostname initialized and maintained only by the Linux kernel as an auxiliary machine name in addition to he static hostname and doesn’t survive reboots.
# sysctl kernel.hostname # sysctl kernel.hostname=new-hostname # sysctl -w kernel.hostname=new-hostname
To display machine transient hostname issue the below commands.
# sysctl kernel.hostname # hostnamectl
Finally, the hostnamectl command can be used to achieve the following hostname setups: –pretty, –static, and –transient.
Although there are other more specific ways to change a Linux machine hostname, such as issuing nmtui command or manually editing some configuration files specific to each Linux distribution (/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ethX for CentOS), the above rules are generally available regardless of the used Linux distribution.






Thank you! This is the only tutorial I followed that actually permanently changed the hostname on my server.
thanks for the write-up, saving it to my library
I tried hostnamectl command suggested, but it leaves old hostname in /etc/hosts even after reboot as suggested..
@Cz,
The file /etc/hosts hold all manually added entries, you need to remove the hostname from the /etc/hosts file..