Configuring a static IP address for your Linux distribution is a fundamental task and should be completed in few easy steps. With the release of RHEL 8 public beta, you can now configure your network interface in a few different ways using NetworkManager utilities.
In this tutorial we are going to show you few different ways to set a static IP address on RHEL 8 installation. Note that this article presumes, that you already know the network settings that you wish to apply for your system.
1. How to Configure Static IP Using Network Scripts Manually
You can configure a static IP address the old fashioned way by editing:
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-(interface-name)
In my case the file is named:
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
To find your network interface name, you can use the following nmcli command.
# nmcli con

To edit the file simply use your favorite editor and open the file:
# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
TYPE="Ethernet" BOOTPROTO="none" NAME="enp0s3" IPADDR="192.168.20.150" NETMASK="255.255.255.0" GATEWAY="192.168.20.1" DEVICE="enp0s3" ONBOOT="yes"
Then restart the NetworkManager with:
# systemctl restart NetworkManager
Alternatively, you can reload the network interface by using:
# nmcli con down enp0s3 && nmcli con up enp0s3
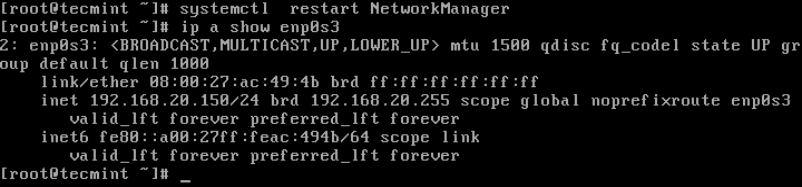
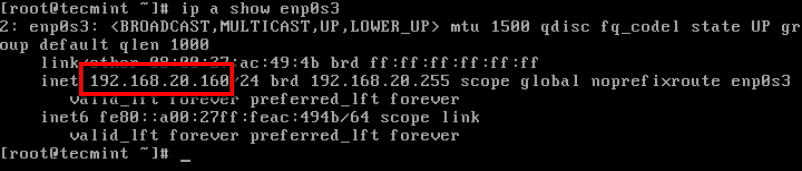
Now you can then check the new IP address using ip command as shown.
# ip a show enp0s3
2. How to Configure Static IP Using Nmtui Tool
Another way to configure static IP address for your RHEL 8 is by using nmtui tool, is a text user interface (TUI). To use it simply type the following command in your terminal.
# nmtui
This is will launch the program:
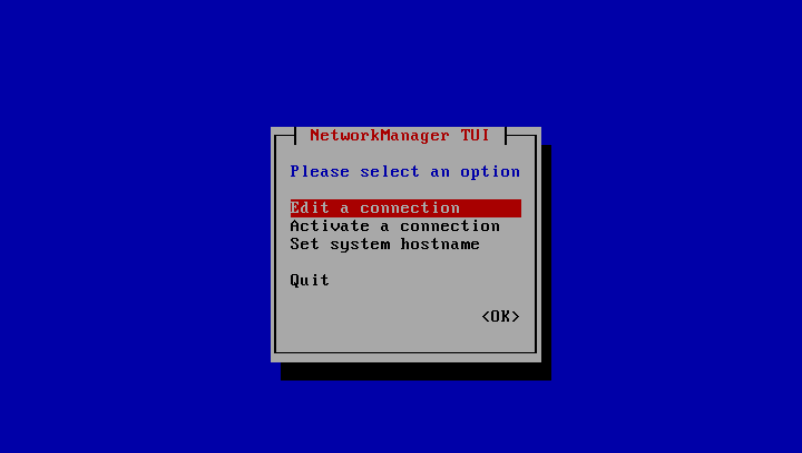
Choose to edit a connection, then select the interface:
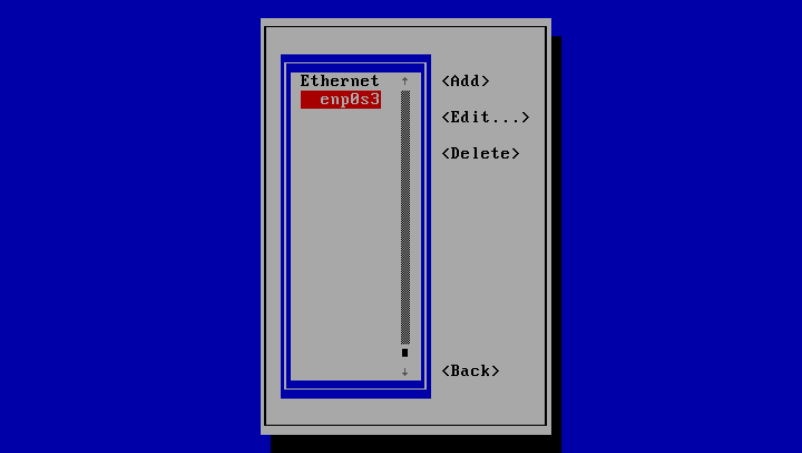
In the next window you will be able to edit the network interface settings by moving the cursor with the arrow keys on your keyboard:
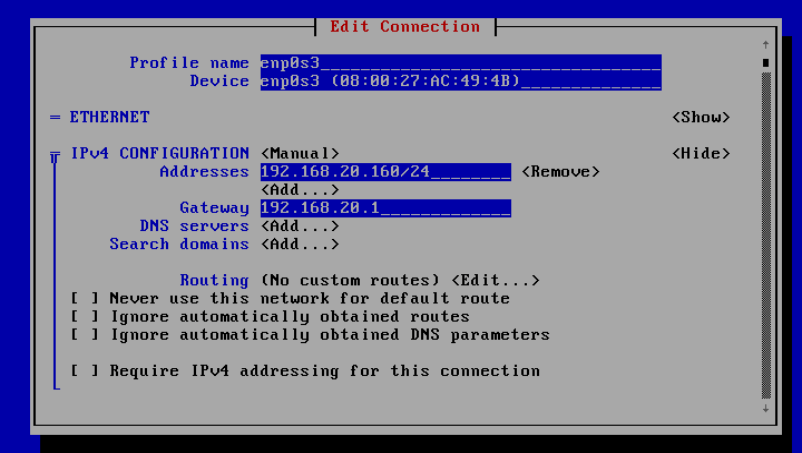
In this example, I have changed my IP address from 192.168.20.150 to 192.168.20.160. To save the changes scroll down to the end of the page and select OK.
Then reload the network interface by choosing “Activate a connection”:
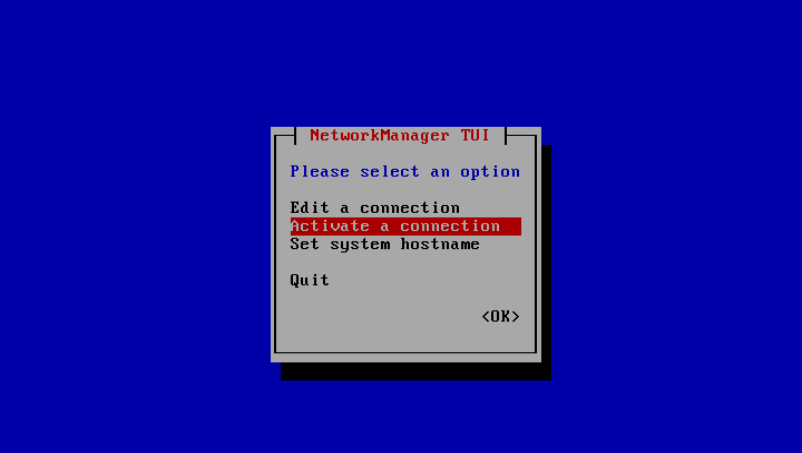
Then choose the connection name and select <Deactivate>:
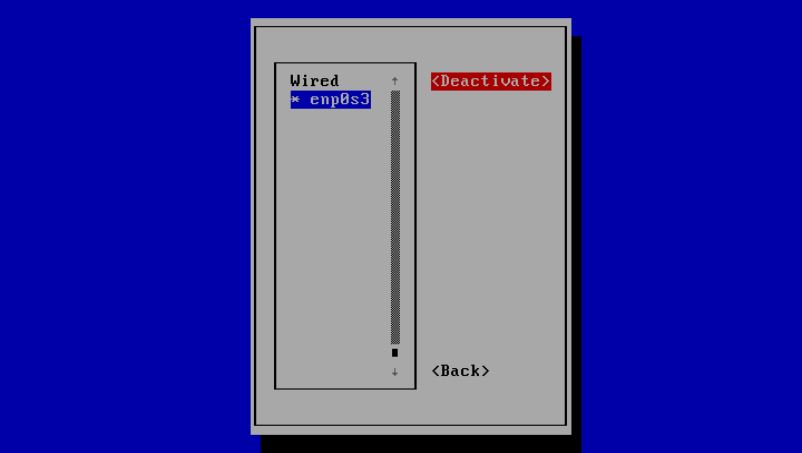
And now select <Activate> to activate the interface with the new settings you have given it.
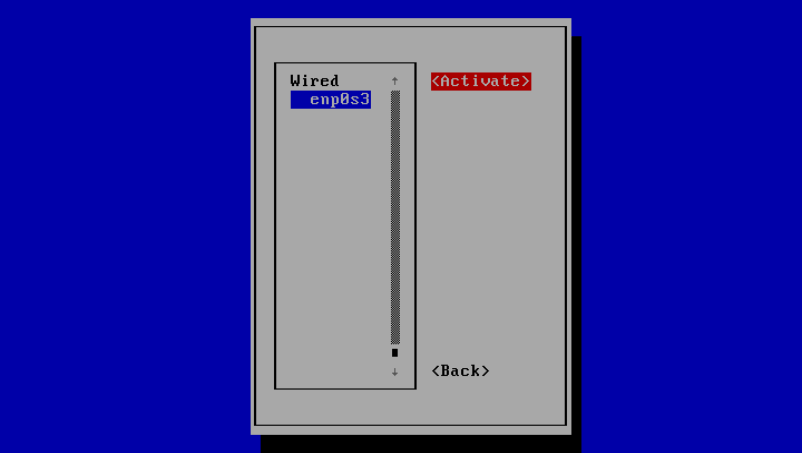
Then select <Back> to return to the main menu and then select “Quit” to exit.
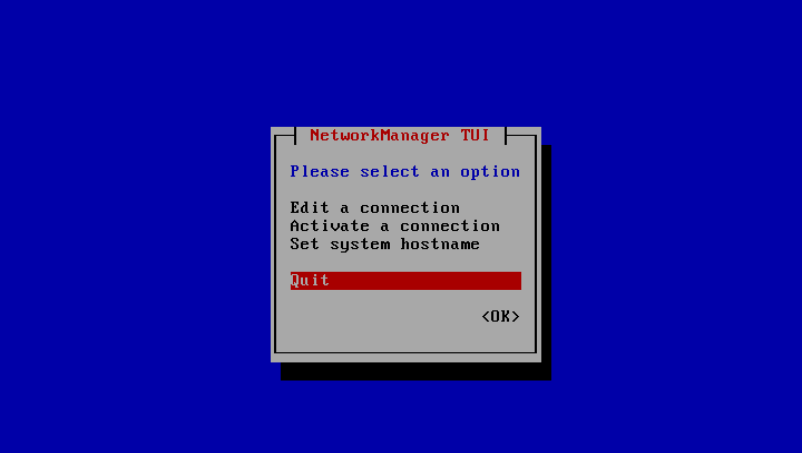
Verify that the new IP address settings have been applied with:
# ip a show enp0s3
3. How to Configure Static IP Using Nmcli Tool
Nmcli is a NetworkManager command line interface that can be used for obtaining information or configuring a network interface.
If you want to set a static IP address, you can use the following options:
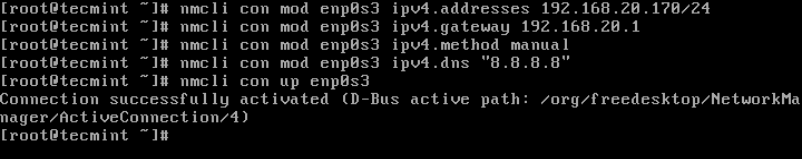
Set the IP address for interface enp0s3 on RHEL 8.
# nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.addresses 192.168.20.170/24
Set the gateway on RHEL 8:
# nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.gateway 192.168.20.1
Inform the interface that it is using manual configuration (not dhcp etc.).
# nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.method manual
Configure DNS:
# nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8"
Reload the interface configuration:
# nmcli con up enp0s3
Your changes will be saved in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-.
Here is the configuration file that has been generated for me:
# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
TYPE="Ethernet" BOOTPROTO="none" NAME="enp0s3" IPADDR="192.168.20.170" NETMASK="255.255.255.0" GATEWAY="192.168.20.1" DEVICE="enp0s3" ONBOOT="yes" PROXY_METHOD="none" BROWSER_ONLY="no" PREFIX="24" DEFROUTE="yes" IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL="no" IPV6INIT="no" UUID="3c36b8c2-334b-57c7-91b6-4401f3489c69" DNS1="8.8.8.8"
Conclusion
In this tutorial you have seen how to configure a static IP address with network scripts, nmtui and nmcli utilities in RHEL 8. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to submit them in the comment section below.




In order to change configuration on a NIC or Bond in RHEL 8, you need to restart networking:
Cycling the interface/bond, or restarting NetworkManager, will not work Or you can reboot, but that’s silly.
I should note that this works if you set your configuration through nmcli, or if you edit the appropriate network scripts. This, I think, is changed since RHEL 7, as it was only necessary to bring down the particular NIC or Bond there, in RHEL 8 this won’t work.
Thank you so much, buddy, it works for me.
If I have Windows os on my base machine and I installed VM-ware for using Linux os and then I type ping command on the command line of Linux with up address of windows machine then can I communicate with both os
Yes! you can do that by putting a Network adapter option in VMWARE as Bridge type, then they both will communicate.
The command for “Set the IP address for interface enp0s3 on RHEL 8” at step 3 is not correct. A “nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.addresses 192.168.20.170/24” sets the ip for the connection-name “enp0s3”, not for the interface “enp0s3”. On my system they are not equal.