Firefox browser is the default browser for most modern Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Mint, and Fedora. Initially, its performance might be impressive, however, with the passage of time, you might notice that your browser is not as fast and responsive as it once was. A sluggish browser can be quite frustrating as it tends to eat into your precious time as you wait for it to load your tabs and respond to input.
[ You might also like: Best Web Browsers for Linux ]
If you are experiencing such performance issues, here are a few quick fixes to help speed up your Firefox browser in Linux.
1. Update Firefox
The first action you might need to take is to update your browser to the latest version. This addresses any underlying issues that impacted the browser’s performance in previous versions.
Firefox typically auto-updates when a new version is available. This happens when you have an active internet connection and you restart Firefox, especially after a system reboot.
If in doubt about the version of your Firefox browser, you can verify the version by clicking the three-line menu at the top-right of the screen and selecting Help –> About Firefox.
From the pop-up shown, we are currently running Firefox 79.0.

However, at the time of publishing this guide, the latest version is Firefox 94.0. So, how do you update to the latest Firefox version?
There are two approaches to this – On command-line and GUI. On the command line, run the following command to update and upgrade all the software packages including Firefox itself.
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo dnf udpate && sudo dnf upgrade [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ emerge --update --deep --with-bdeps=y @world [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo pacman -Syu [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper update [On OpenSUSE]
The other alternative is using the software updater which lists all the packages with pending updates. You can choose to update Firefox alongside other packages or simply select Firefox alone for updates.
Once the update is done, be sure to restart your browser for the changes to apply. Upon confirmation, we now have the latest Firefox version as indicated in the pop-up below.

2. Enable Hardware Acceleration in Firefox
By default, Firefox comes with hardware acceleration disabled on all Linux distributions. Enabling hardware acceleration is known to cause a noticeable improvement in Firefox’s responsiveness.
To enable hardware acceleration, follow the steps below:
- Browse about:preferences on the URL bar.
- Scroll down to the General section and then navigate to Performance.
- Uncheck the ‘Use recommended performance settings’ option.
- Then check the ‘Use hardware acceleration when available’ setting to enable hardware acceleration.
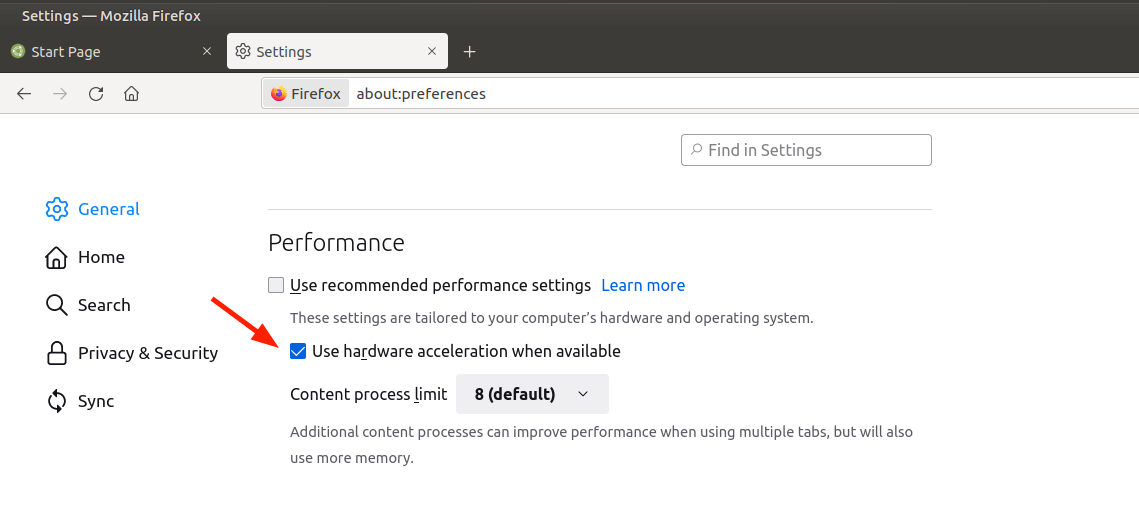
Below the hardware acceleration option is the ‘Content process limit’.
If your PC has more than 8GB & has a dedicated GPU such as NVIDIA, set it to 8. Else, just leave it to the default 4 value. It is perfectly safe to leave it at 5 for 16GB RAM and 6 in case you have 32GB RAM.
3. Disable Firefox Data Collection & Use
Generally, Firefox collects and sends anonymous data about browser activity to its servers in a bid to make improvements to its features. While it doesn’t compromise your privacy it slows down your browser.
You can prevent Firefox from sending data anonymously with a few simple steps.
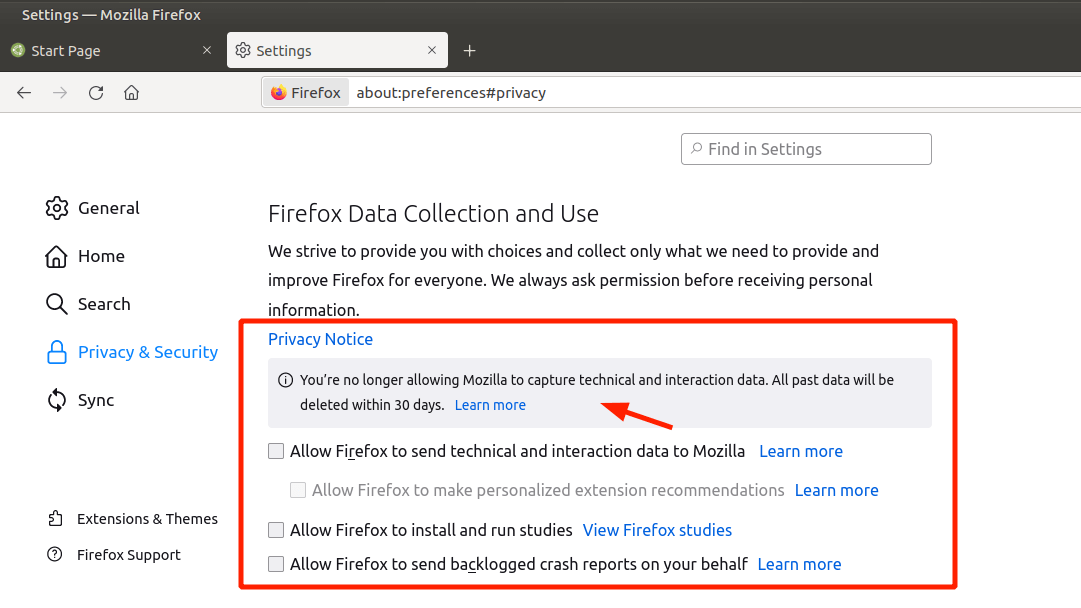
- Head over to about: preferences.
- Proceed to ‘Privacy & Security’ and then proceed to ‘Firefox Data Collection and Use’.
- Uncheck all the options.
- Then restart Firefox.
4. Free Up Firefox Memory
In case you are still having issues with your browser, consider freeing up some memory. To do this, follow the following simple steps:
- On the URL bar, browse about:memory.
- In the ‘Free memory’ section, click on ‘Minimize memory usage’.
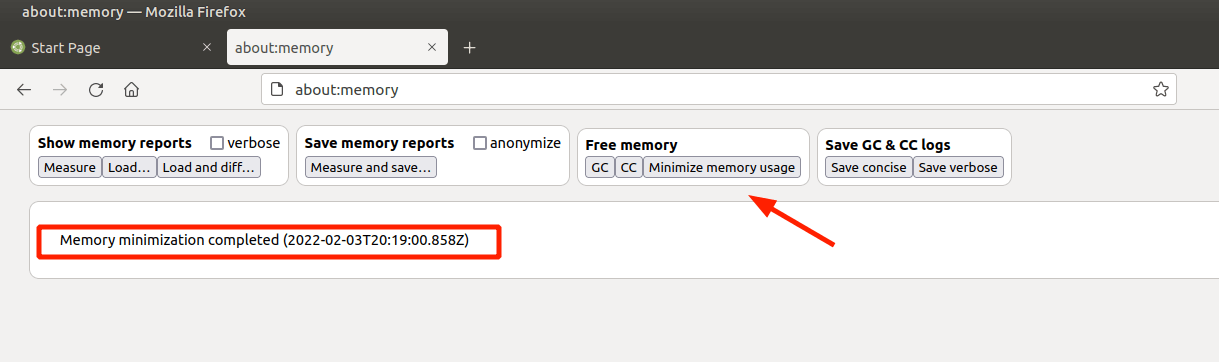
This should provide the much-needed boost in speed.
5. Manage Firefox Browser Tabs
Keeping multiple active tabs open usually drives up the memory usage and impacts the performance of not only your browser but the overall system performance. If you are in the habit of keeping several tabs open, consider trying out an extension called Auto Tab Discard.
This is a lightweight browser extension that automatically scales down memory load as a result of open but inactive tabs.
To get the extension, follow these steps:
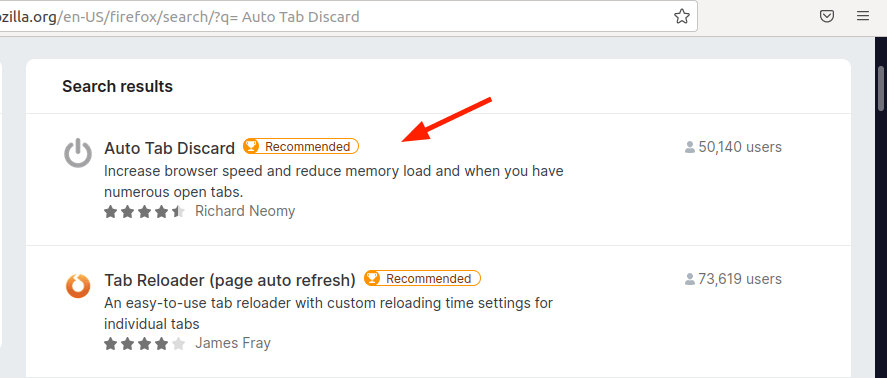
- Click the three-line menu at the top-right of the screen.
- Select Add-ons and themes.
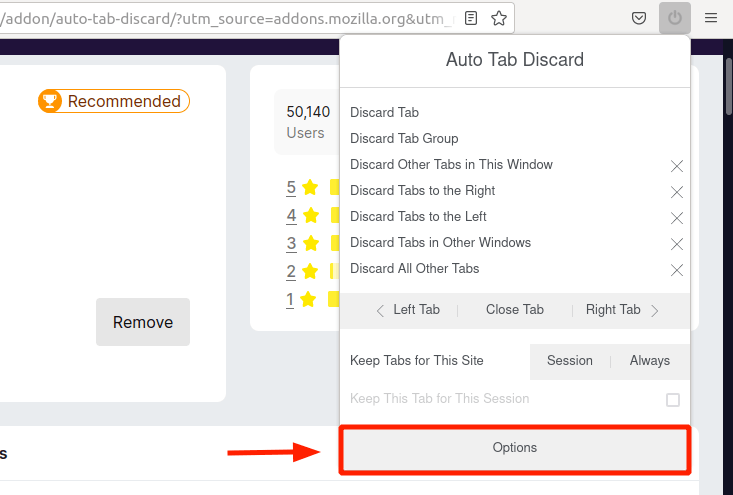
- Search for Auto Tab Discard extension and install it.
Launch it and select ‘Options’ and modify a few settings regarding discarding inactive tabs and later, save the changes.
6. Modify Firefox Settings
You might also consider making a few tweaks to the advanced settings in Firefox which are absent in the Options panel. Be sure to make the following changes to speed up your Firefox browser.
So, here are the steps to follow:
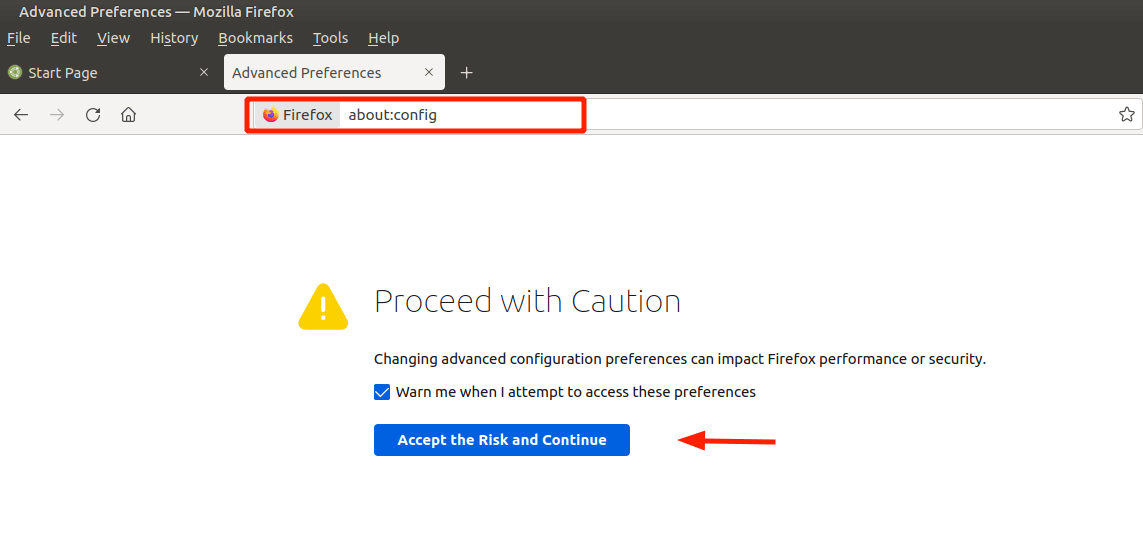
- On the URL bar, browse about:config.
You will get a warning as shown. To proceed, simply click on ‘Accept the Risk and continue’.
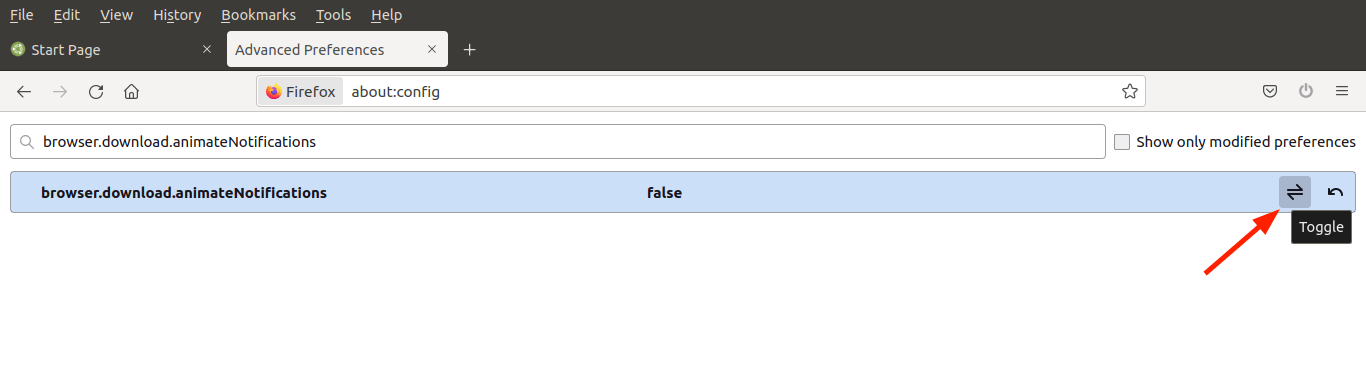
Set the preference listed below to ‘False’.
browser.download.animateNotifications
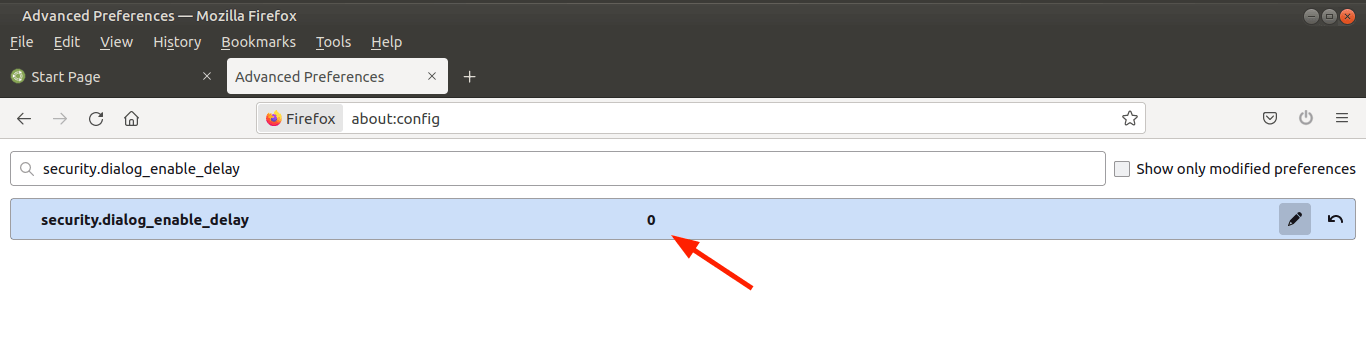
Additionally, set this preference to the numerical value ‘0‘.
security.dialog_enable_delay
Next, type ‘Telemetry‘ in the search field and press ENTER. Then set the following preferences to false.
browser.newtabpage.activity-stream.telemetry browser.newtabpage.activity-stream.feeds.telemetry browser.ping-centre.telemetry toolkit.telemetry.bhrPing.enabled toolkit.telemetry.archive.enabled toolkit.telemetry.firstShutdownPing.enabled toolkit.telemetry.reportingpolicy.firstRun toolkit.telemetry.hybridContent.enabled toolkit.telemetry.newProfilePing.enabled toolkit.telemetry.unified toolkit.telemetry.shutdownPingSender.enabled toolkit.telemetry.updatePing.enabled
7. Refresh Firefox
If all else fails, then, consider refreshing your browser. This resets the browser to its default state and allows you to start on a clean slate. Refreshing purges all the preferences including preferences such as add-ons and themes.
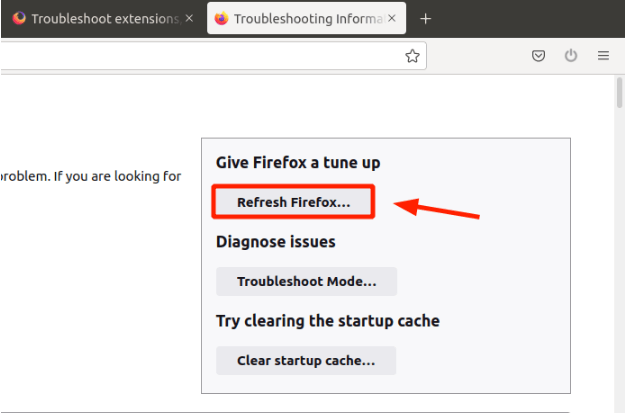
To refresh Firefox,
- Click the three-line menu at the top-right of the screen.
- Select ‘Help’ then click on ‘More troubleshooting information’.
- On the right sidebar, click on ‘Refresh Firefox’.
Hopefully, the steps outlined in this tutorial will help improve your browser’s performance and improve the user experience when browsing. Any tips you felt we have left out? We are eager to listen to your feedback in the comment section.


It really helped (Debian 12 GNOME), now it’s like Firefox on Windows.
I have a question, some of the items in telemetry have been kept in true, so what happens if all are selected as false? Does it affect in the performance or in the security issues?
Thanks in advance.
@Ceaualbi,
If you turn off all the options for sending data in telemetry, it shouldn’t make your computer slower or less secure. But this data helps software makers see how people use their programs and find ways to make them better.
I have the same issue and it appears to be related to a number of tabs open in and/or an extended period with no activity from the internet or user.
This article has fixed Firefox clinching. However, my browser freezes now and then. It asks me to restart Firefox. I have no idea why this is happening. Can anyone help with this? I’m running Ubuntu Mate on a 2015 iMac with 16GB ram. If anyone has any ideas, it would be much appreciated. :)
Great articles. ;)
Don’t use Number 6. At least not without a backup of your profile. It completely bricked my firefox.
Hello Sir,
I like your post and it is quite good. Sir i have a query i am running RHEL 6.2 and i am using remi repository and epel also but unable to install firefox 21 on that system because of those dependencies please suggest me something.