SSH stands for Secure Shell is a network protocol, used to access remote machine in order to execute command-line network services and other commands over a Network. SSH is Known for its high security, cryptographic behavior and it is most widely used by Network Admins to control remote web servers primarily.

Here in this Interview Questions series article, we are presenting some useful 10 SSH (Secure Shell) Questions and their Answers.
1. SSH is configured on what Port Number, by default? How to change the port of SSH?
We can check port number of SSH by running the below one liner script, directly on terminal.
# grep Port /etc/ssh/sshd_config [On Red Hat based systems] # grep Port /etc/ssh/ssh_config [On Debian based systems]
To change the port of SSH, we need to modify the configuration file of SSH which is located at ‘/etc/ssh/sshd_config‘ or ‘/etc/ssh/ssh_config‘.
# nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config [On Red Hat based systems] # nano /etc/ssh/ssh_config [On Debian based systems]
Searh for the Line.
Port 22
And replace ‘22‘ with any UN-engaged port Number say ‘1080‘. Save the file and restart the SSH service to take the changes into effect.
# service sshd restart [On Red Hat based systems] # service ssh restart [On Debian based systems]
2. As a security implementation, you need to disable root Login on SSH Server, in Linux. What would you suggest?
To disable SSH root login, open the configuration file located at ‘/etc/ssh/sshd_config‘ or ‘/etc/ssh/ssh_config‘.
# nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config [On Red Hat based systems] # nano Port /etc/ssh/ssh_config [On Debian based systems]
Change the parameter ‘PermitRootLogin‘ to ‘no‘ and restart the SSH service as show above.
3. SSH or Telnet? Why?
4. Is it possible to login to SSH server without password? How
Create ssh-keygen using the command below.
$ ssh-keygen
Copy public keys to remote host using the command below.
$ ssh-copy-id -i /home/USER/.ssh/id_rsa.pub REMOTE-SERVER
Note: Replace USER with user name and REMOTE-SERVER by remote server address.
The next time we try to login to SSH server, it will allow login without asking password, using the keygen. For more detailed instructions, read how to login remote SSH server without password.
5. How will you allows users and groups to have access to SSH Sever?
Here again we need to edit the configuration file of SSH service. Open the configuration file and add users and groups at the bottom as show below and then, restart the service.
AllowUsers Tecmint Tecmint1 Tecmint2 AllowGroups group_1 group_2 group_3
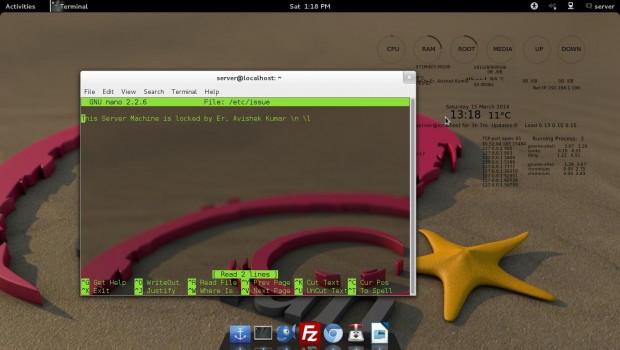
6. How to add welcome/warning message as soon as a user login to SSH Server?
# nano /etc/issue
And add your custom message in this file. See, below a screen grab that shows a custom message as soon as user logged into server.
7. SSH has two protocols? Justify this statement.
Again, we need to open the SSH configuration file and add/edit the lines as shown below.
# protocol 2,1 to Protocol 2
Save the configuration file and restart the service.
8. Is it possible to trace unauthorized login attempts to SSH Server with date of Intrusion along with their corresponding IP.
# cat /var/log/secure | grep “Failed password for”
Note: The grep command can be tweaked in any other way to produce the same result.
9. Is it possible to copy files over SSH? How?
A dummy SCP command in action is depicted below:
$ scp text_file_to_be_copied Your_username@Remote_Host_server:/Path/To/Remote/Directory
For more practical examples on how to copy files/folders using scp command, read the 10 SCP Commands to Copy Files/Folders in Linux.
10. Is it possible to pass input to SSH from a local file? If Yes! How?
# ssh username@servername < local_file.txt
SSH is a very hot topic from interview point, of all times. The above questions would have surely added to your knowledge.
That’s all for now. I’ll soon be here with another interesting article. Till then Stay Tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in our comment section.