The main purpose of writing this article is to provide a step-by-step guide on how to mount remote Linux file system using SSHFS client over SSH.
This article is useful for those users and system administrators who want to mount remote file system on their local systems for whatever purposes. We have practically tested by installing SSHFS client on one of our Linux system and successfully mounted remote file systems.
Before we go further installation let’s understand about SSHFS and how it works.
What Is SSHFS?
SSHFS stands for (Secure SHell FileSystem) client that enable us to mount remote filesystem and interact with remote directories and files on a local machine using SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
Suggested Read: 10 sFTP Command Examples to Transfer Files on Remote Servers in Linux
SFTP is a secure file transfer protocol that provides file access, file transfer and file management features over Secure Shell protocol. Because SSH uses encryption while transferring files over the network from one computer to another computer and SSHFS comes with built-in FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace) kernel module that allows any non-privileged users to create their file system without modifying kernel code.
In this article, we will show you how to install and use SSHFS client on any Linux distribution to mount remote Linux filesystem or directory on a local Linux machine.
Step 1: Install SSHFS Client in Linux Systems
By default sshfs packages does not exists on all major Linux distributions, you need to enable epel repository under your Linux systems to install sshfs with the help of Yum command with their dependencies.
# yum install sshfs # dnf install sshfs [On Fedora 22+ releases] $ sudo apt-get install sshfs [On Debian/Ubuntu based systems]
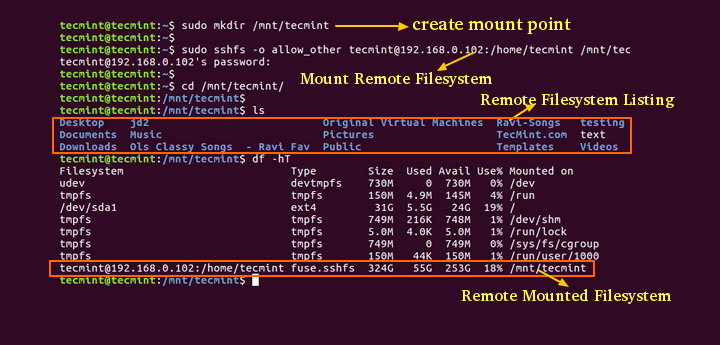
Step 2: Creating SSHFS Mount Directory
Once the sshfs package installed, you need to create a mount point directory where you will mount your remote file system. For example, we have created mount directory under /mnt/tecmint.
# mkdir /mnt/tecmint $ sudo mkdir /mnt/tecmint [On Debian/Ubuntu based systems]
Step 3: Mounting Remote Filesystem with SSHFS
Once you have created your mount point directory, now run the following command as a root user to mount remote file system under /mnt/tecmint. In your case the mount directory would be anything.
The following command will mount remote directory called /home/tecmint under /mnt/tecmint in local system. (Don’t forget replace x.x.x.x with your IP Address and mount point).
# sshfs tecmint@x.x.x.x:/home/tecmint/ /mnt/tecmint $ sudo sshfs -o allow_other tecmint@x.x.x.x:/home/tecmint/ /mnt/tecmint [On Debian/Ubuntu based systems]
If your Linux server is configured with SSH key based authorization, then you will need to specify the path to your public keys as shown in the following command.
# sshfs -o IdentityFile=~/.ssh/id_rsa tecmint@x.x.x.x:/home/tecmint/ /mnt/tecmint $ sudo sshfs -o allow_other,IdentityFile=~/.ssh/id_rsa tecmint@x.x.x.x:/home/tecmint/ /mnt/tecmint [On Debian/Ubuntu based systems]
Step 4: Verifying Remote Filesystem is Mounted
If you have run the above command successfully without any errors, you will see the list of remote files and directories mounted under /mnt/tecmint.
# cd /mnt/tecmint # ls
[root@ tecmint]# ls 12345.jpg ffmpeg-php-0.6.0.tbz2 Linux news-closeup.xsl s3.jpg cmslogs gmd-latest.sql.tar.bz2 Malware newsletter1.html sshdallow epel-release-6-5.noarch.rpm json-1.2.1 movies_list.php pollbeta.sql ffmpeg-php-0.6.0 json-1.2.1.tgz my_next_artical_v2.php pollbeta.tar.bz2
Step 5: Checking Mount Point with df -hT Command
If you run df -hT command you will see the remote file system mount point.
# df -hT
Sample Output
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on udev devtmpfs 730M 0 730M 0% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 150M 4.9M 145M 4% /run /dev/sda1 ext4 31G 5.5G 24G 19% / tmpfs tmpfs 749M 216K 748M 1% /dev/shm tmpfs tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock tmpfs tmpfs 749M 0 749M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs tmpfs 150M 44K 150M 1% /run/user/1000 tecmint@192.168.0.102:/home/tecmint fuse.sshfs 324G 55G 253G 18% /mnt/tecmint
Suggested Read: 12 Useful “df” Commands to Check Disk Space in Linux
Step 6: Mounting Remote Filesystem Permanently
To mount remote filesystem permanently, you need to edit the file called /etc/fstab. To do, open the file with your favorite editor.
# vi /etc/fstab $ sudo vi /etc/fstab [On Debian/Ubuntu based systems]
Go to the bottom of the file and add the following line to it and save the file and exit. The below entry mount remote server file system with default settings.
sshfs#tecmint@x.x.x.x:/home/tecmint/ /mnt/tecmint fuse.sshfs defaults 0 0
Make sure you’ve SSH Passwordless Login in place between servers to auto mount filesystem during system reboots..
If your server is configured with SSH key based authorization, then add this line:
sshfs#tecmint@x.x.x.x:/home/tecmint/ /mnt/tecmint fuse.sshfs IdentityFile=~/.ssh/id_rsa defaults 0 0
Next, you need to update the fstab file to reflect the changes.
# mount -a $ sudo mount -a [On Debian/Ubuntu based systems]
Step 7: Unmounting Remote Filesystem
To unmount remote filesystem, jun issue the following command it will unmount the remote file system.
# umount /mnt/tecmint
That’s all for now, if you’re facing any difficulties or need any help in mounting remote file system, please contact us via comments and if you feel this article is much useful then share it with your friends.


Hi, Thanks for the article.
When I do
mount -aI get message as:fuse: mountpoint is not empty
fuse: if you are sure this is safe, use the ‘nonempty’ mount option
Can you please help with what this could be?
Check the /etc/fstab file. There seems to be a directory that is not empty on which you are mounting an FS. With this you could lose the files if the mount goes through.
Thanks for your reply.
I am not getting that error now. But now the error is different, after
sudo mount -ait’s asking for the remote server’s password 3 times and then getting the message as Connection reset by peer.I have enabled the SSH passwordless but still not sure whats the issue is.
I have mounted the remote server on my mac. However, there are some mounted paths on the remote server which are not accessible from my mac. How can this be tackled?
Mounted on Mac using the below command:
Below are the folders in /build which are not accessible.
Is it not working with a custom port?
Already done with passwordless, but on fstab when I save and add some custom port.
When I type mount -a, it’s always asking for password 3 times and after that I got notice Connection reset by a peer.
Hi, I am facing the same issue, Did you get any resolution for this?
remove sshfs# in front of the command.
source https://superuser.com/questions/669287/automount-sshfs-using-fstab-without-mount-a
If my remote folder is accessible on a port different than 22? can I just do:
Every time I do the:
It kills my mounts and I cant do anything with them after that.
My apologies, I was doing it wrong.
What is the syntax to add to automount?
@Dmitriy,
Following is the correct command to permanently mount.
Hi,
I am trying to mount a folder from remote Centos machine to my local Ubuntu machine (with SSH based authorization). But on step 6, I am getting parse error.
Following is my entry in file and then error output on mount :
sshfs#root@x.x.x.x:/home/vagrant/automation/ /mnt/tdc_automn_remote104/ fuse IdentityFile=~/.ssh/id_rsa defaults,allow_other 0 0
also tried with :
sshfs#root@x.x.x.x:/home/vagrant/automation/ /mnt/tdc_automn_remote104/ fuse IdentityFile=~/.ssh/id_rsa defaults 0 0
Error :
TSS\pbisht@punlinvdi160:~$ sudo mount -a
mount: /etc/fstab: parse error: ignore entry at line 6.
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Thanks
@Pankaj,
Use the following command, it will show any spurious character causing any problems.
Your options should be separated by commas, IdentityFile is an option as are defaults, and allow_other.
Thank you for the article. I have mounted a directory on my worker nodes but when I gave input file path to my Spark program, it gave me error as invalid checkpoint directory. I wanted to know if I want to mount a directory for a cluster with one master node and two worker node what is the correct way of doing it.How should I give path of mounted directory in my Spark program.
Through this article, can we write or update in that file system or folder.
Thanks
@Chandra,
Yes, you can update or add files to these filesystem, without any issues…
This article is excellent, thank you very much.
I did run into one snag on my CentOS 7 server. I have password-less SSH enabled, but when I edited /etc/fstab as instructed it would result in a parse error.
What ended up working in my case was
sshfs#tecmint@x.x.x.x:/home/tecmint/ /mnt/tecmint fuse defaults, allow_other 0 0I hope this helps someone.
I am getting this error while running mount -a command on ubuntu 14.04
fuse: mountpoint is not empty
fuse: if you are sure this is safe, use the ‘nonempty’ mount option
Thank you for the wonderful article…
I followed the steps and created the mount. I am able to see the server files in my local Linux env. But I am not able to read or copy the file.
It is throwing error as
the file and folder user name is changed to users with permission 700
What am I doing wrong?
The adding of line in fstab is ‘either I’m doing it wrong’ or there’s some issue with the command itself.
I added the line below in my fstab:
But the mount -a gives me the following error:
However, when I mount normally without fstab, it works fine.
Any suggestions?
Works like charm. But unmounting from Caja gives me an error. I have to do “fusermount -u /path/to/mounted/dir” to unmount the share. Any Ideas?
@Fedrico,
Thanks for sharing the tip, but I don’t have idea why you have to mention full path to mounted directory unmount it, the simple command unmount will work in most cases..
Hello everyone:
When I mount the files I need, I get two passwords from the remote server and the local one, as specified in the fstab?
Example: sudo sshfs -o allow_other xxx@xxx.xxx.xxx.xx:/pdf /home/xxx/pdf
@Lizbeth,
Its because you running the mount command as sudo user, to avoid asking password twice, try to run with root login..
Aside from the added security, what is the advantage to using this versus something like Samba?
@Andy,
Nothing any advantages over Samba or NFS, but in Samba and NFS you need to setup and create a Share directory or filesystem on the server, and in client side you need to install client packages, but in Sshfs, you don’t need to install any packages on Server, just install the sshfs client package on local machine and mount any remote Linux directory over secure layer using SSH…
I’ve disabled password logins on my SSH server. I connect to my ssh server with my private RSA key. How do I do that in fstab method ?
@Parijatha,
We’ve updated the article and included SSH key based instructions for mounting remote Linux filesystem using sshfs via /etc/fstab.
Thanks for such a fast response.
What’s the benefit of using this method instead of nfs?
@Dwasifar,
In NFS method, you need to setup both NFS Server and NFS client to share Linux filesystem, whereas in Sshfs, you don’t need to setup any server, just install the sshfs client on the local machine and mount any remote Linux server filesystem or directory over SSH.
It’s SSHFS more secure than NFS?
@Rafael,
Yes, ofcourse, as it uses SSH secure layer protocol to connect and mount any remote Linux directory or filesystem over secure network layer, so I can say its safe, fast and more secure..
How do I know the proper IP address to use?
@Richard,
You mean how to find out IP address of server? if yes, use ifconfig or ip command to find the IP address of your server..
You can also specify the address thorugh user@servername:/path/to/directory
What needs to be done on the remote client to get this working? Perhaps this is my ignorance but this part of the instructions seems to be missing. Useful concept if I can get this working though, so that is for the article.
@Graham,
As I said in the beginning of this article that Sshfs is client side tool, you don’t need to install anything on remote machine, just install the sshfs client on the local machine to mount any remote Linux filesystem….
When I Put the Entry in the fstab as sshfs#root@192.168.1.103:/data /data-sshfs
And Reboots the system, System is not able to remount the directory
Any Solutions?
@Akash,
Can you show me the correct entry in fstab? how you added?
thanks , very usefully
Only root has read rights after mounting, so not even root’s crontab can read those files. How do you mount readonly, all-users can access?
Hi,
What about to keep Alive? I use that and work propertly but sometimes the conection is broken but not reconnect automatically. Can you help me with that?
Thanks!
Very nice and friendly guide! Easy to do!
Hi,
What about if my user name at the FTP is user@email.com
how to set it up?
Works well with Ubuntu 13.04 too
hi..!! im geting this error when trying to mount
fuse: failed to open /dev/fuse: Permission denied
OS Centos 6 64 bits
Solution, do the following.
And run the command again..
Hi, using default installed CENTOS 6.3 ..
# yum install sshfs
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: http://ftp.telus.net
* extras: http://ftp.telus.net
* updates: http://ftp.telus.net
Setting up Install Process
No package sshfs available.
Error: Nothing to do
@David,
Sorry, the article is updated now, you just need to enable epel repository under your centos 6.3 to install sshfs.