As we enter 2025, we thought it right to share with Linux enthusiasts out there the most popular distributions of the year so far.
DistroWatch has been the most reliable source of information about open-source operating systems, with a particular focus on Linux distributions and flavors of BSD. It collects and presents a wealth of information about Linux distributions consistently to make them easier to access.
Although it is not a good indicator of a distribution’s popularity or usage, DistroWatch remains the most accepted measure of popularity within the Linux community. It uses Page Hit Ranking (PHR) statistics to measure the popularity of Linux distributions among the visitors of the website.
To find out what the most widely used distros of this year are, let’s head to Distrowatch and check the Page Hit Ranking (PHR for short) table. There you can choose a wide variety of time spans that will allow you to check the ranking of Linux and BSD distributions in that period of time.
In this post, we will review the top 10 most popular Linux distributions based on the usage statistics and market share as per Distrowatch, in descending order, as of Jan 6, 2025.
10. openSUSE
openSUSE remains one of the most respected Linux distributions, known for its flexibility and robust tools. Available in two versions – openSUSE Leap and openSUSE Tumbleweed – it caters to both stable and rolling release users.
openSUSE is particularly favored by developers and system administrators due to its powerful YaST configuration tool and its ability to scale from personal desktops to enterprise-level servers.
9. Fedora
Built and maintained by the Fedora Project (and sponsored by Red Hat), a worldwide community of volunteers and developers, Fedora continues to be one of the top-used distributions for years now due to its three main available versions (Workstation (for desktops), Server edition, and Cloud image), along with the ARM version for ARM-based (typically headless) servers.
However, perhaps the most distinguishing characteristic of Fedora is that it’s always in the lead of integrating new package versions and technologies into the distribution. In addition, new releases of Red Hat Enterprise Linux are based on Fedora.
8. Ubuntu
Perhaps this distribution does not need any introduction. Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu, has devoted great efforts to make it a popular and widespread distro to the point that you can now find it in smartphones, tablets, PCs, servers, and cloud VPS.
Also, Ubuntu has the plus of being based on Debian and is a very popular distribution among new users – which is maybe the reason for its sustained growth over time. Although not taken into consideration in this ranking, Ubuntu is the base for other distributions of the Canonical family such as Kubuntu, Xubuntu, and Lubuntu.
On top of all that, the installation image includes the Try Ubuntu feature, which lets you try Ubuntu before actually installing it on your hard drive. Not many major distributions provide such features nowadays.
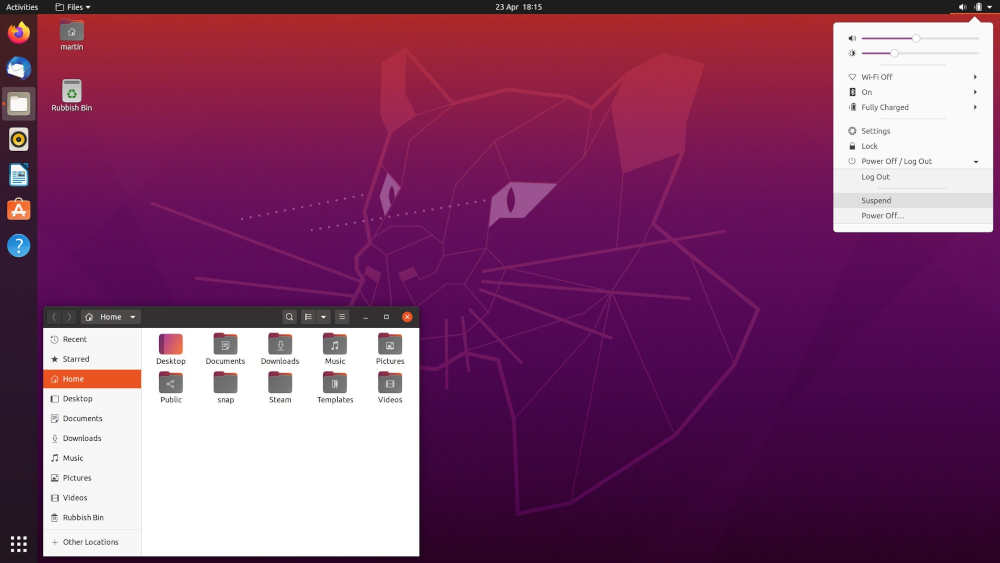
7. Pop!_OS
Developed by System76, Pop!_OS is a distribution that has gained significant traction in recent years. Based on Ubuntu, it is designed with a focus on developers, gamers, and professionals who need a streamlined and efficient environment.
Pop!_OS comes with excellent hardware support, particularly for System76 machines, but it also works well on a variety of other hardware. Its user-friendly interface and deep integration with GNOME make it a favorite for many.
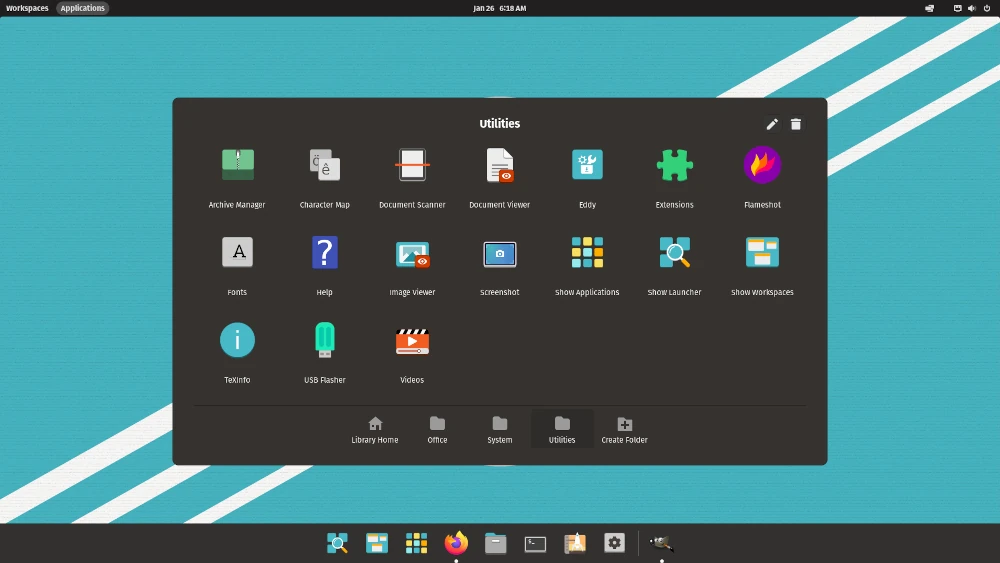
6. Manjaro
Based on Arch Linux, Manjaro aims to take advantage of the power and the features that make Arch a great distribution while providing a more pleasant installation and operation experience out of the box both for new and experienced Linux users.
Manjaro comes with preinstalled desktop environments, graphical applications (including a software center), and multimedia codecs to play audio and videos.
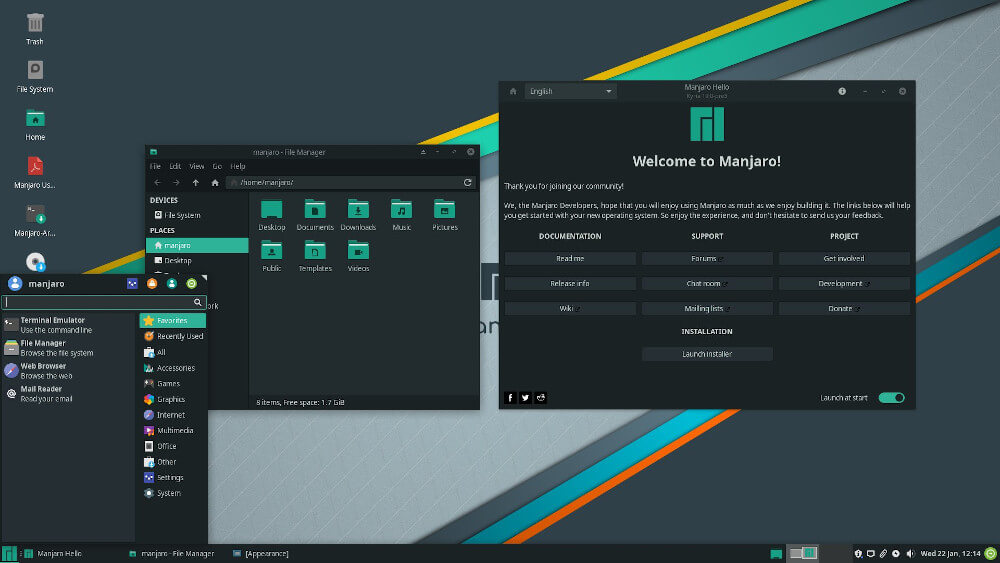
5. CachyOS
CachyOS is a relatively new distribution that has quickly gained popularity. It is based on Arch Linux and focuses on providing a fast and efficient experience while maintaining a high degree of customization.
CachyOS uses a unique kernel that prioritizes performance, making it ideal for users who want a high-speed, minimalistic setup.
4. Debian
As a rock-solid Linux distribution, Debian Linux is so committed to free software (so it will always remain 100% free) but it also allows users to install and use non-free software on their machines for productivity. It is used both on desktop and server computers and also to run the infrastructure that runs the cloud.
Being one of the two oldest and most famous Linux distributions (the other being RedHat Enterprise Linux), it is the basis of numerous popular Linux distributions notably Ubuntu and Kali Linux.
At the time of this writing, the Debian repositories for the current stable version (codename Bookworm) contain 96,000 packages in total, making it one of the most complete Linux distributions.
Although its strength is mainly visible in servers, the desktop edition has seen remarkable improvements in features and appearance.
3. EndeavourOS
EndeavourOS is a relatively new distribution that has quickly become a favorite among Arch Linux users, which provides a user-friendly installation process for Arch while retaining the flexibility and power of the Arch base.
EndeavourOS aims to be a lightweight and minimal distribution, giving users the freedom to build their system from the ground up while offering a helpful and active community.
2. MX Linux
MX Linux continues to be a top contender in the Linux world, due to its high stability, elegant and efficient desktop, and also an easy learning curve. It is a midweight desktop-oriented Linux operating system based on Debian. It comes with a simple configuration, solid performance, and a medium-sized footprint. It is built for all types of users and applications.
Additionally, it is essentially user-oriented, to assure that the system works out of the box, it comes with a certain amount of non-free software.
One unique thing about MX Linux is that it ships with systemd (system and service manager) included by default but disabled because of the controversies surrounding it, instead, it uses systemd-shim which emulates most if not all systemd functions that are required to run the helpers without employing the init service.
1. Linux Mint
Linux Mint’s well-known motto (“From freedom came elegance“), takes the top spot once again in 2024, which is based on Ubuntu, it is a stable, powerful, complete, and easy-to-use Linux distribution – and we could go on and on with a list of positive adjectives to describe Mint.
Among Mint’s most distinguishing features we can mention that during installation, you are allowed to choose from a list of desktop environments, and you can rest assured that once it’s installed, you will be able to play your music and video files without any extra configuration steps since the standard installation provides multimedia codecs out of the box.

Summary
In this article, we have briefly described the top 10 Linux distributions for the year 2024 so far. If you are a new user trying to decide which distro to adopt to start your journey, or if you are an experienced user wanting to explore new options, we hope this guide will allow you to make an informed decision.
As always, don’t hesitate to let us know What do you think about these top 10 distros? and which Linux distro would you recommend for newbies and why?