If you’re a Linux user who loves working with images, whether for personal projects, professional work, or just for fun, you might have encountered the challenge of low-resolution images.
Fortunately, there’s a powerful tool available to solve this problem: Upscayl, which is a free and open-source desktop application that offers a unique solution for enhancing image quality by upscaling low-resolution images to higher resolutions without losing too much detail.
In this blog post, we will explore what Upscayl is, how to install it on Linux, and how it can benefit your image editing workflow.
What is Upscayl?
Upscayl is an open-source image upscaling application designed to improve the resolution of images while maintaining their quality. It uses AI-powered algorithms to upscale images by up to 4x their original resolution.
Whether you’re dealing with pixelated images, old photographs, or low-res graphics, Upscayl can help you achieve a cleaner, sharper, and more detailed version of your image.
Being free and open-source, Upscayl is an excellent alternative to proprietary software that may come with a hefty price tag. It’s lightweight, easy to use, and designed specifically for Linux users, though it is also available for Windows and macOS.
How to Install Upscayl on Linux
Installing Upscayl on Linux is straightforward. You can install it from the official repository or download the latest release from GitHub. Here’s a step-by-step guide to installing Upscayl on your Linux system:
Method 1: Install Upscayl Using Flatpak
Flatpak is a popular package manager for Linux that allows you to install applications in a sandboxed environment.
To install Upscayl via Flatpak, run the following commands:
sudo apt install flatpak flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo flatpak install flathub org.upscayl.Upscayl flatpak run org.upscayl.Upscayl
Method 2: Install Upscayl Using AppImage
If you prefer not to use Flatpak, you can install Upscayl as an AppImage, which is a self-contained executable that doesn’t require installation.
First, visit the Upscayl GitHub releases page and download the latest AppImage file.
Once the file is downloaded, navigate to the folder where the AppImage is located and run the following command to make it executable:
chmod +x upscayl-x.xx.-linux.AppImage
Now, you can run Upscayl by double-clicking the AppImage file or using the terminal:
./upscayl-x.xx.-linux.AppImage
How to Use Upscayl to Enhance Image Quality in Linux
Launch the application by clicking on the icon in your applications menu or using the terminal and then click the “Open” button to browse and select the image you want to upscale.
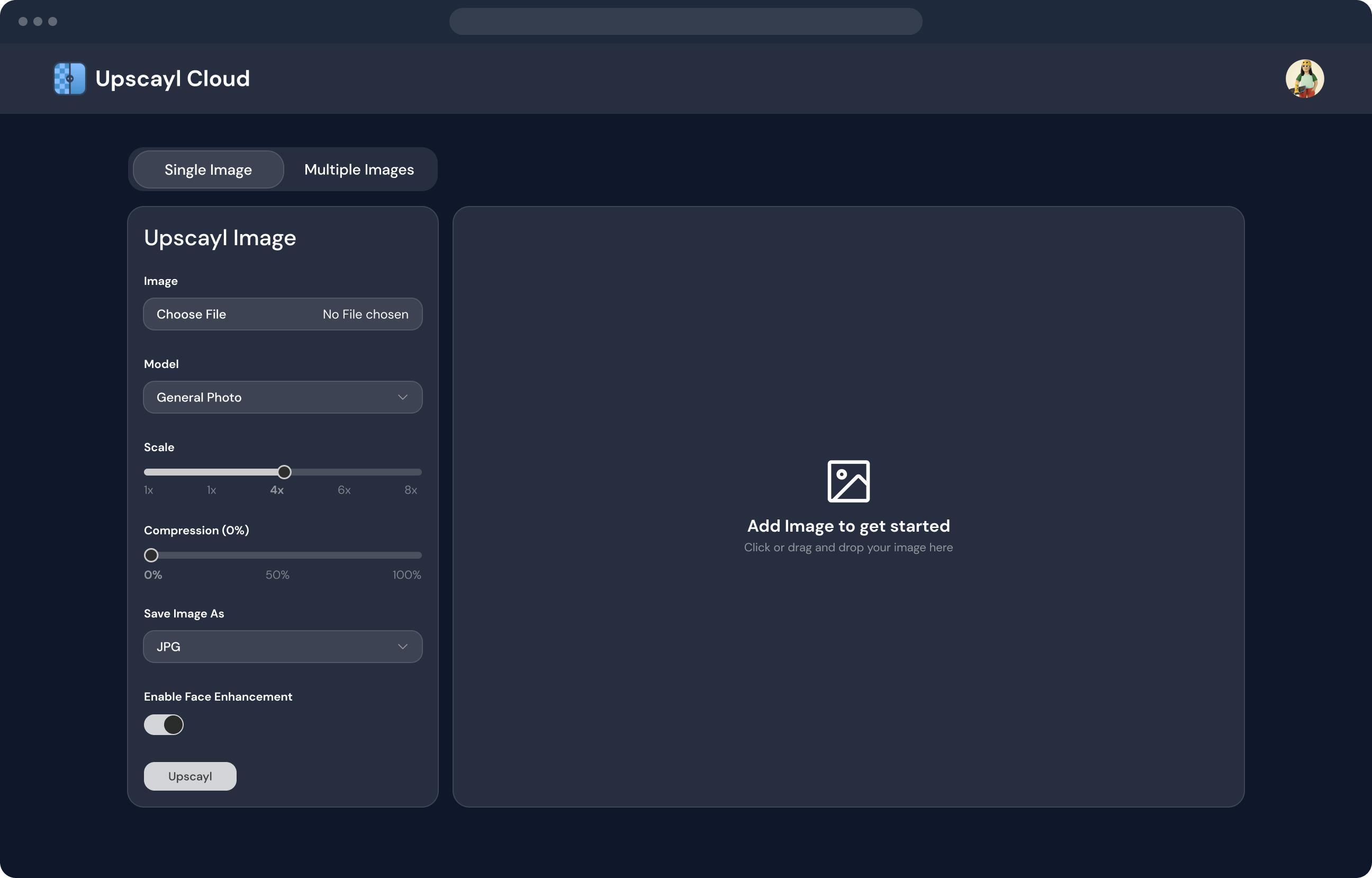
Once the image is loaded, you can select the upscaling factor (2x, 4x, or 8x). The higher the scaling factor, the more detailed the final image will be, but it may also take longer to process.
After selecting the upscaling factor, click the “Upscale” button to begin the process. The application will process the image and display a preview of the result.
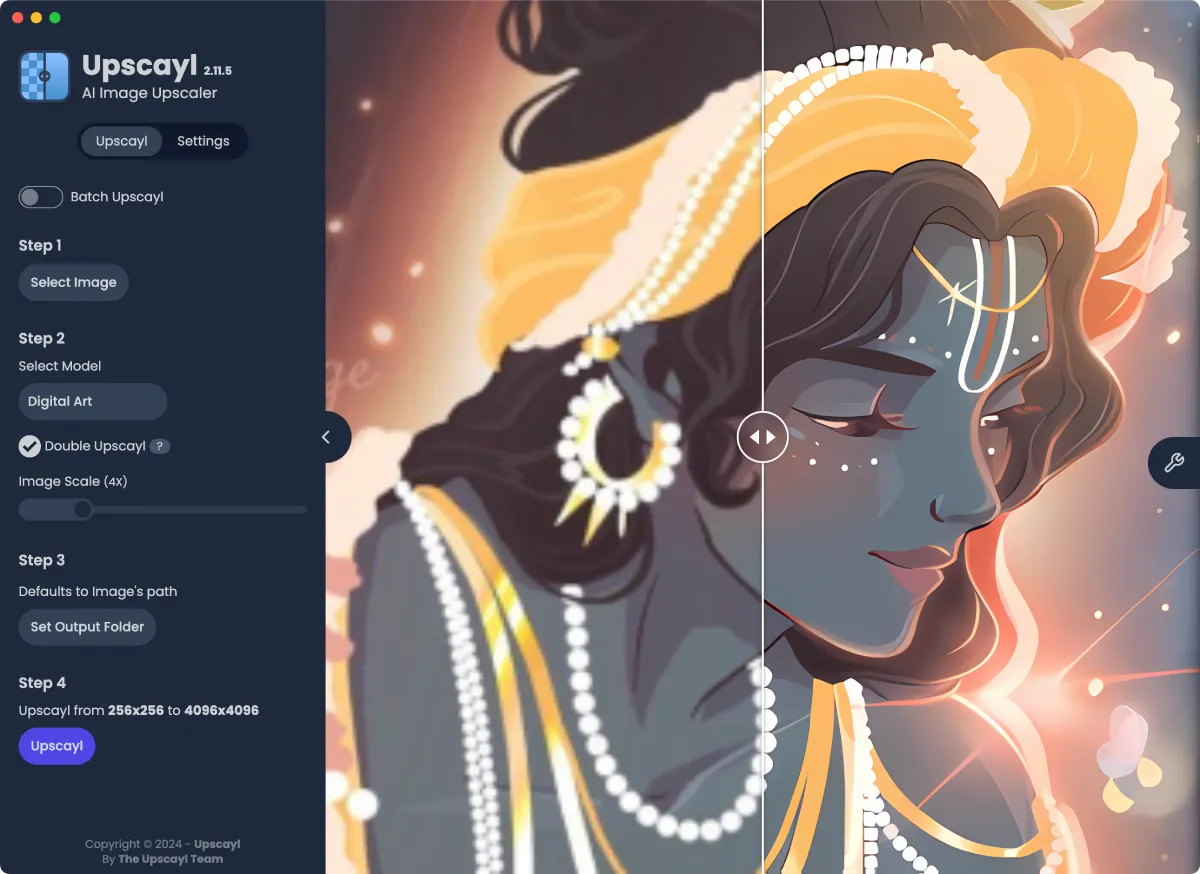
If you’re satisfied with the result, you can save the upscaled image to your desired location by clicking the “Save” button.
Conclusion
Upscayl is a fantastic tool for Linux users who need to upscale images without compromising on quality. Its AI-powered upscaling, ease of use, and offline functionality make it a great addition to any image editing workflow.
Whether you’re a photographer, graphic designer, or just someone who loves working with images, Upscayl is a must-have tool for enhancing your images. Plus, being free and open-source, it’s an accessible option for everyone.







The flatpak address listed failed for me, this one worked:
@Stephen,
Thank you for bringing this to my attention! I’ve updated the commands in the article to reflect the correct Flatpak address.
Please let me know if you encounter any other issues. I appreciate your feedback!