Java is a General Purpose, class based, object oriented, Platform independent, portable, Architecturally neutral, multithreaded, dynamic, distributed, Portable and robust interpreted Programming Language.

Why Java is a called:
General Purpose
Java capabilities are not limited to any specific application domain rather it can be used in various application domain and hence it is called General Purpose Programming Language.
Class based
Java is a class based/oriented programming language which means Java supports inheritance feature of object-oriented Programming Language.
Object oriented
Java is object-oriented means software developed in Java are combination of different types of object.
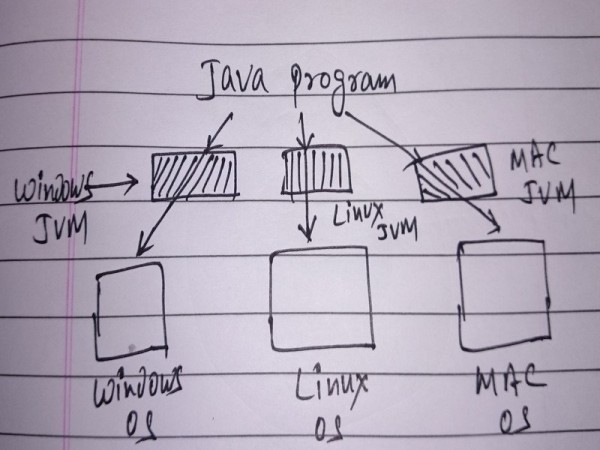
Platform Independent
A Java code will run on any JVM (Java Virtual Machine). Literally you can run same Java code on Windows JVM, Linux JVM, Mac JVM or any other JVM practically and get same result every time.
Architecturally Neutral
A Java code is not dependent upon Processor Architecture. A Java Application compiled on 64 bit architecture of any platform will run on 32 bit (or any other architecture) system without any issue.
Multithreaded
A thread in Java refers to an independent program. Java supports multithread which means Java is capable of running many tasks simultaneously, sharing the same memory.
Dynamic
Java is a Dynamic programming language which means it executes many programming behavior at Runtime and don’t need to be passed at compile time as in the case of static programming.
Distributed
Java Supports distributed System which means we can access files over Internet just by calling the methods.
Portable
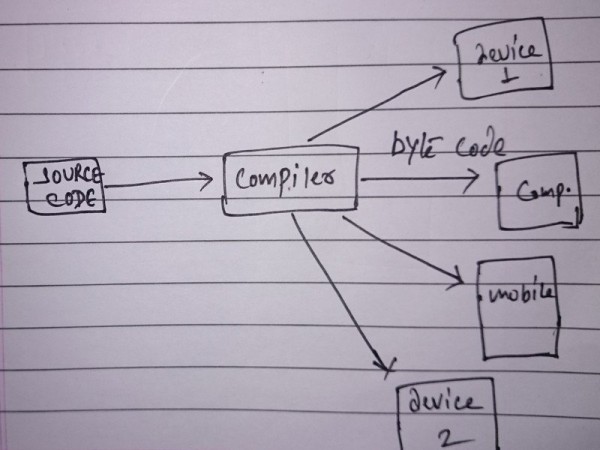
A Java program when compiled produce bytecodes. Bytecodes are magic. These bytecodes can be transferred via network and can be executed by any JVM, hence came the concept of ‘Write once, Run Anywhere(WORA)’.
Robust
Java is a robust programming Language which means it can cope with error while the program is executing as well as keep operating with abnormalities to certain extent. Automatic Garbage collection, strong memory management, exception handling and type checking further adds to the list.
Interpreted
Java is a compiled programming Language which compiles the Java program into Java byte codes. This JVM is then interpreted to run the program.
Other than the above discussed feature, there are a few other remarkable features, like:
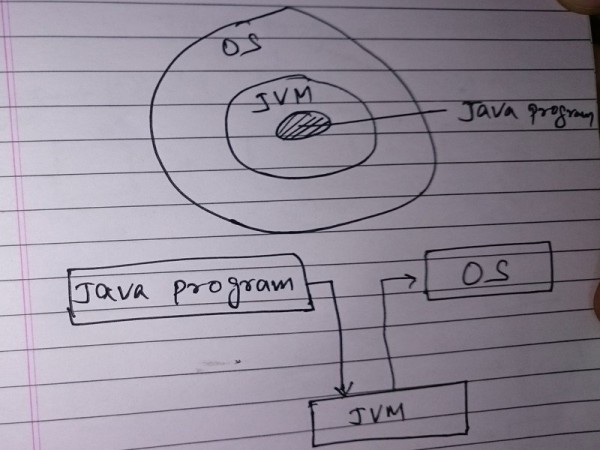
Security
Unlike other programming Language where Program interacts with OS using User runtime environment of OS, Java provides an extra layer of security by putting JVM between Program and OS.
Simple Syntax
Java is an improved c++ which ensures friendly syntax but with removed unwanted features and inclusion of Automatic Garbage collection.
High Level Programming Language
Java is a High Level Programming Language the syntax of which is human readable. Java lets programmer to concentrate on what to achieve and not how to achieve. The JVM converts a Java Program to Machine understandable language.
High Performance
Java make use of Just-In-Time compiler for high performance. Just-In-Time compiler is a computer program that turns Java byte codes into instructions that can directly be sent to compilers.
History of Java
Java Programming Language was written by James Gosling along with two other person ‘Mike Sheridan‘ and ‘Patrick Naughton‘, while they were working at Sun Microsystems. Initially it was named oak Programming Language.
Java Releases
- Initial Java Versions 1.0 and 1.1 was released in the year 1996 for Linux, Solaris, Mac and Windows.
- Java version 1.2 (Commonly called as java 2) was released in the year 1998.
- Java Version 1.3 codename Kestrel was released in the year 2000.
- Java Version 1.4 codename Merlin was released in the year 2002.
- Java Version 1.5/Java SE 5 codename ‘Tiger’ was released in the year 2004.
- Java Version 1.6/Java SE 6 Codename ‘Mustang’ was released in the year 2006.
- Java Version 1.7/Java SE 7 Codename ‘Dolphin’ was released in the year 2011.
- Java Version 1.8 is the current stable release which was released this year (2015).
Five Goals which were taken into consideration while developing Java:
- Keep it simple, familiar and object oriented.
- Keep it Robust and Secure.
- Keep it architecture-neural and portable.
- Executable with High Performance.
- Interpreted, threaded and dynamic.
Why we call it Java 2, Java 5, Java 6, Java 7 and Java 8, not their actual version number which 1.2, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 and 1.8?
Java 1.0 and 1.1 were Java. When Java 1.2 was released it had a lots of changes and marketers/developers wanted a new name so they called it Java 2 (J2SE), remove the numeric before decimal.
This was not the condition when Java 1.3 and Java 1.4 were released hence they were never called Java 3 and Java 4, but they were still Java 2.
When Java 5 was released, once again it was having a lots of changes for the developer/marketers and need a new name. The next number in sequence was 3, but calling Java 1.5 as Java 3 was confusing hence a decision was made to keep the naming as per version number and till now the legacy continues.
Places where Java is used
Java is implemented over a number of places in modern world. It is implemented as Standalone Application, Web Application, Enterprise Application and Mobile Application. Games, Smart Card, Embedded System, Robotics, Desktop, etc.
Keep connected we are coming up with “Working and code Structure of Java”.






Very nice and helpful
Thank you so much sir.
It is very useful for me and this article was helpful to all..
thank you sir…
this article is so helpful..
This is very useful to learn and know many information thanks so much
Send java version with date and version wise feature and why release new version
This content is really helpful to me . . Thnx for this information. :)
@Priti,
Thanks for finding this article helpful, hope you know now about JAVA history..
It is helpful to me….thank you